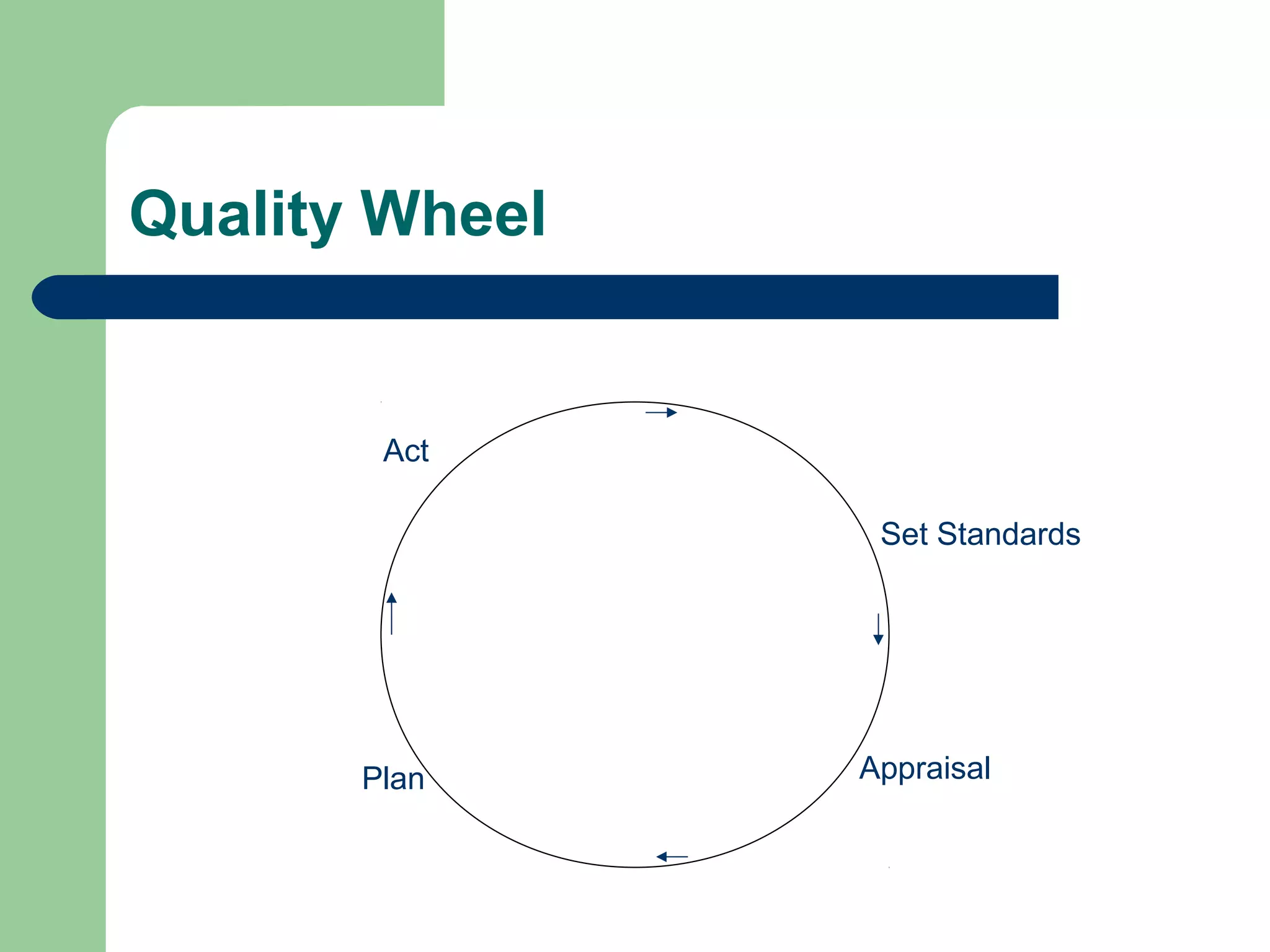
Quality assurance is a system to monitor outcomes of nursing care and activities to ensure they meet established standards. It involves setting standards, assessing actual performance, planning improvements, and taking corrective actions. Quality assurance is important to improve patient care quality, decrease costs, and meet professional, legal and social responsibilities. It requires establishing criteria and evaluating care structures, processes and outcomes. Nurses play a key role by developing quality assurance programs, implementing standards, monitoring performance, and evaluating changes to continually improve nursing services.