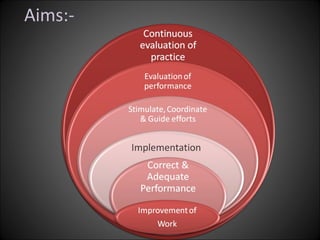
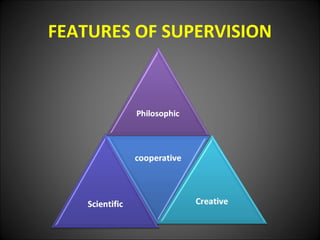
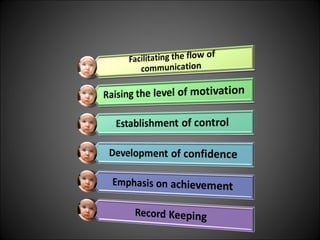
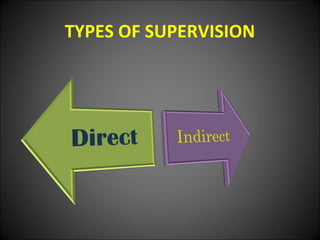
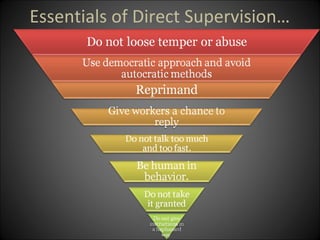
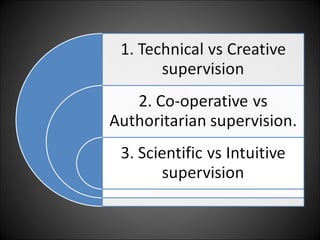
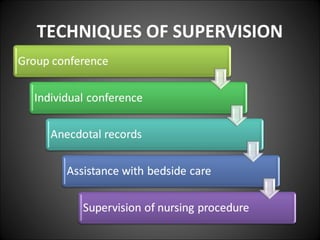
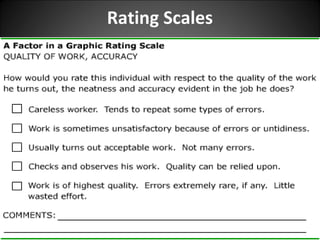
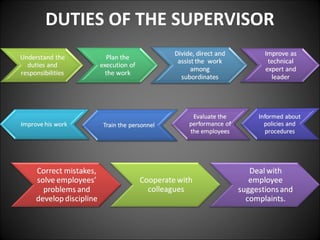
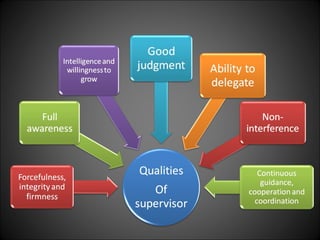
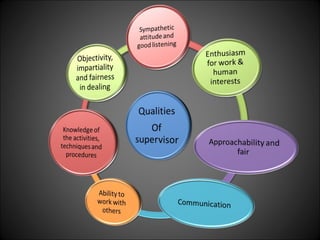
This document discusses supervision in healthcare organizations. It defines supervision as helping workers learn, use their skills effectively, and improve their abilities to do their jobs well and be satisfied. The objectives of supervision include helping staff work skillfully, developing their capacities, guiding them to meet targets, and motivating them. Supervision functions include developing team spirit, improving knowledge and skills, maintaining relationships, and identifying and solving problems. Principles of supervision are that it should not overburden workers, foster independent thinking, encourage participation, and respect staff. Techniques include direct observation, indirect review of records and reports, checklists, rating scales, and nurse reports.