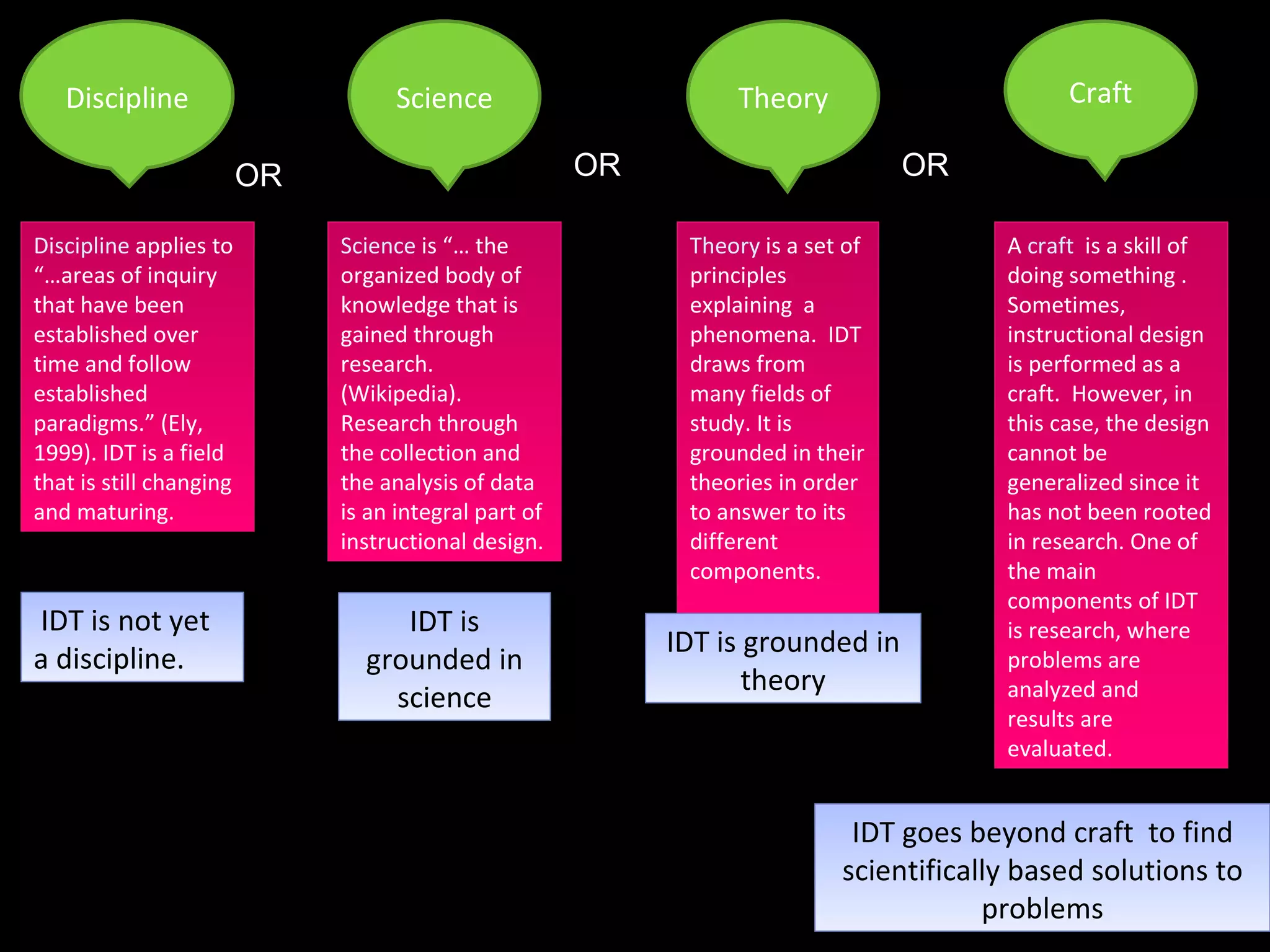
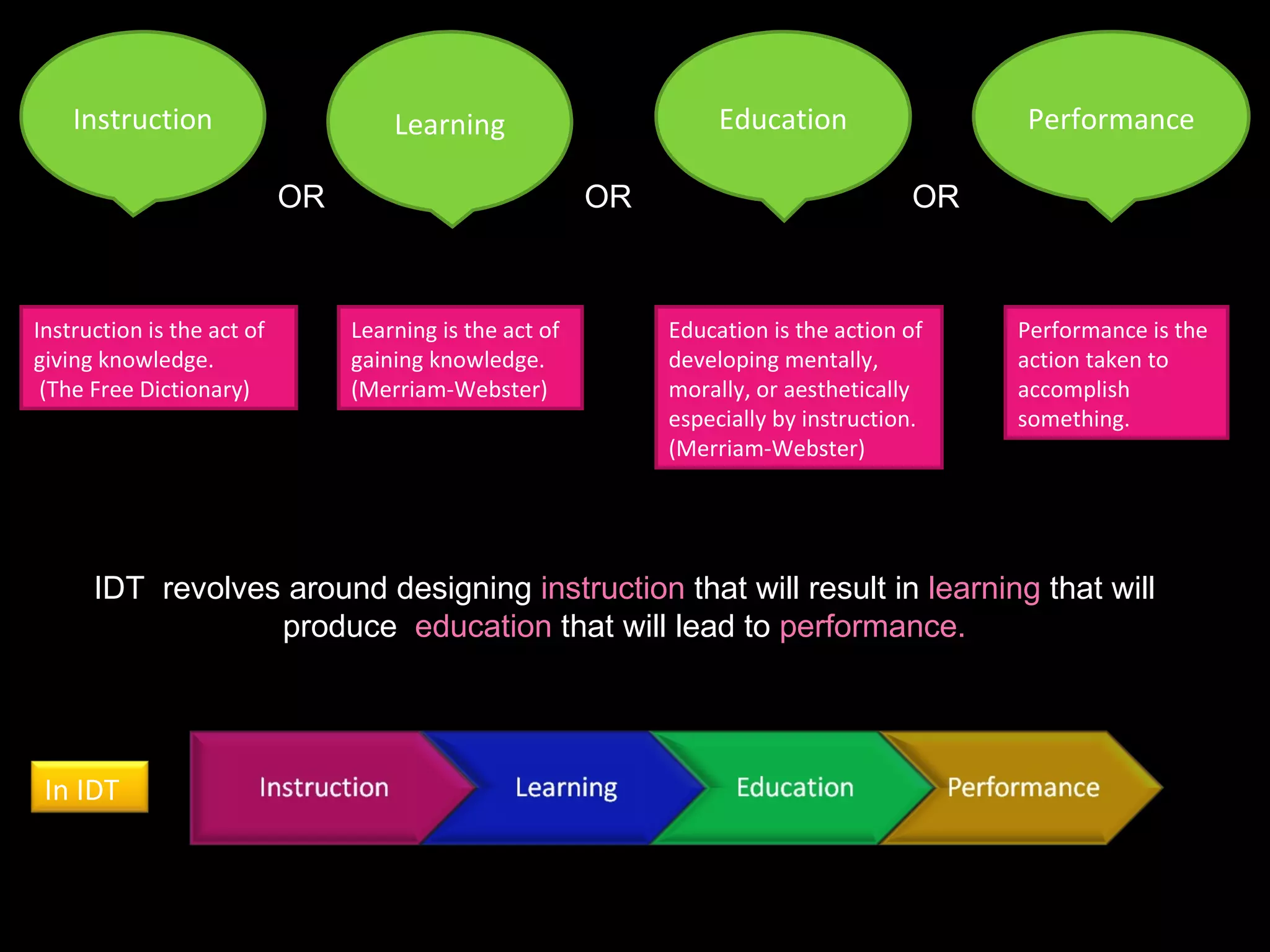
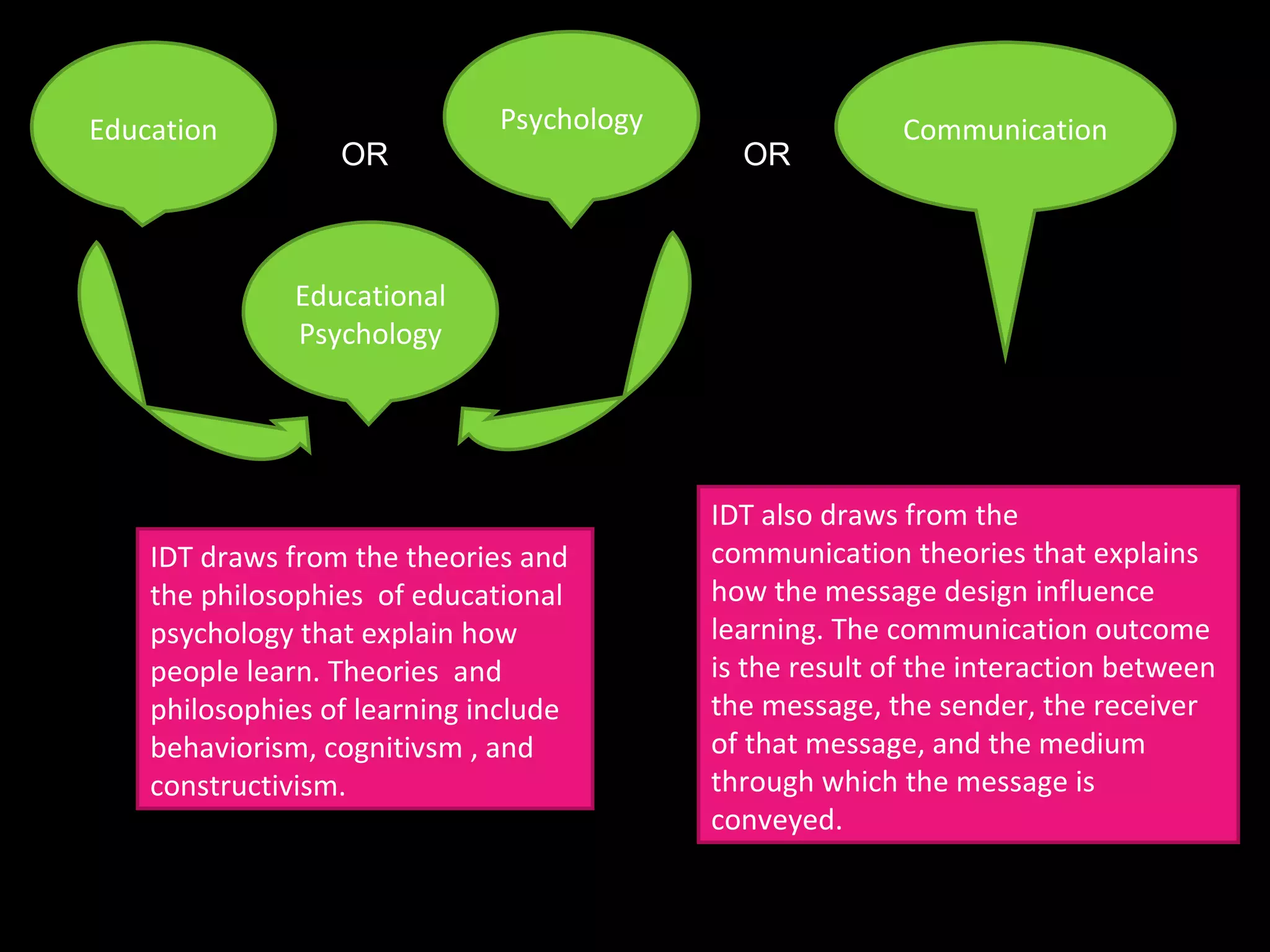
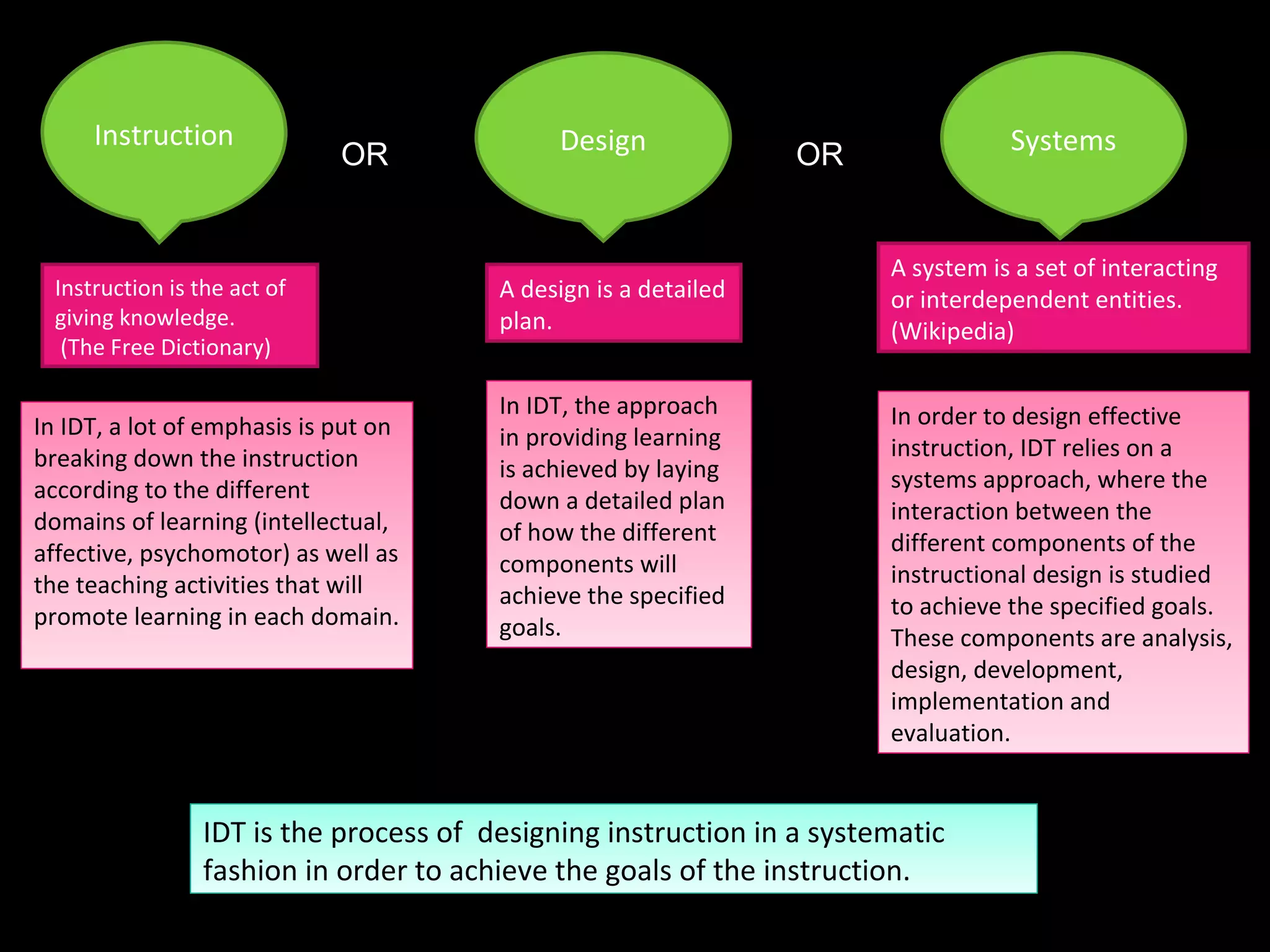
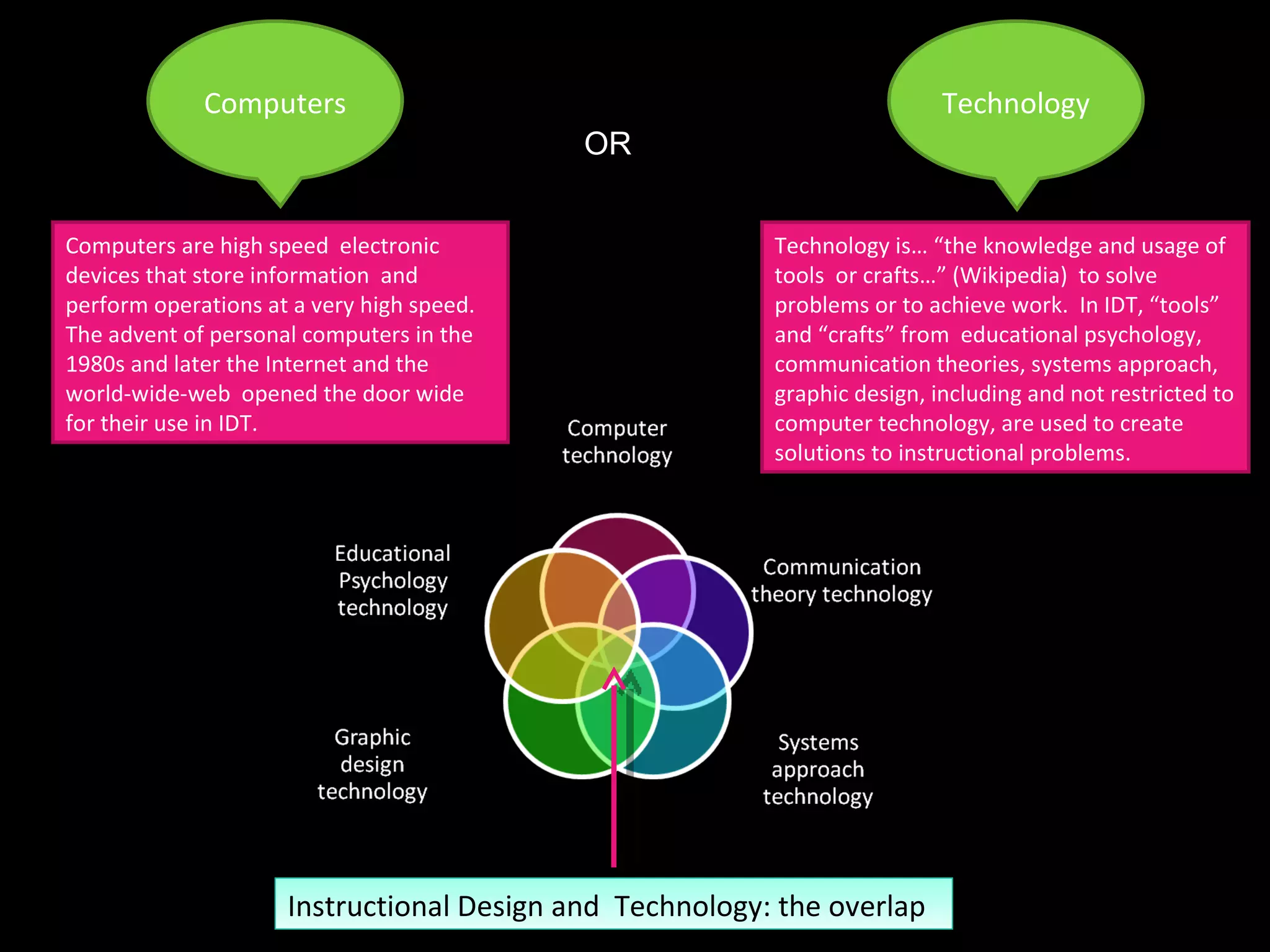
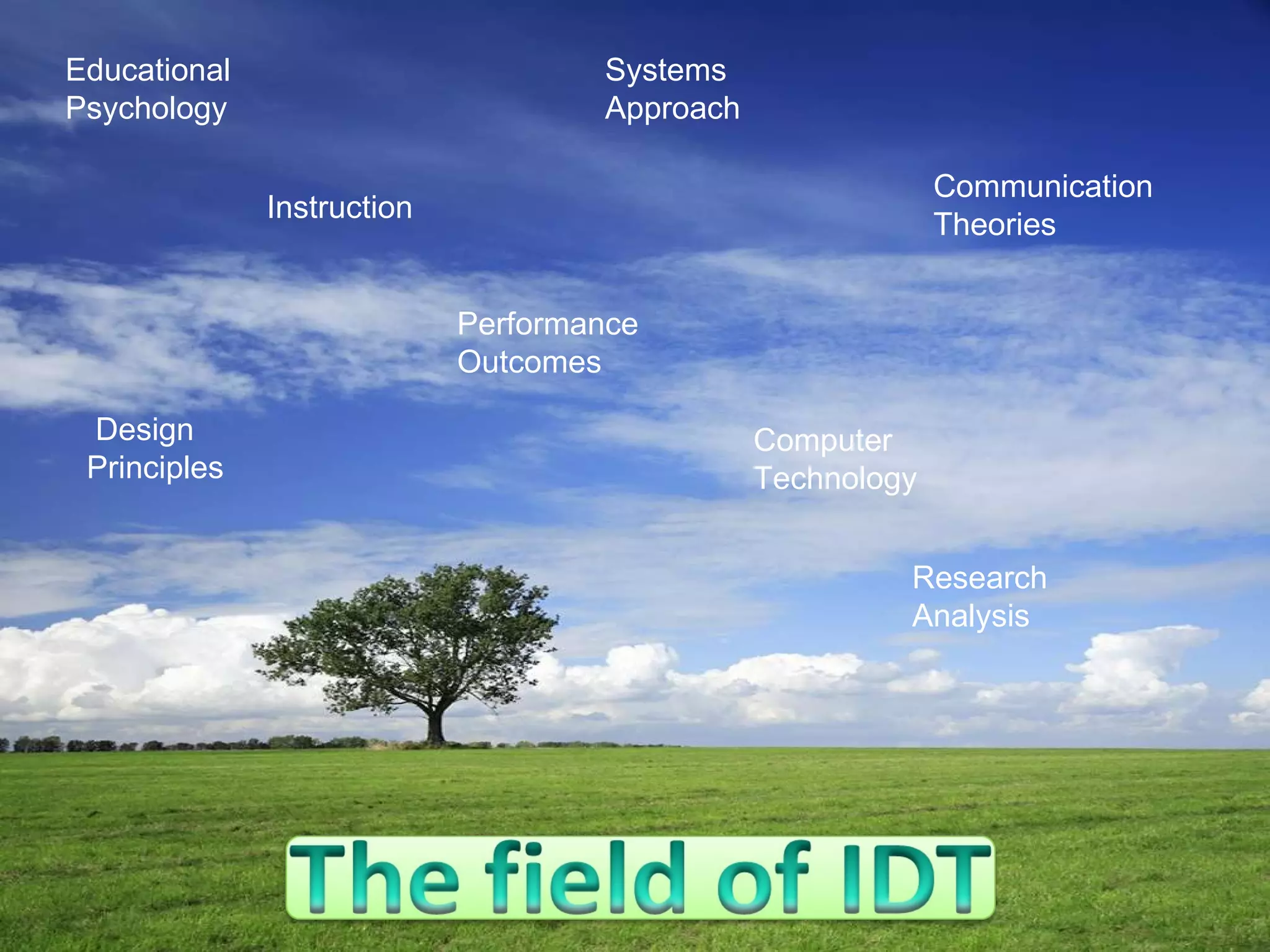
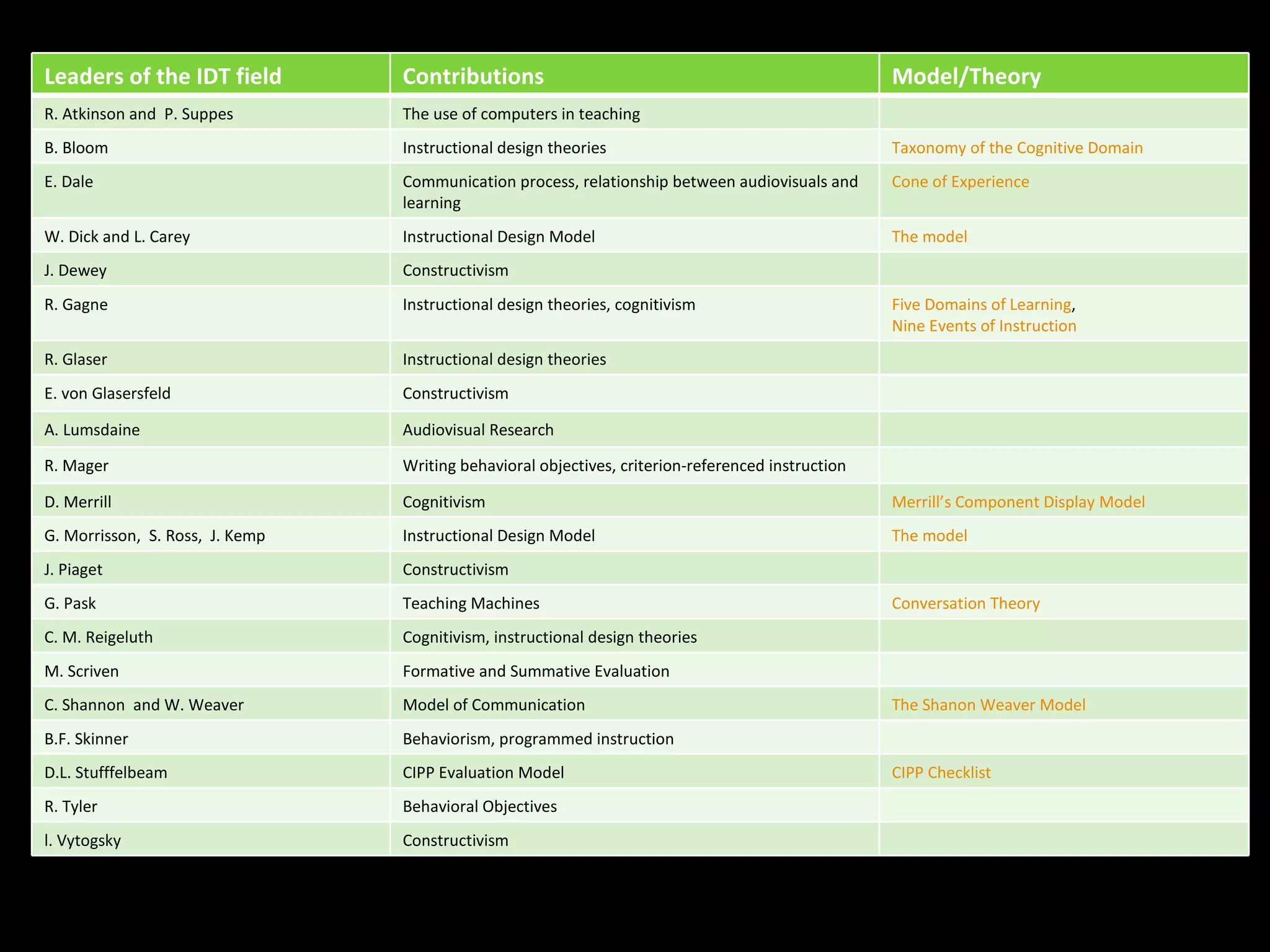
The document discusses different perspectives on instructional design and technology (IDT), including whether it is a discipline, science, or craft. While IDT draws from research and theory, it is still evolving as a field. The document also examines how IDT relates to concepts like instruction, learning, education, and performance. IDT utilizes theories from educational psychology, communication, and systems design to create effective instructional solutions.