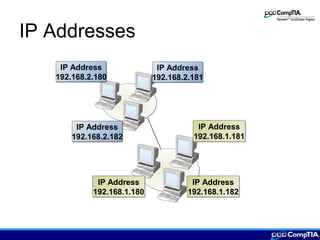
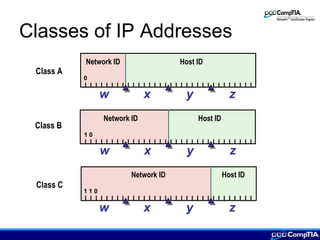
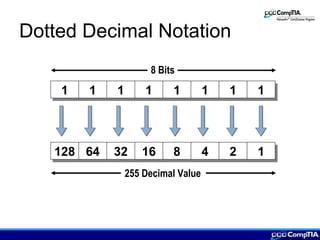
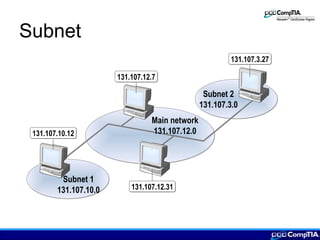
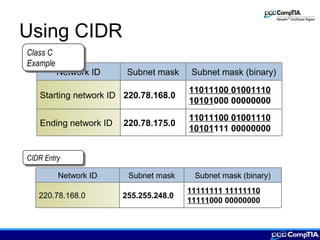
This document provides an overview of IP addressing concepts including assigning IP addresses, creating subnets, IPv4 and IPv6 addressing, and TCP/IP protocols. Key topics covered include the classes of IP addresses, dotted decimal notation, subnetting, public and private IP addresses, protocols like ICMP, ARP, RARP, DHCP, Telnet, and FTP.