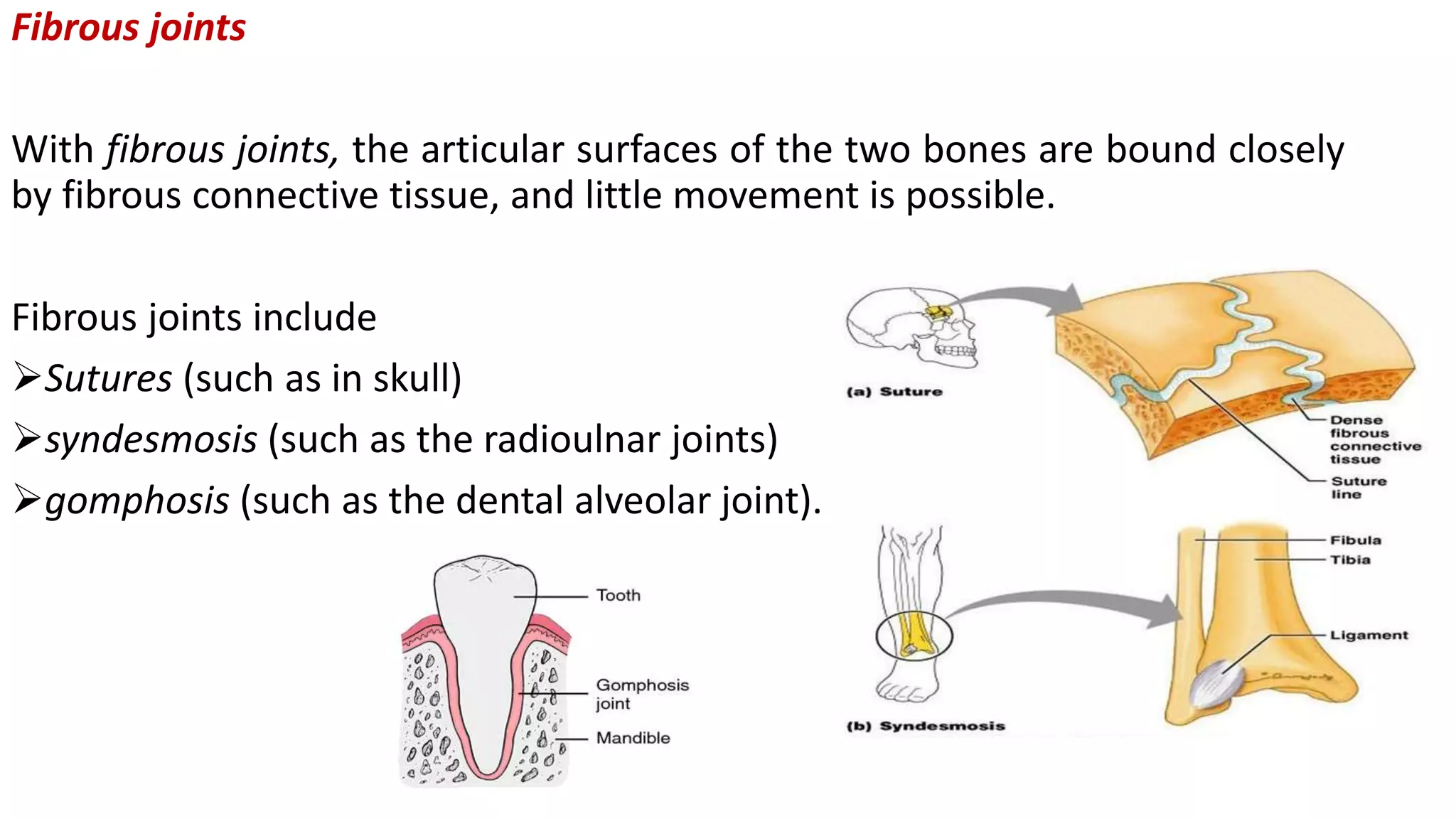
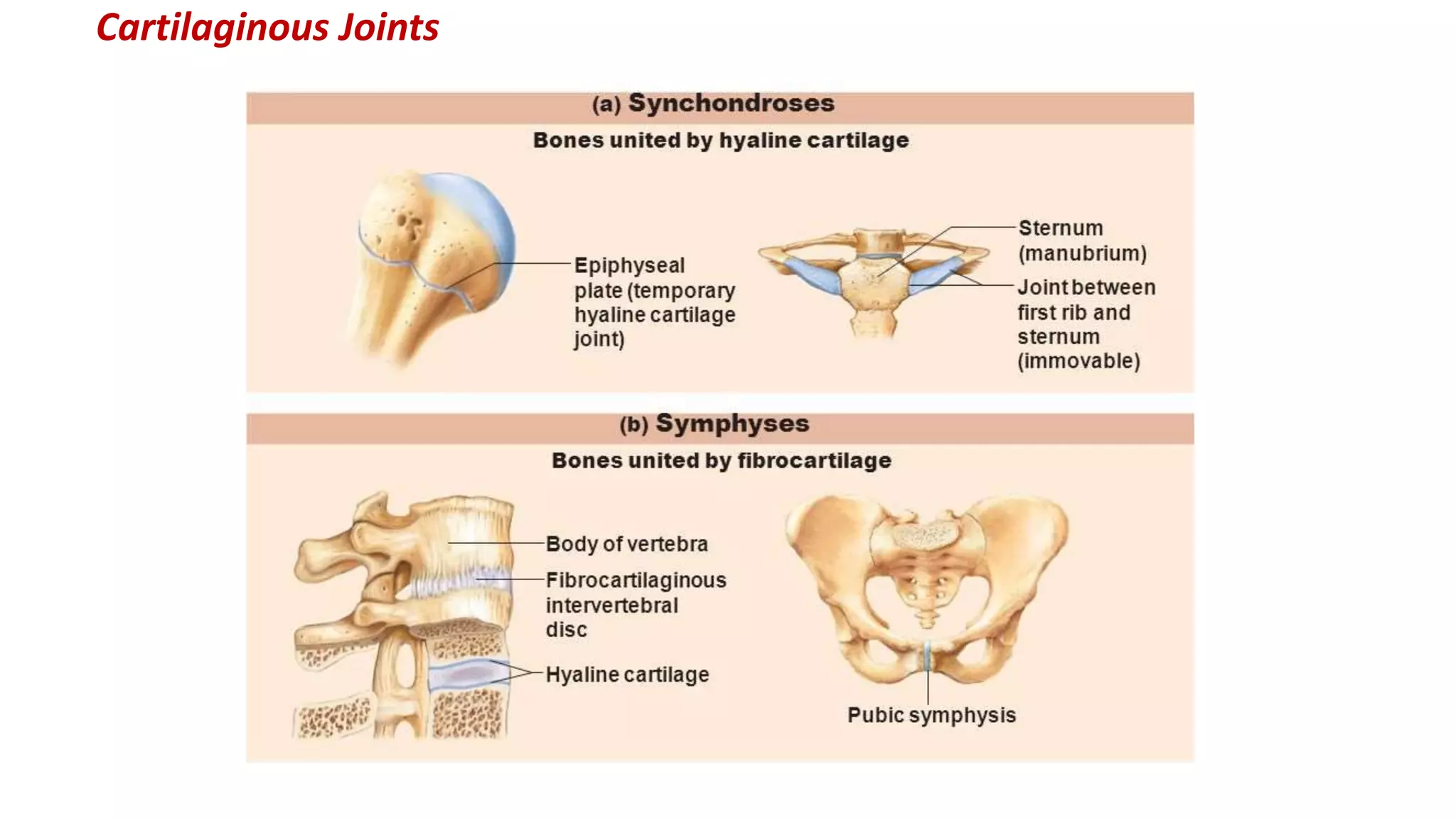
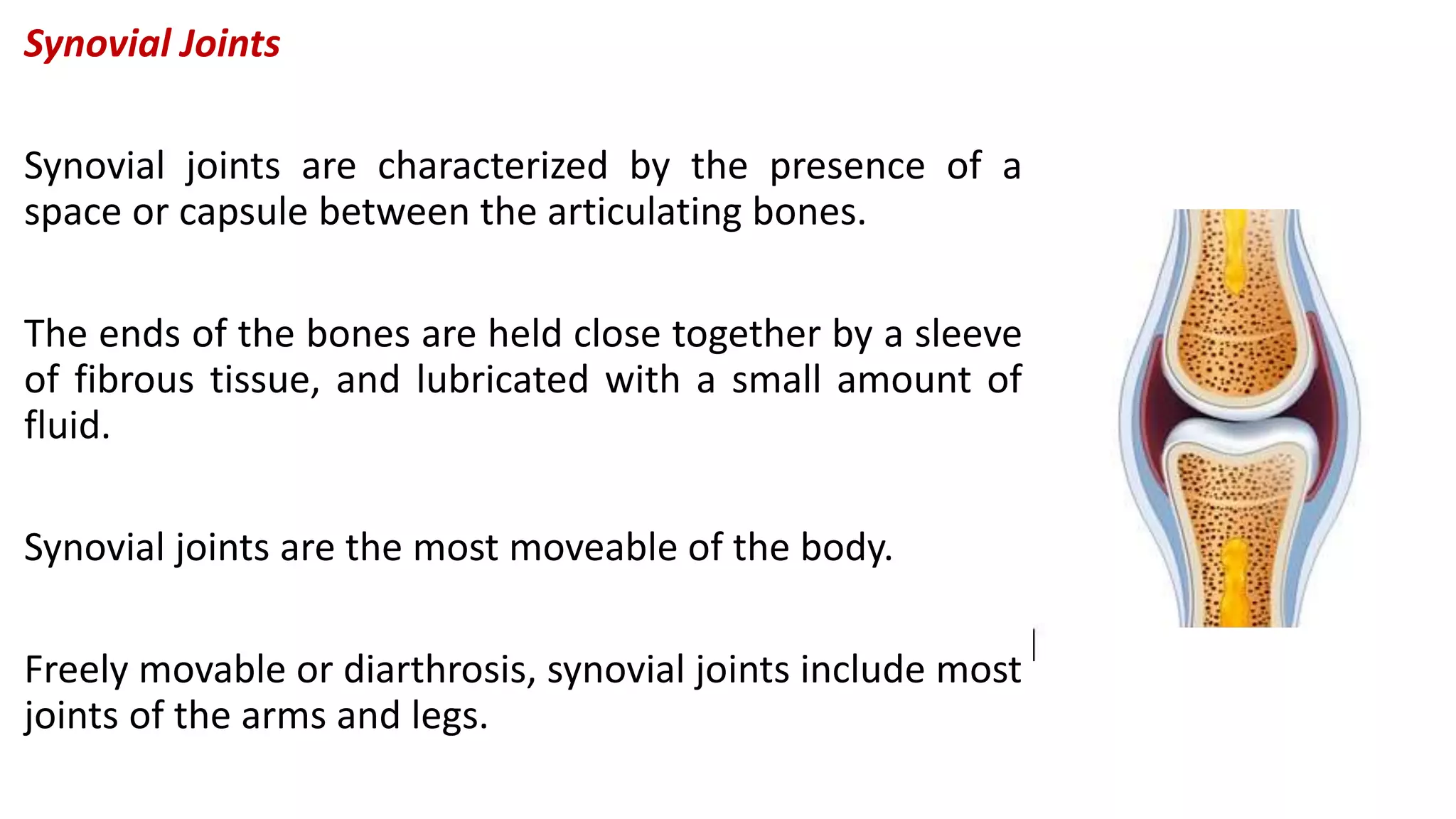
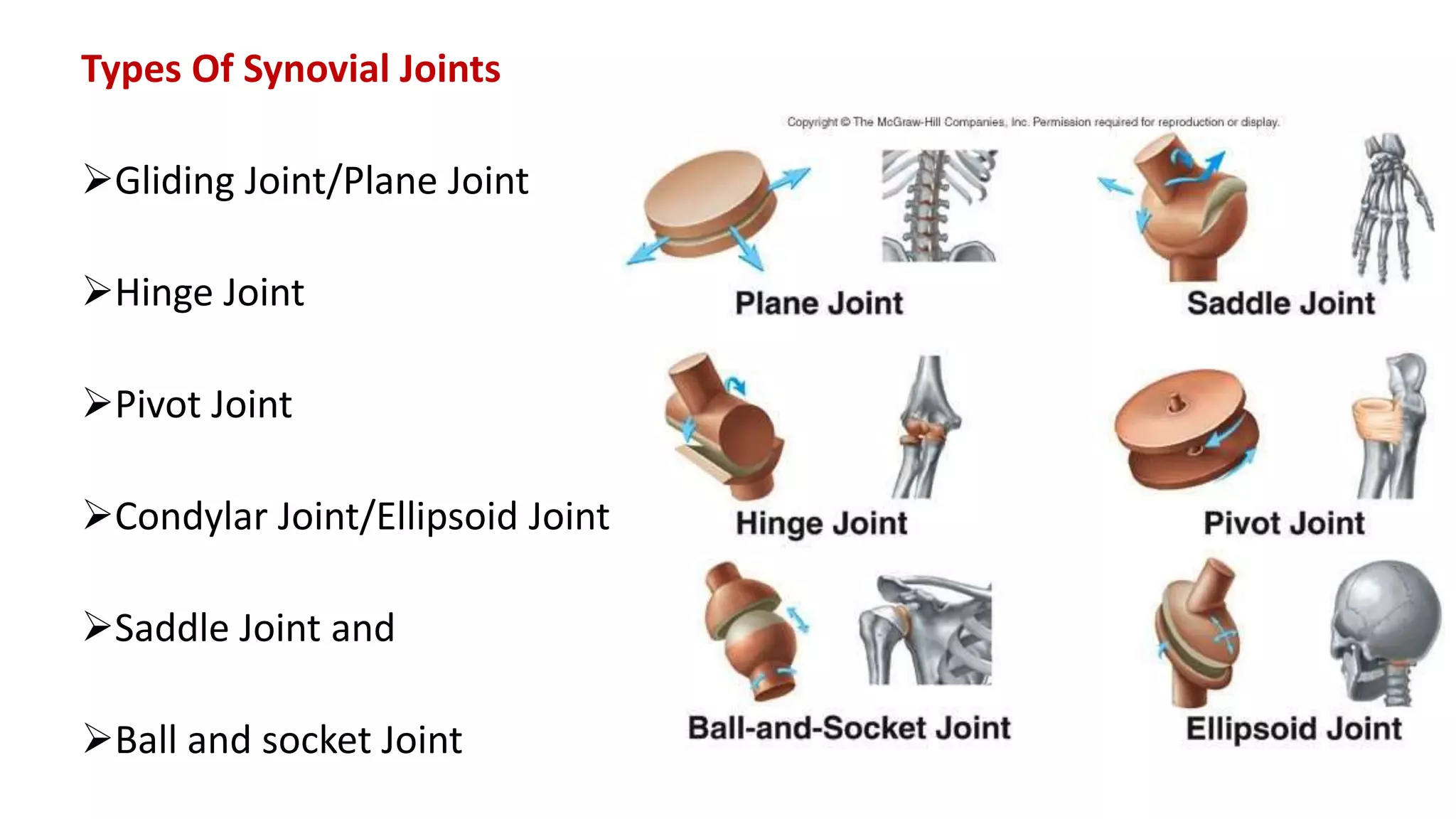
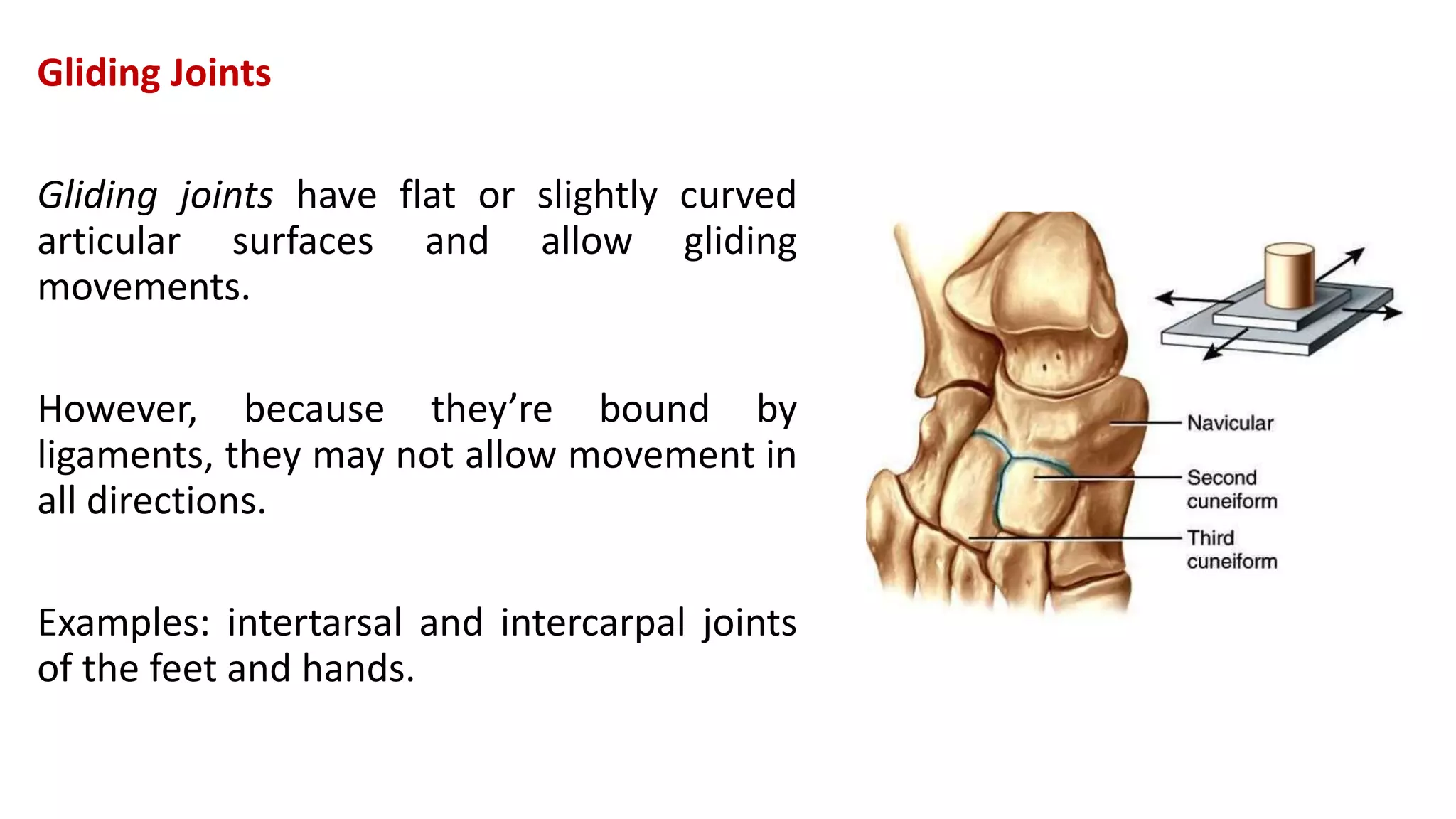
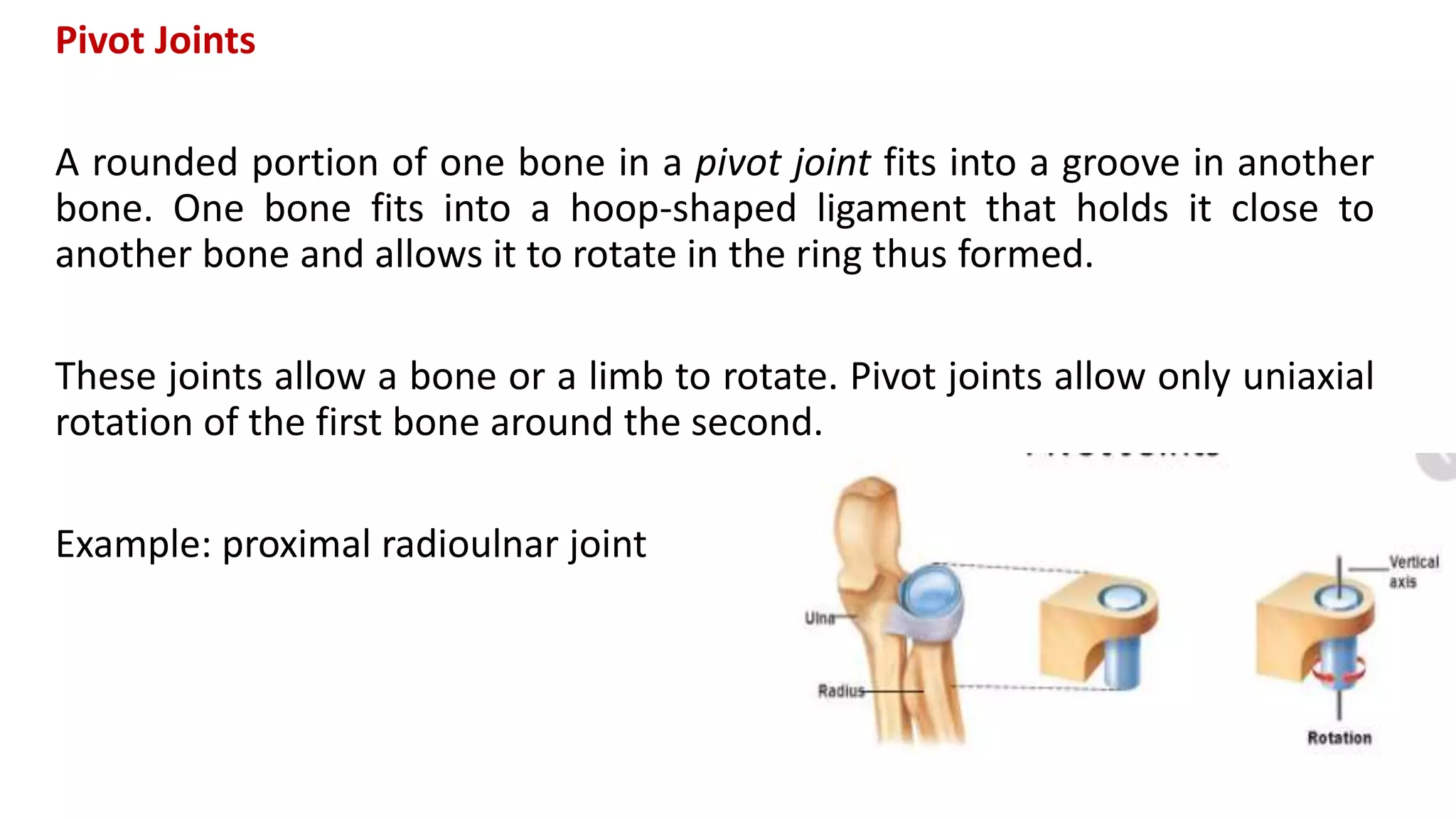
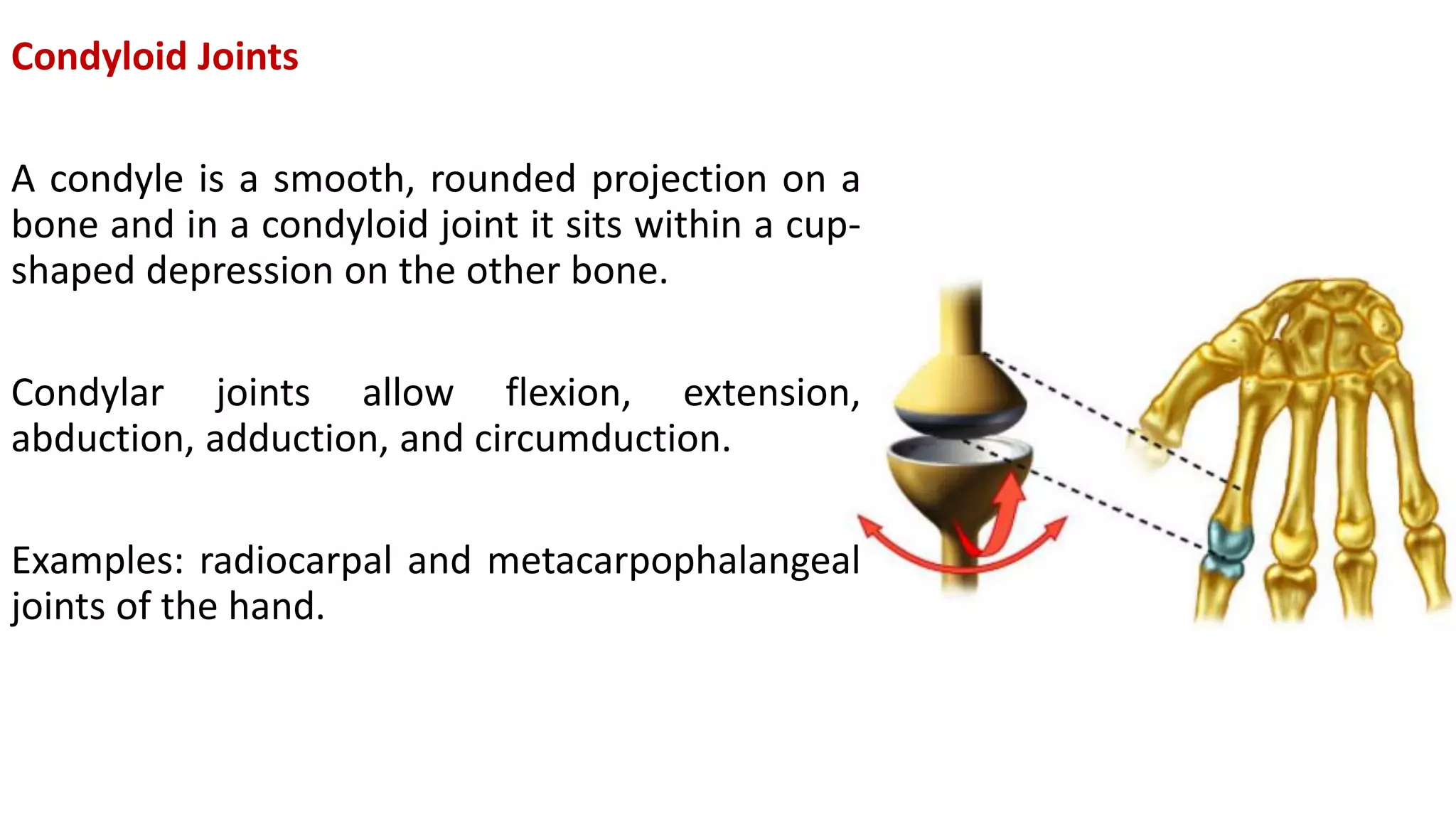
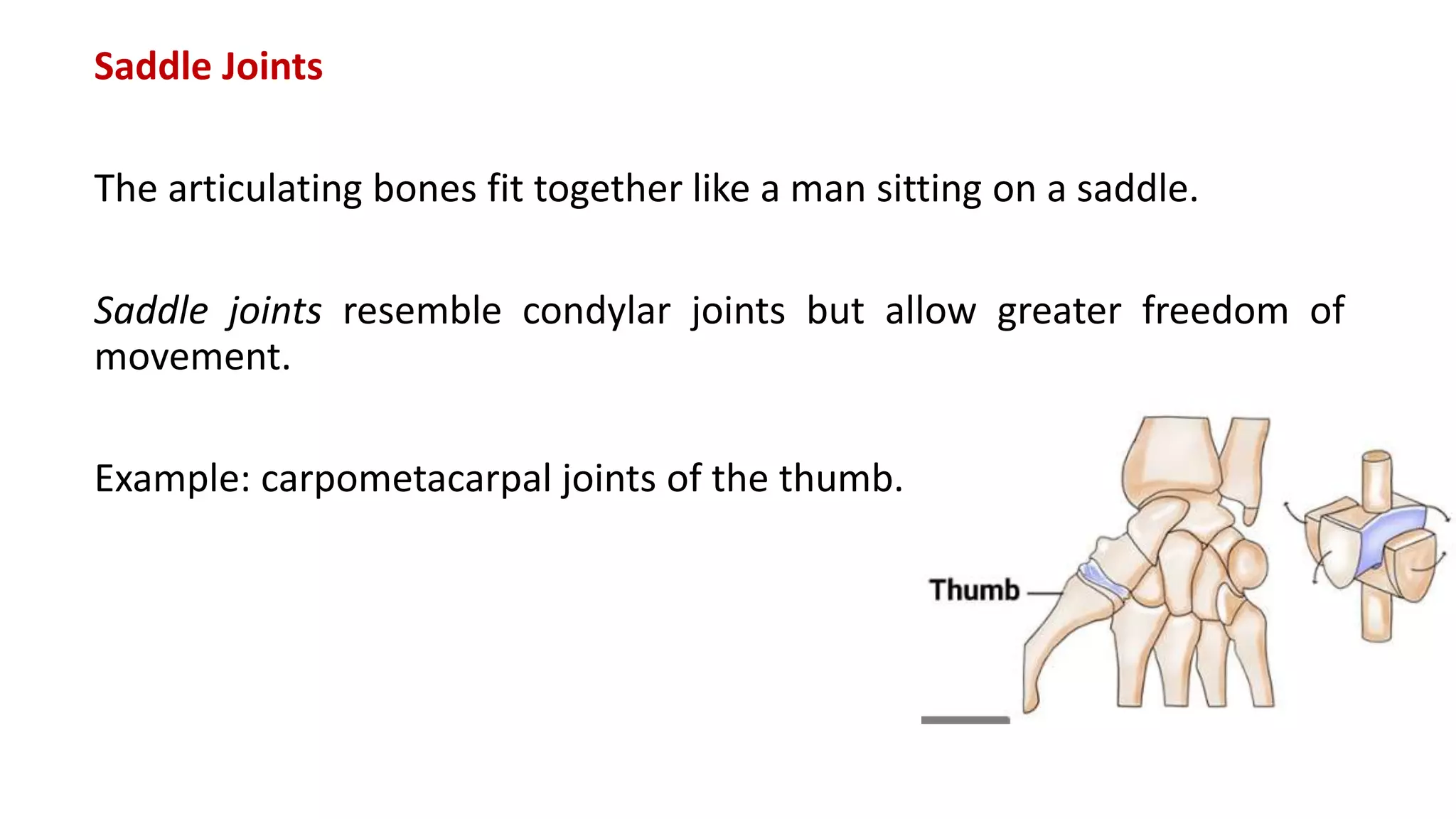
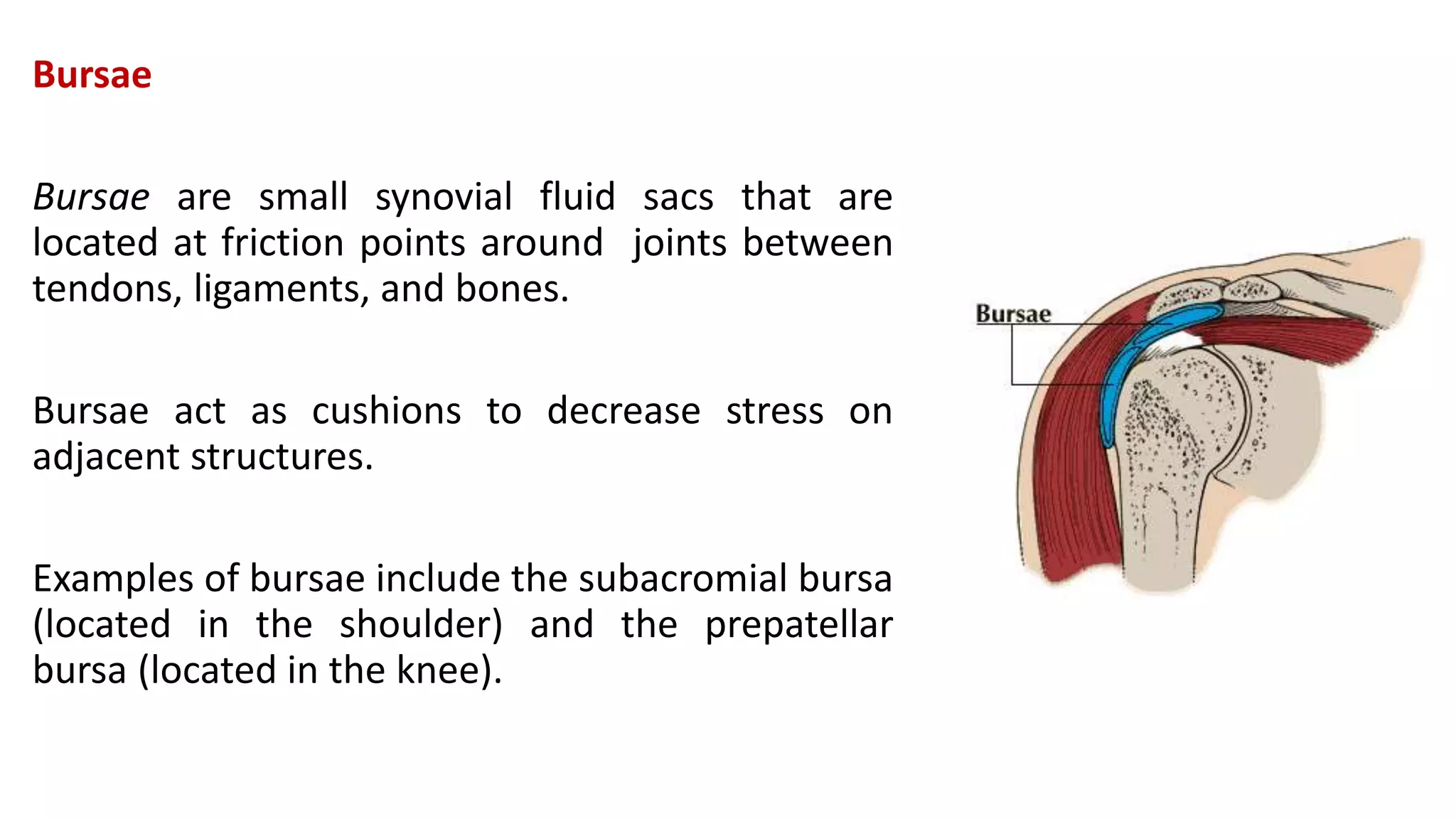
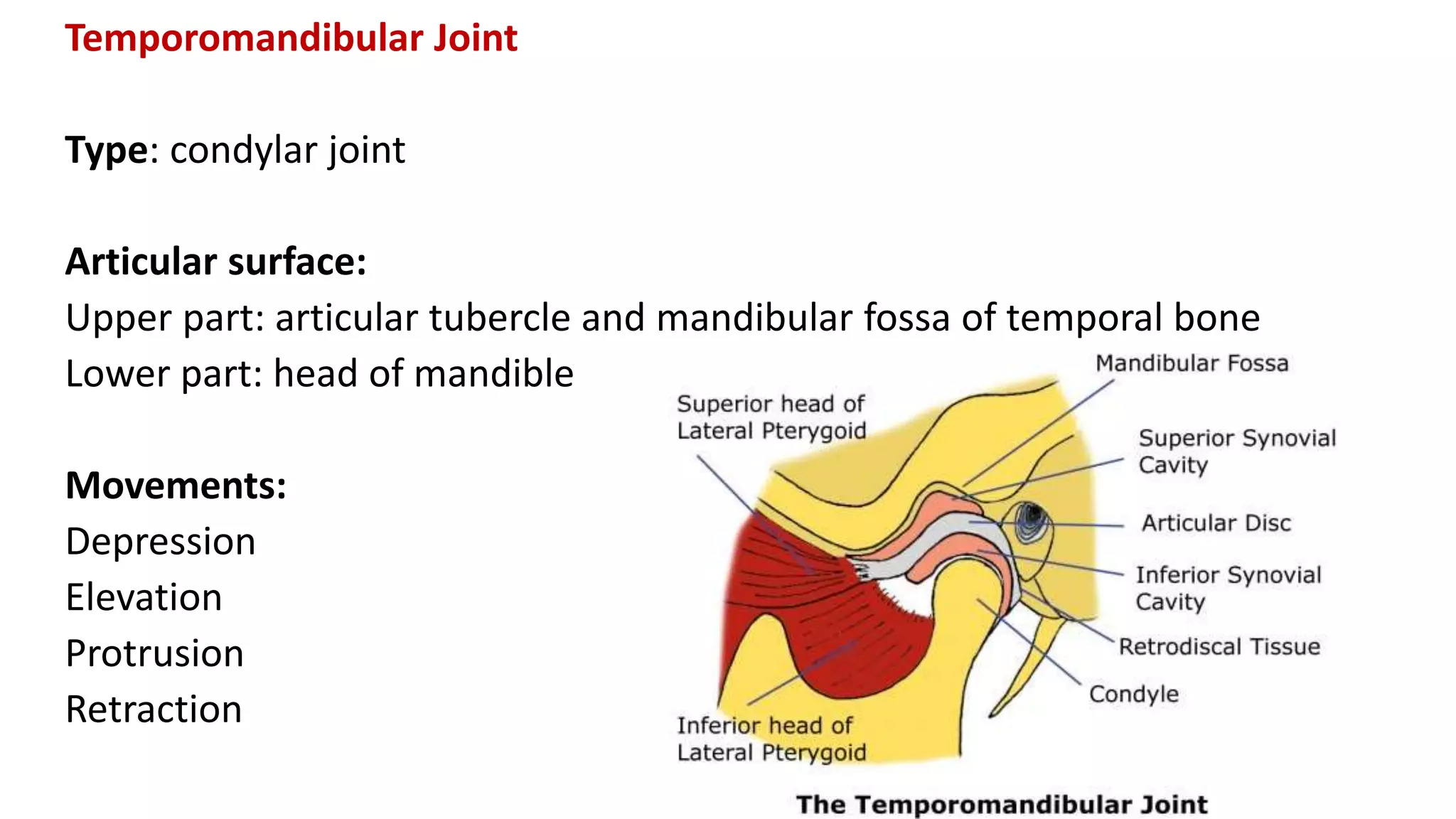
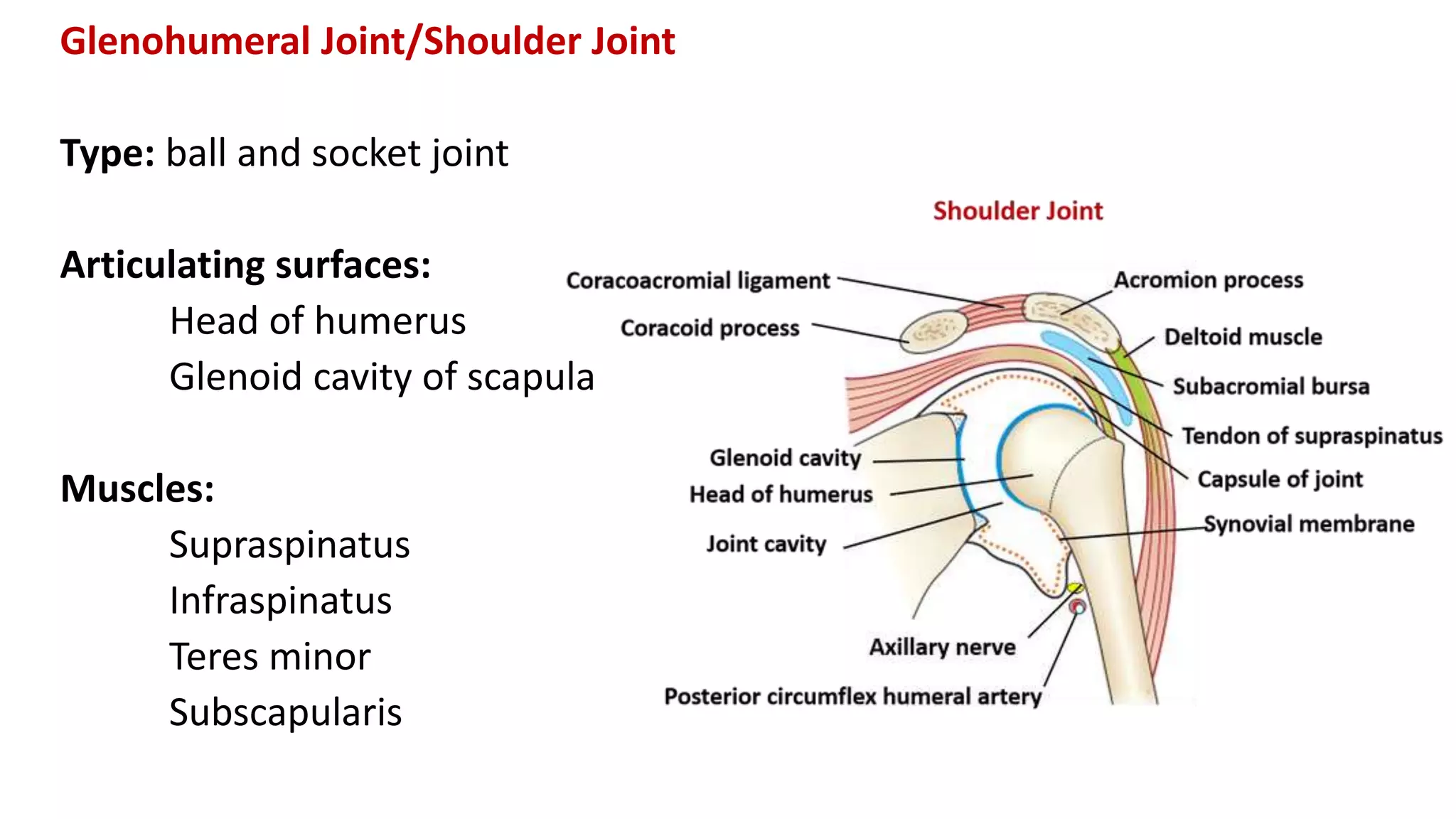
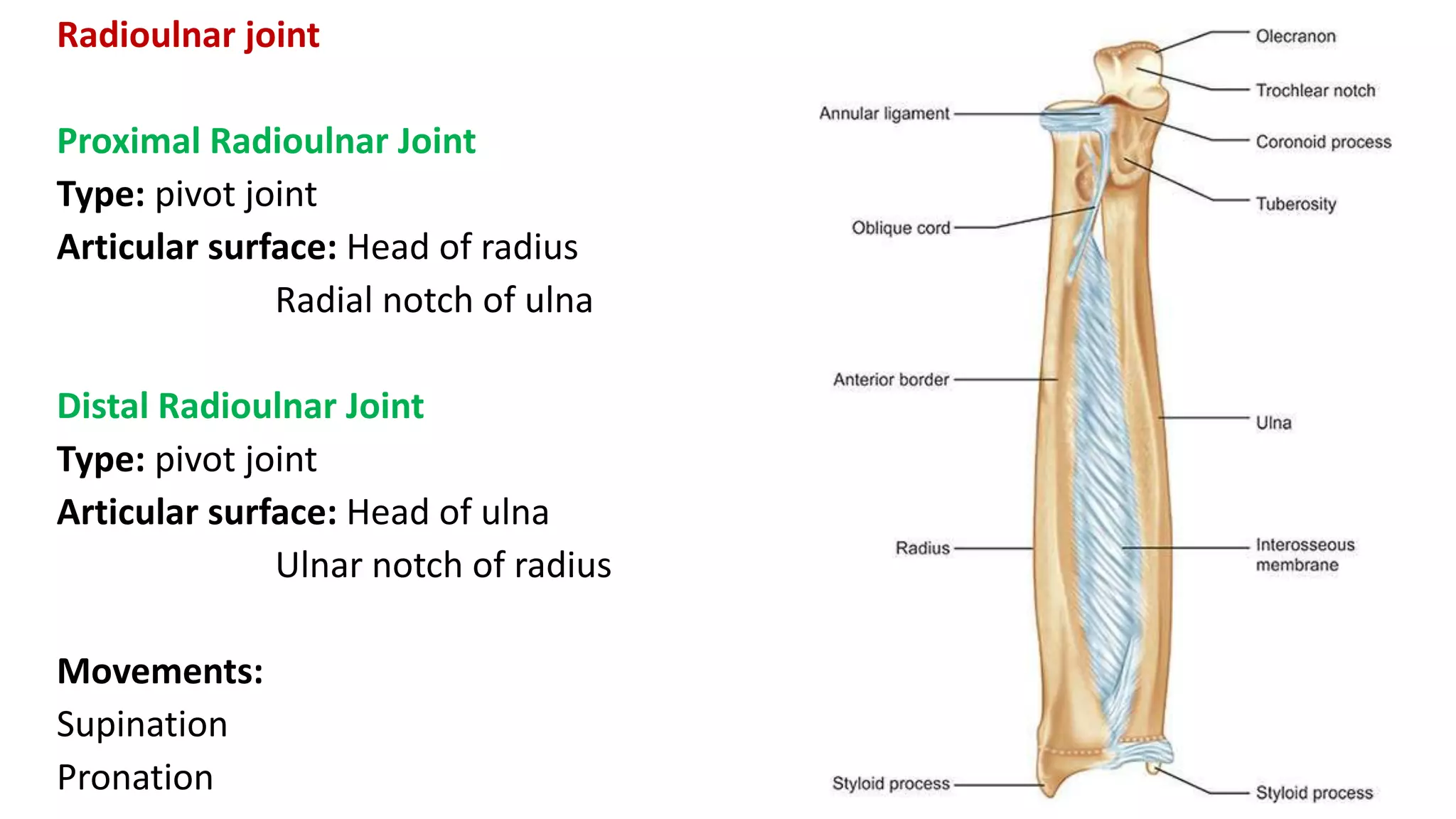
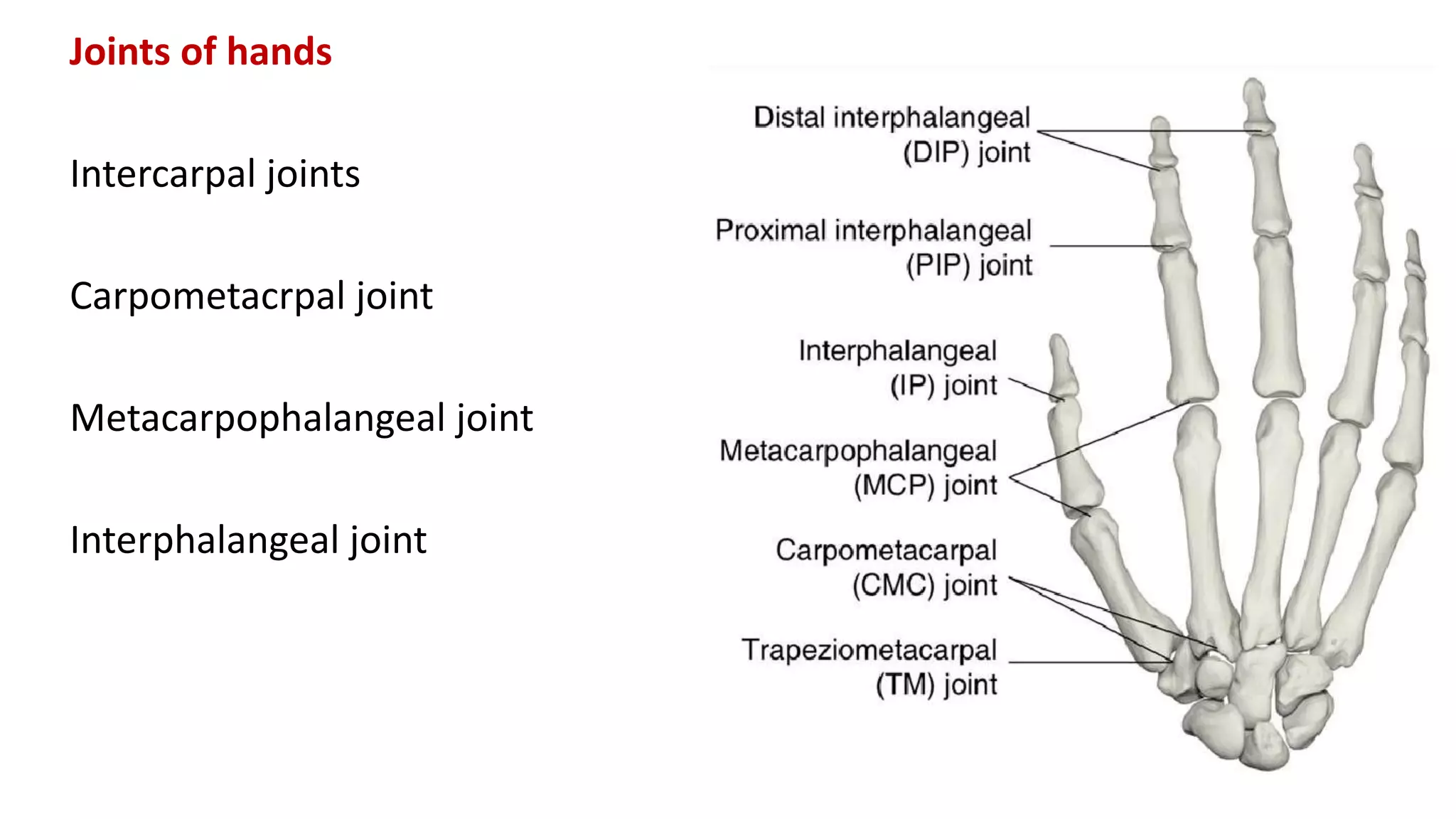
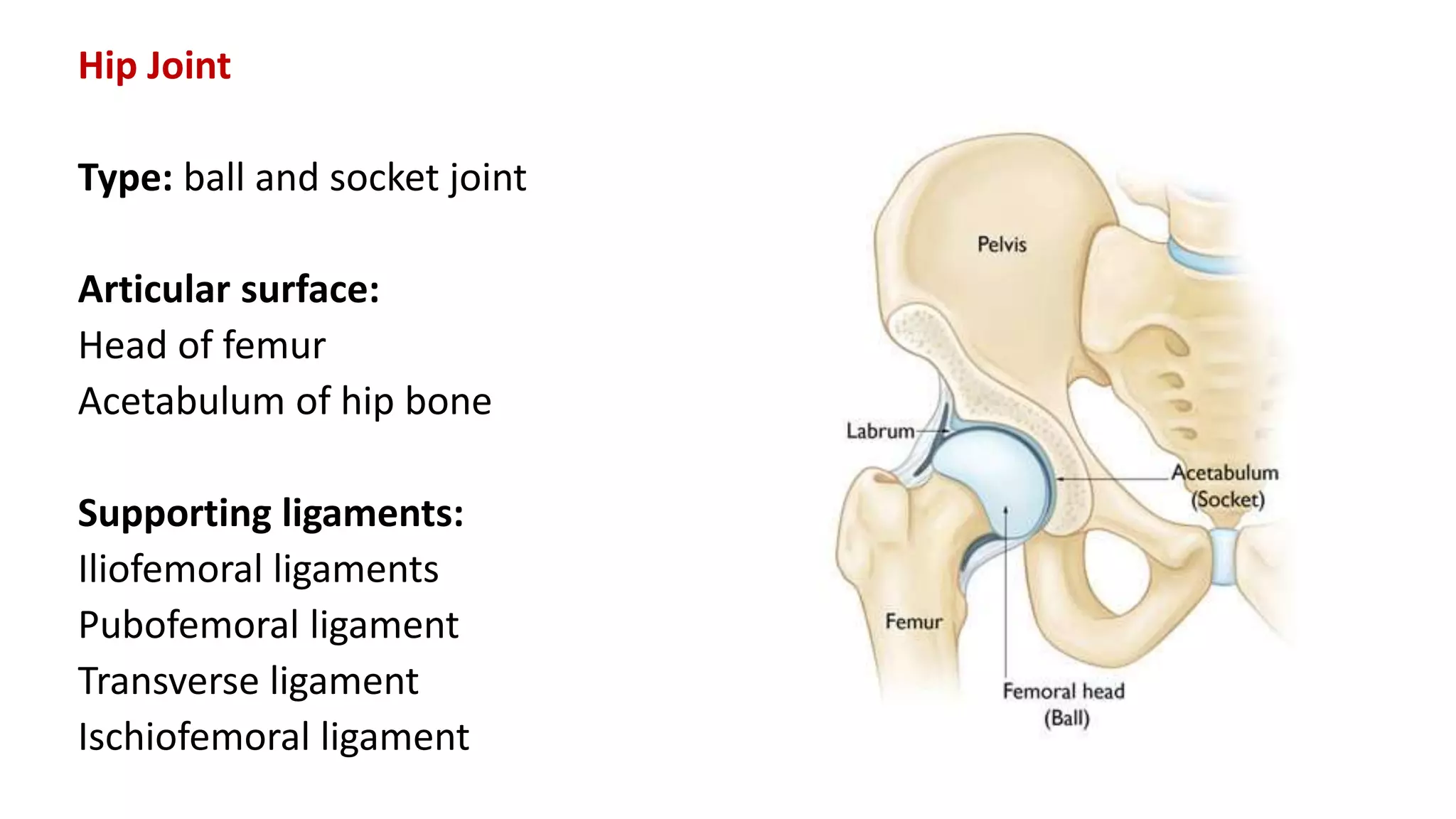
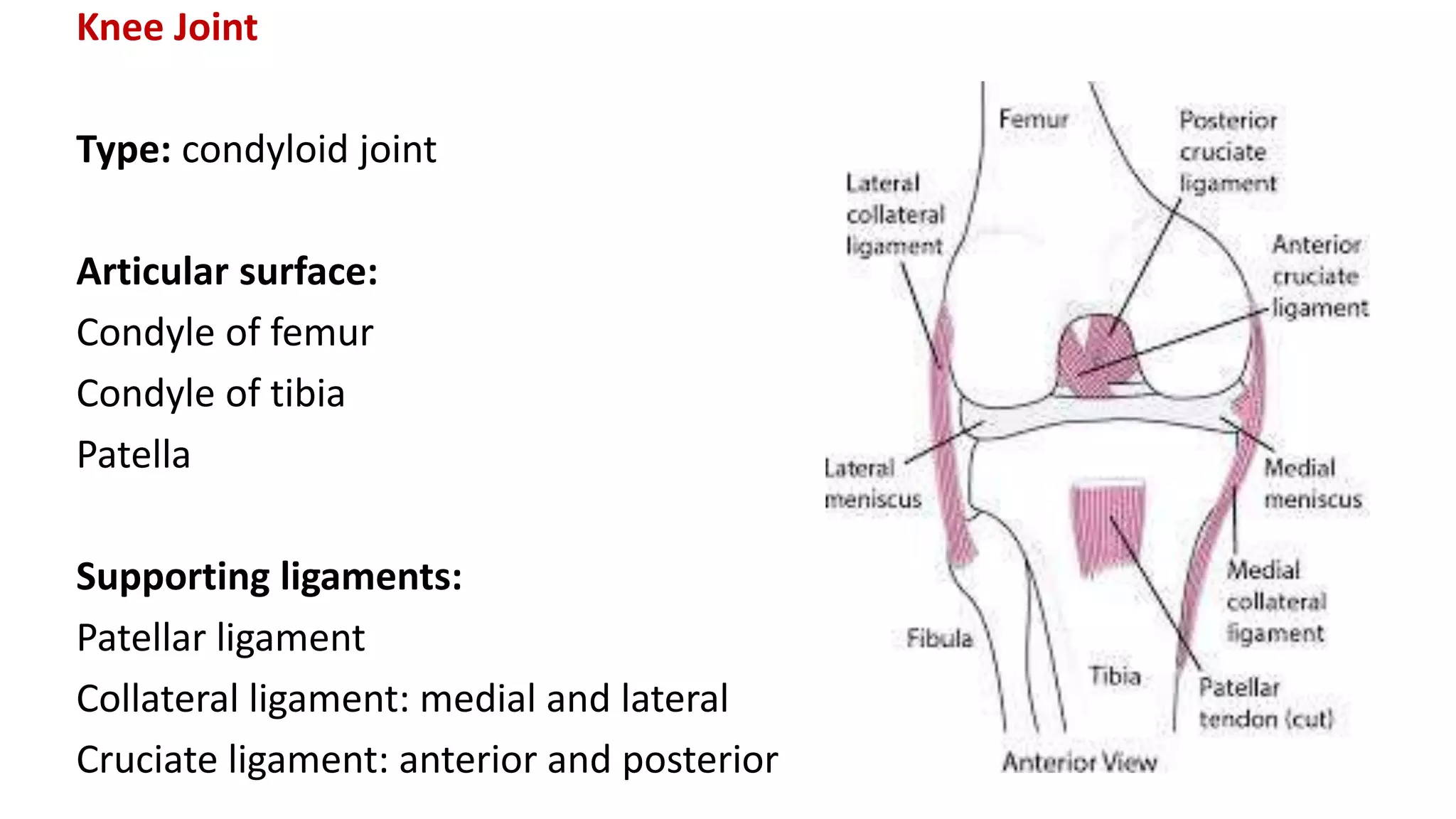
This document discusses the different types of joints in the human body. It begins by defining a joint and classifying joints by function and structure. The three main types by function are synarthrosis (immovable), amphiarthrosis (slightly movable), and diarthrosis (freely movable). The three main types by structure are fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints. It then provides details on the different types of synovial joints and examples of various joints in the body like the shoulder, elbow, hip, knee, ankle joints. It concludes with a brief description of bursae and fontanels.