1. The document discusses the definition, objectives, functions, management, and classification of hospitals. Hospitals are defined as institutions for caring for the sick and injured, curing diseases, training medical professionals, and conducting research.
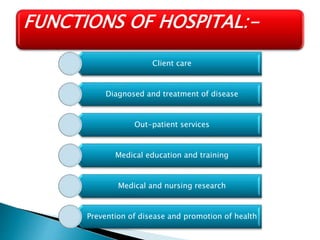
2. Hospitals have objectives like providing health services, treatment, and education. Their functions include patient care, education, research, and disease prevention. Hospitals are managed by governing bodies and have departments led by directors.
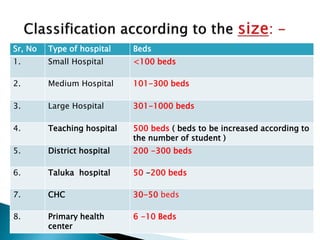
3. Hospitals can be classified by length of stay, clinical focus, ownership, objectives, size, management, and systems. Classification types include general, specialty, teaching, isolation, and ayurvedic hospitals.