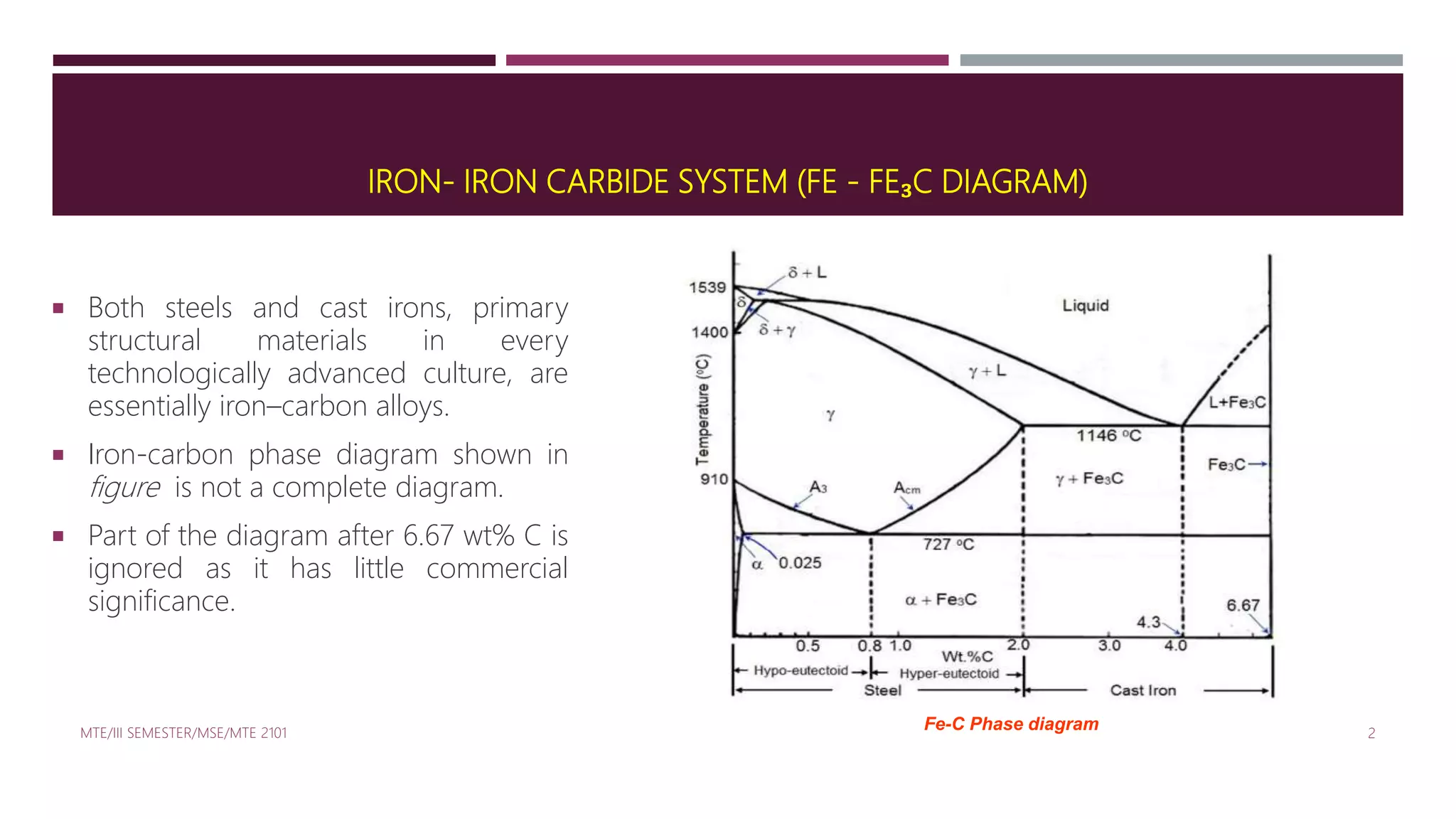
The iron-carbon system, pivotal in metallurgy, consists of iron and iron carbide (Fe3C) and is represented by a phase diagram that illustrates various phases and reactions influenced by temperature and carbon content. The diagram includes five phases (α-ferrite, γ-austenite, δ-ferrite, Fe3C, and liquid Fe-C) and three key invariant reactions: peritectic, eutectic, and eutectoid, each occurring at specific temperatures. This system is essential in understanding the properties of different ferrous alloys, namely iron, steels, and cast irons based on their carbon content.