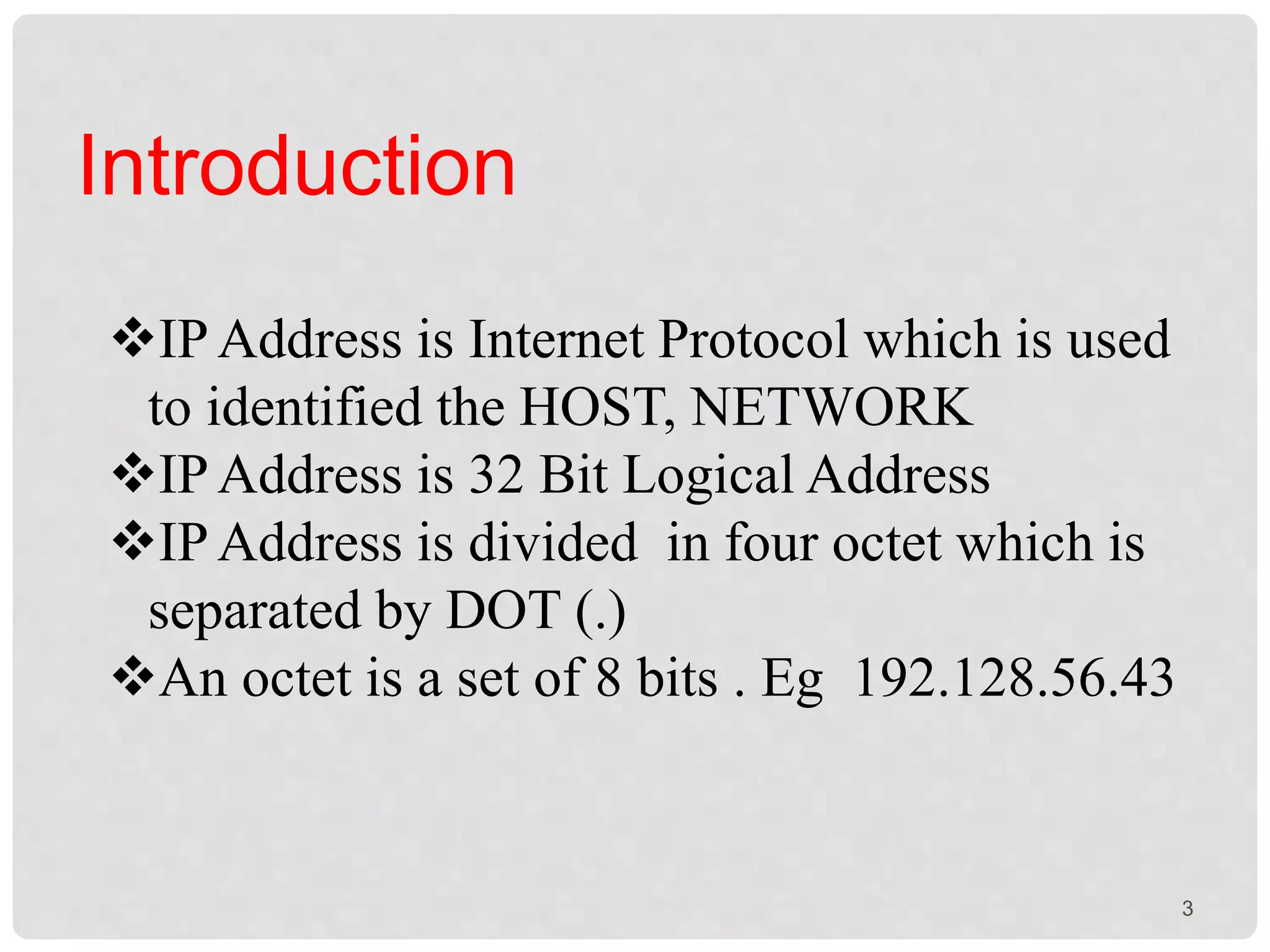
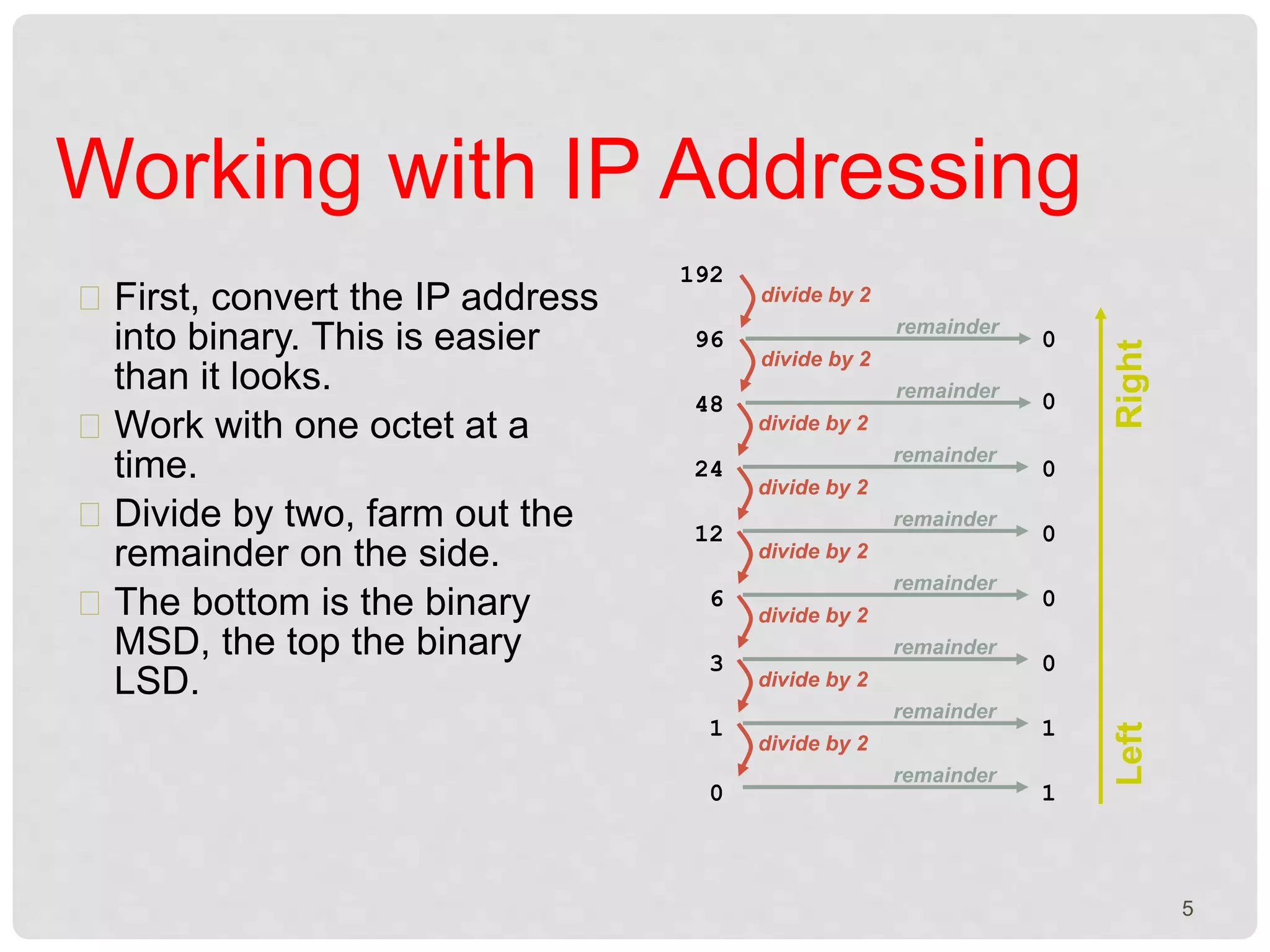
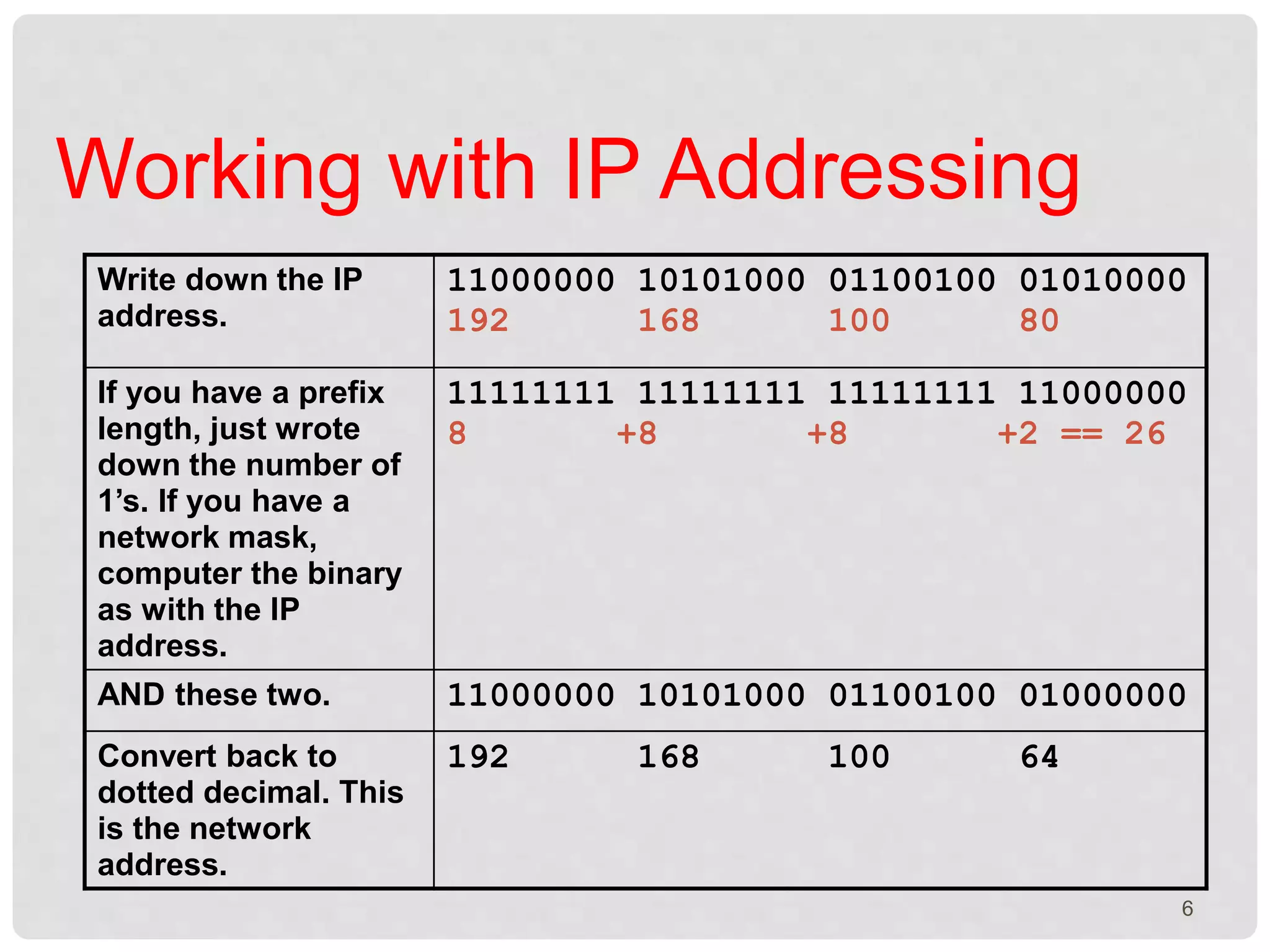
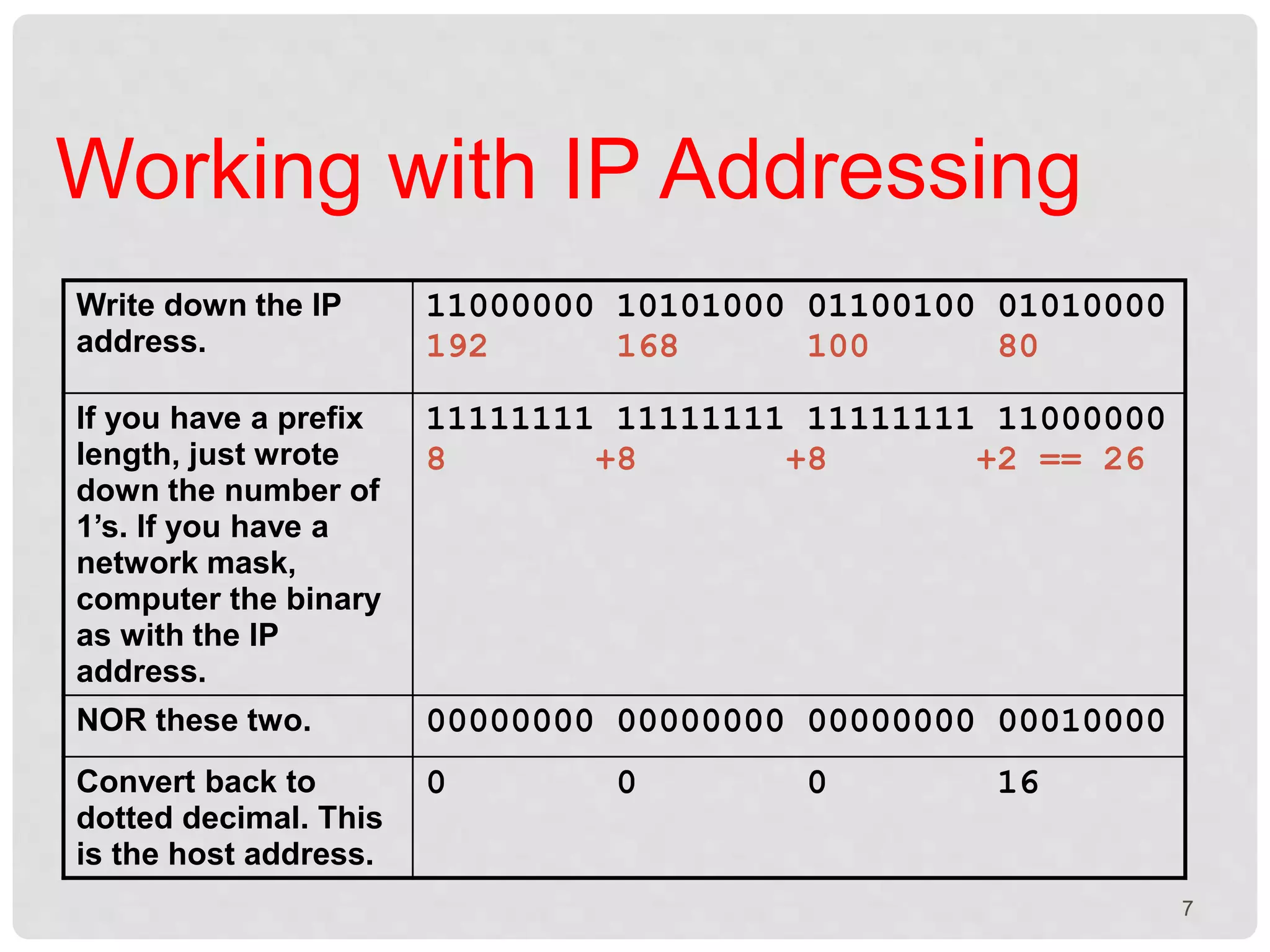
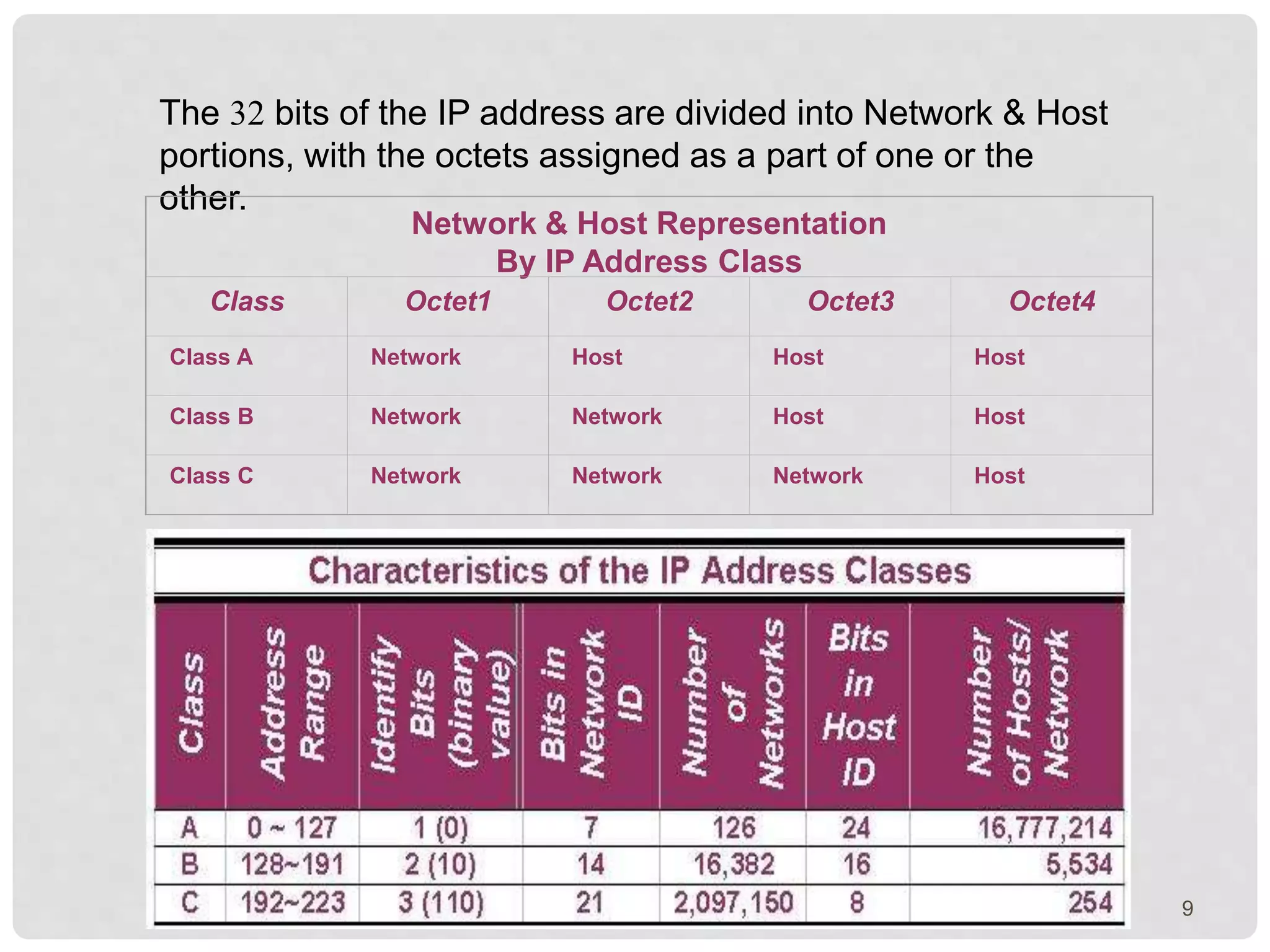
The document is a presentation on IP addressing, discussing its fundamentals, including the structure of IP addresses, their classes, and the concept of subnetting. It covers how to convert IP addresses to binary format and determine network and host information. Additionally, the document explains subnet masks and their role in network segmentation.