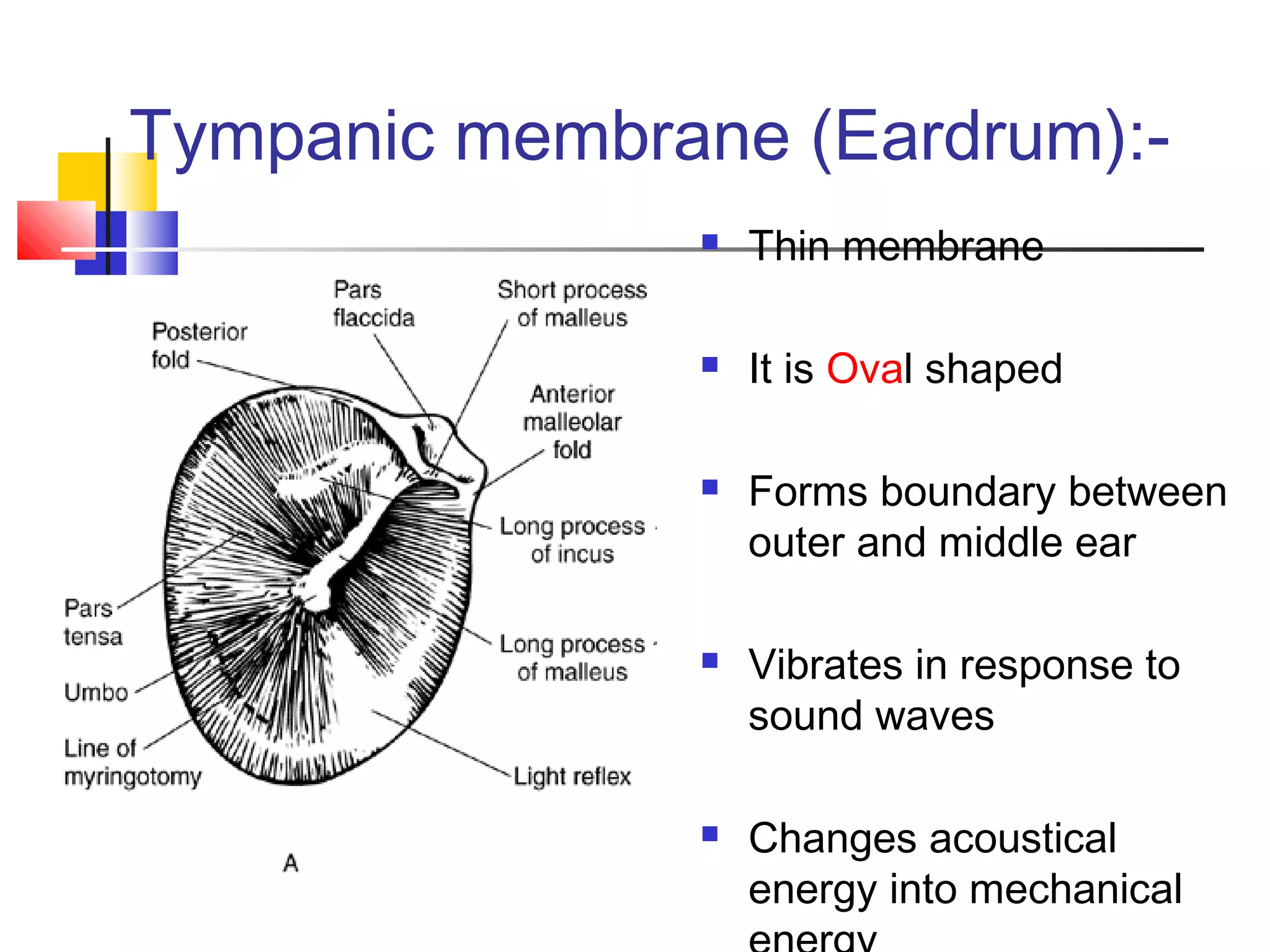
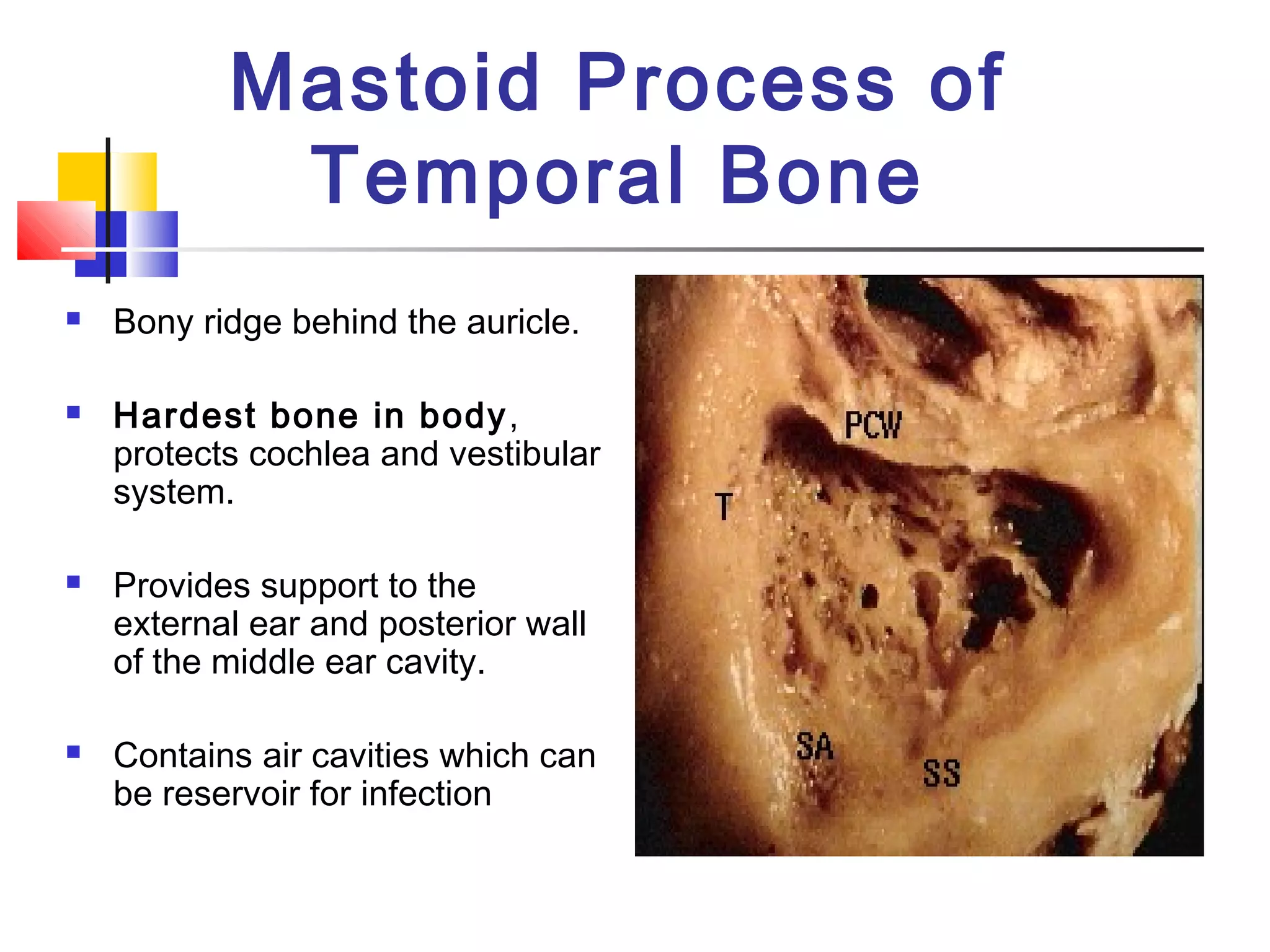
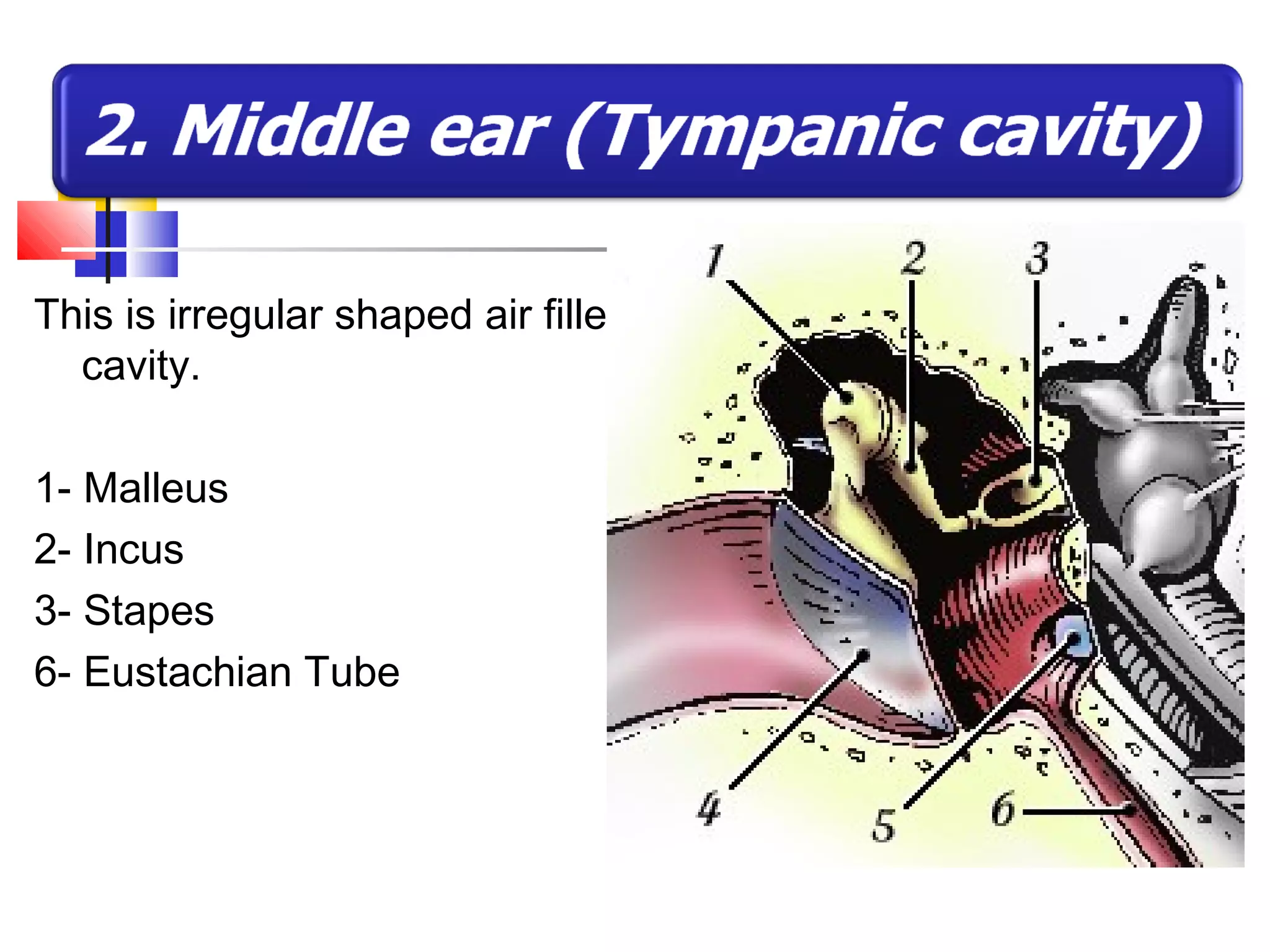
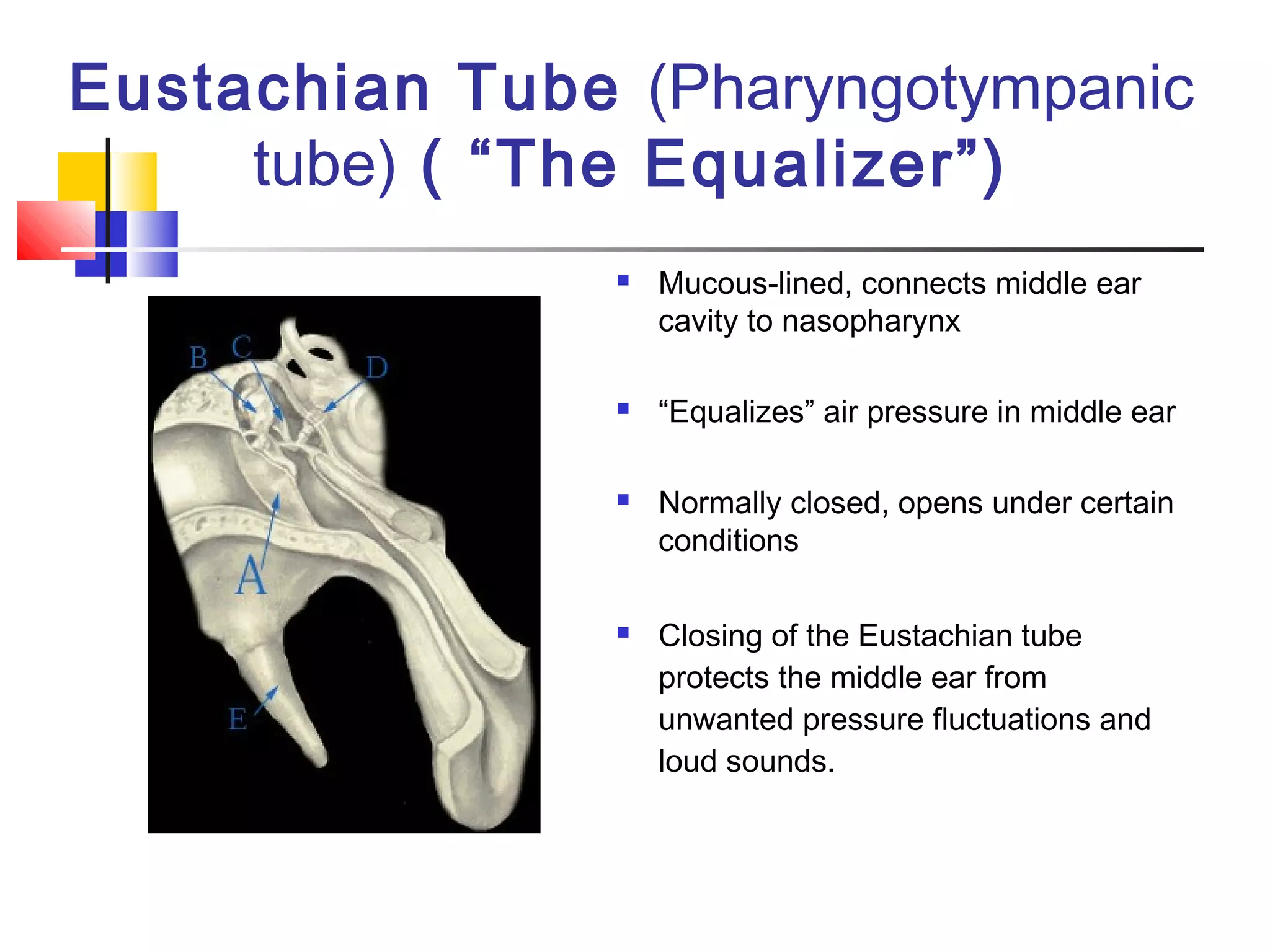
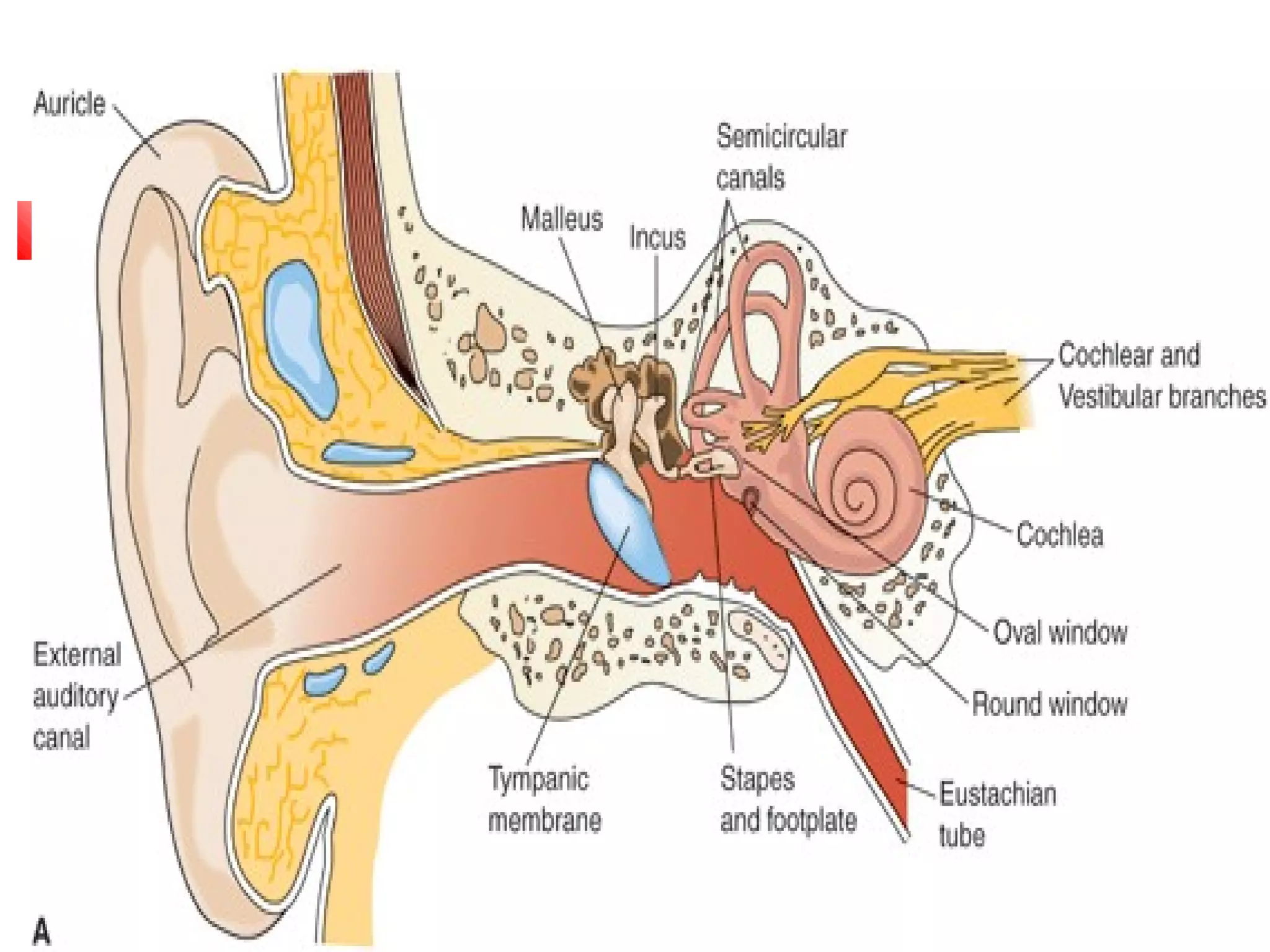
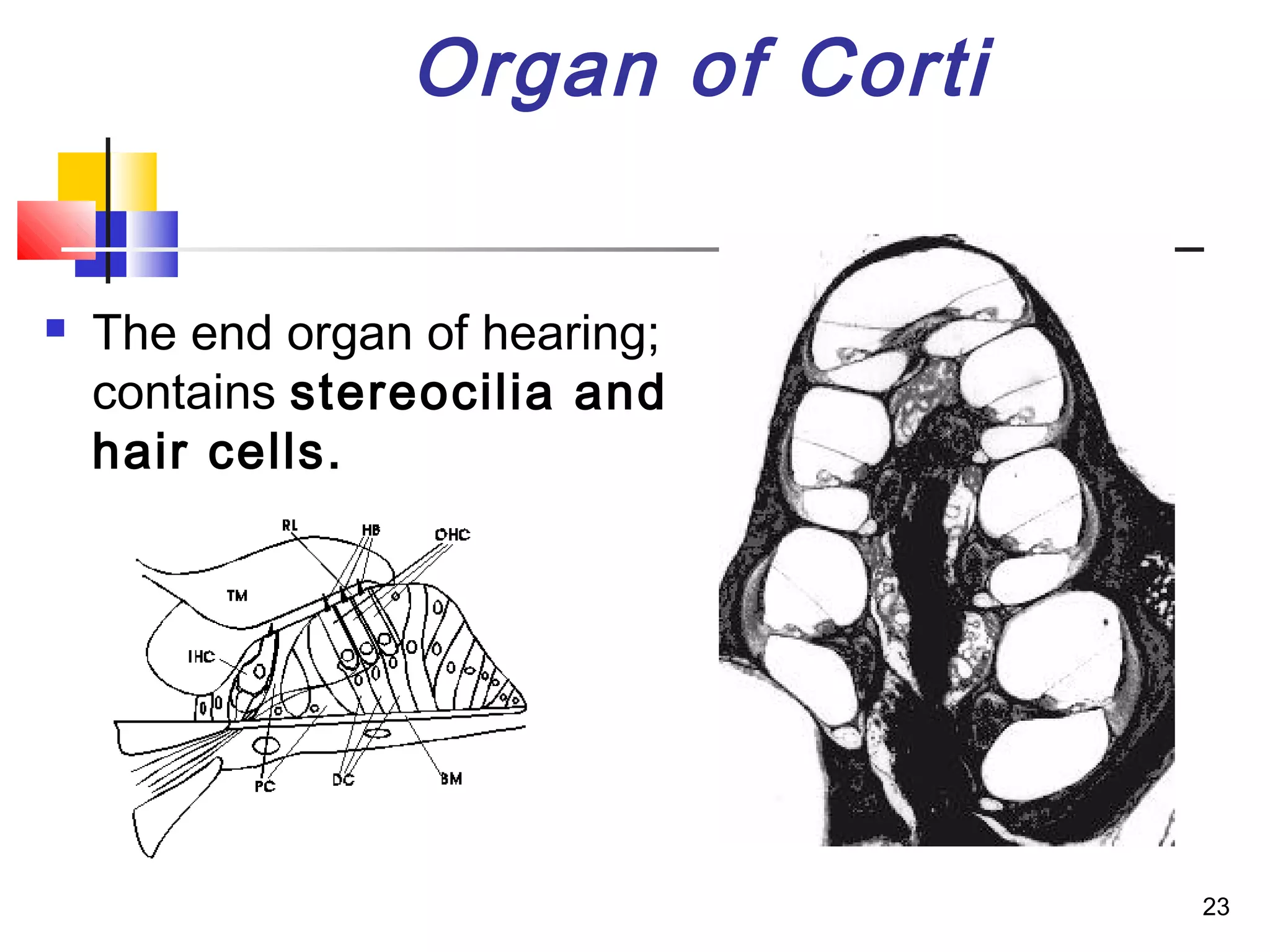
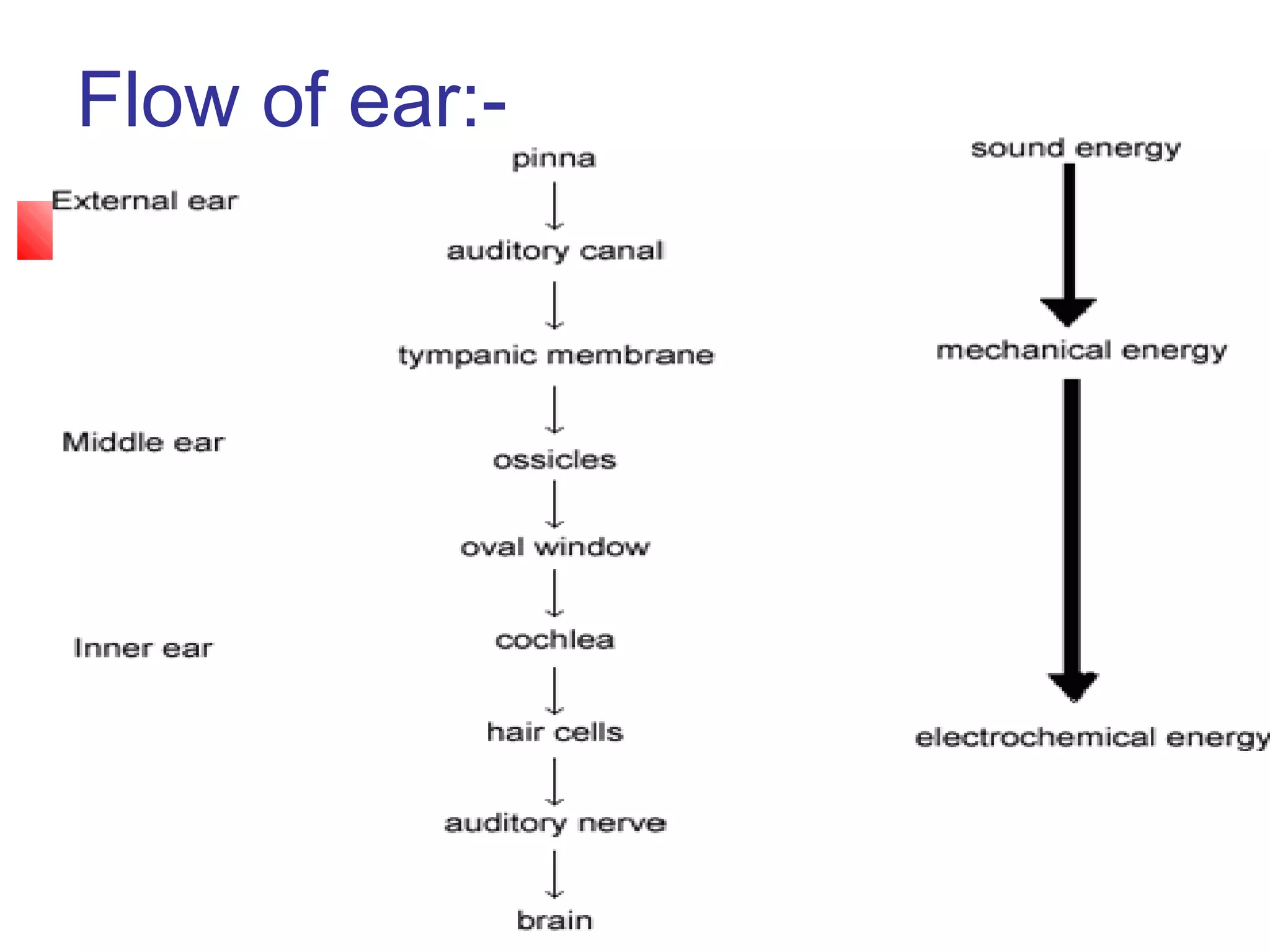
The ear is divided into three parts: the outer, middle, and inner ear. The outer ear collects sound waves and directs them through the external auditory canal to the eardrum. The middle ear contains three small bones (ossicles) that amplify vibrations through bone conduction to the inner ear. The inner ear converts vibrations into neural signals for hearing and balance via the cochlea and semicircular canals. Sound waves are transduced into mechanical, then hydraulic, then electrical energy as they travel through the ear to be interpreted by the brain.