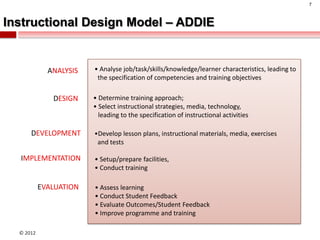
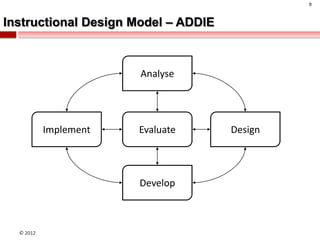
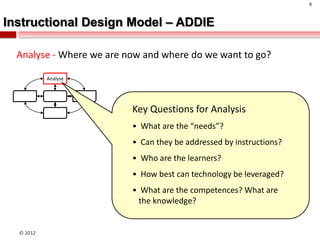
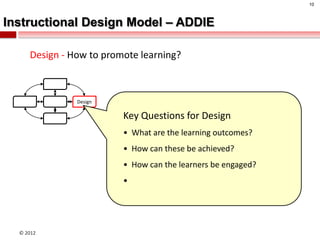
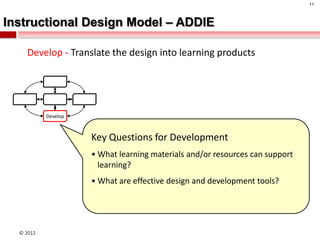
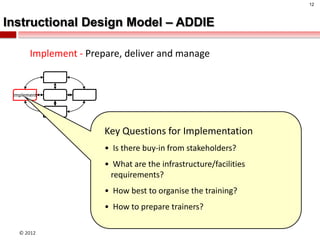
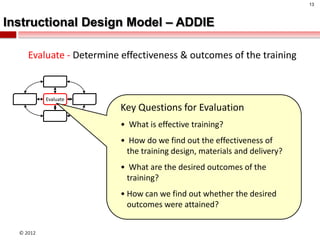
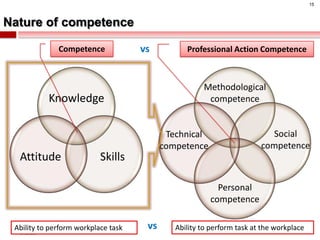
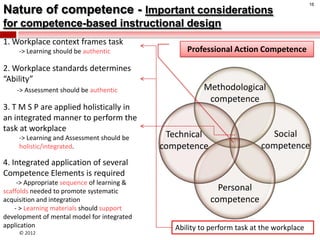
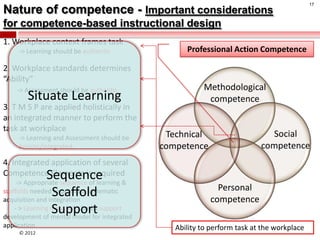
The document summarizes an instructional design presentation on competence-based learning. It begins with an overview of instructional design and the ADDIE model of analysis, design, development, implementation and evaluation. It then discusses the nature of competence and its implications for instructional design, focusing on situating, sequencing, scaffolding and supporting learning through authentic and integrated acquisition of competence. The document provides examples of instructional design models and discusses applying cognitive load theory and assessment for learning to scaffold support for learners.