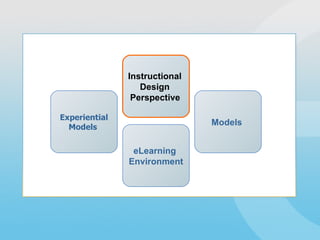
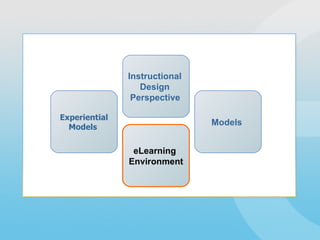
The document discusses instructional design models and perspectives for developing eLearning environments. It describes how instructional designers use formal models like ADDIE as well as experiential models to make design decisions. Formal models provide structure but may not reflect real-world practice, while experiential models emphasize qualitative evaluation and teamwork. The document also examines how instructional designers analyze content, learners, and context to create optimal learning experiences within eLearning environments.