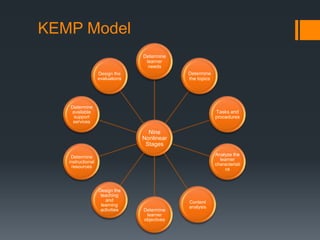
This document discusses and compares several instructional design models for developing asynchronous online curriculum: the Indiana Partnership for Stateside Education guidelines, ADDIE, Dick and Carey, KEMP, the Three-Dimensional ITD Model, and the use of learning objects. It provides an overview of the key stages and components of each model. The models vary in their structure and focus areas, but generally involve analyzing learner and instructional needs, designing assessments and content, developing materials, implementing the course, and evaluating effectiveness.