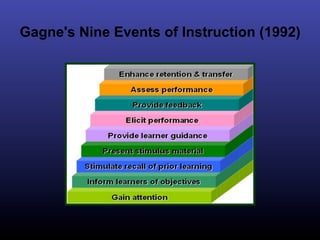
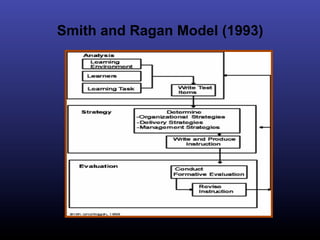
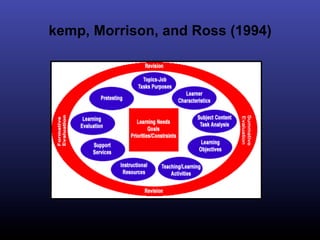
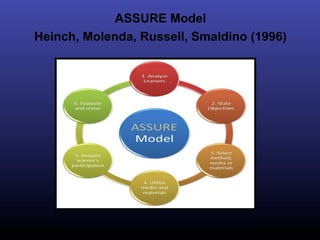
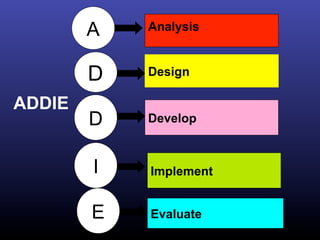
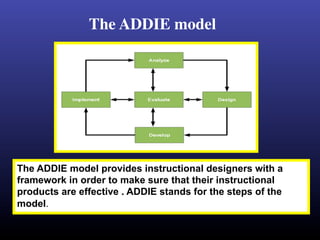
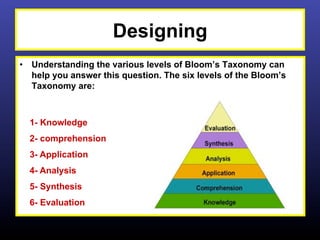
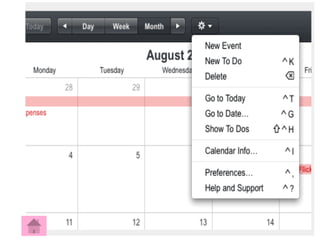
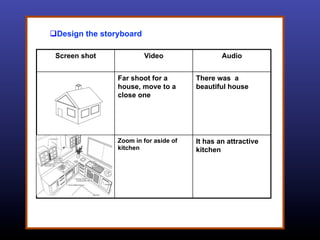
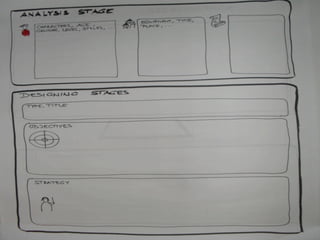
The ADDIE model is a systematic instructional design model consisting of 5 phases: Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation. In the Analysis phase, instructional problems are identified and analyzed. In the Design phase, learning objectives and assessments are developed. During the Development phase, materials are created. In the Implementation phase, instruction is delivered. Finally, in the Evaluation phase, the effectiveness of the instruction is evaluated. The ADDIE model provides a framework to systematically design effective instruction.