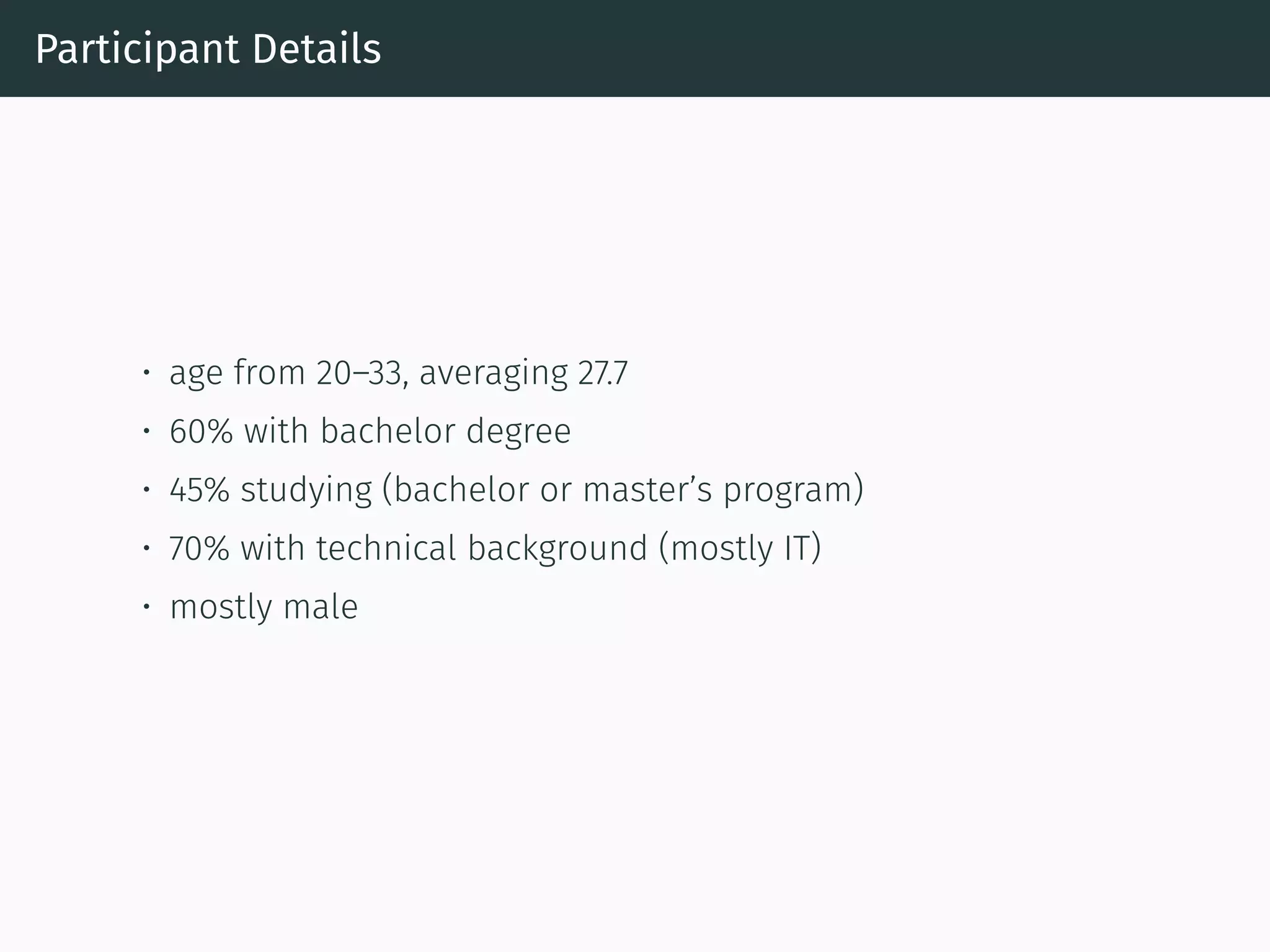
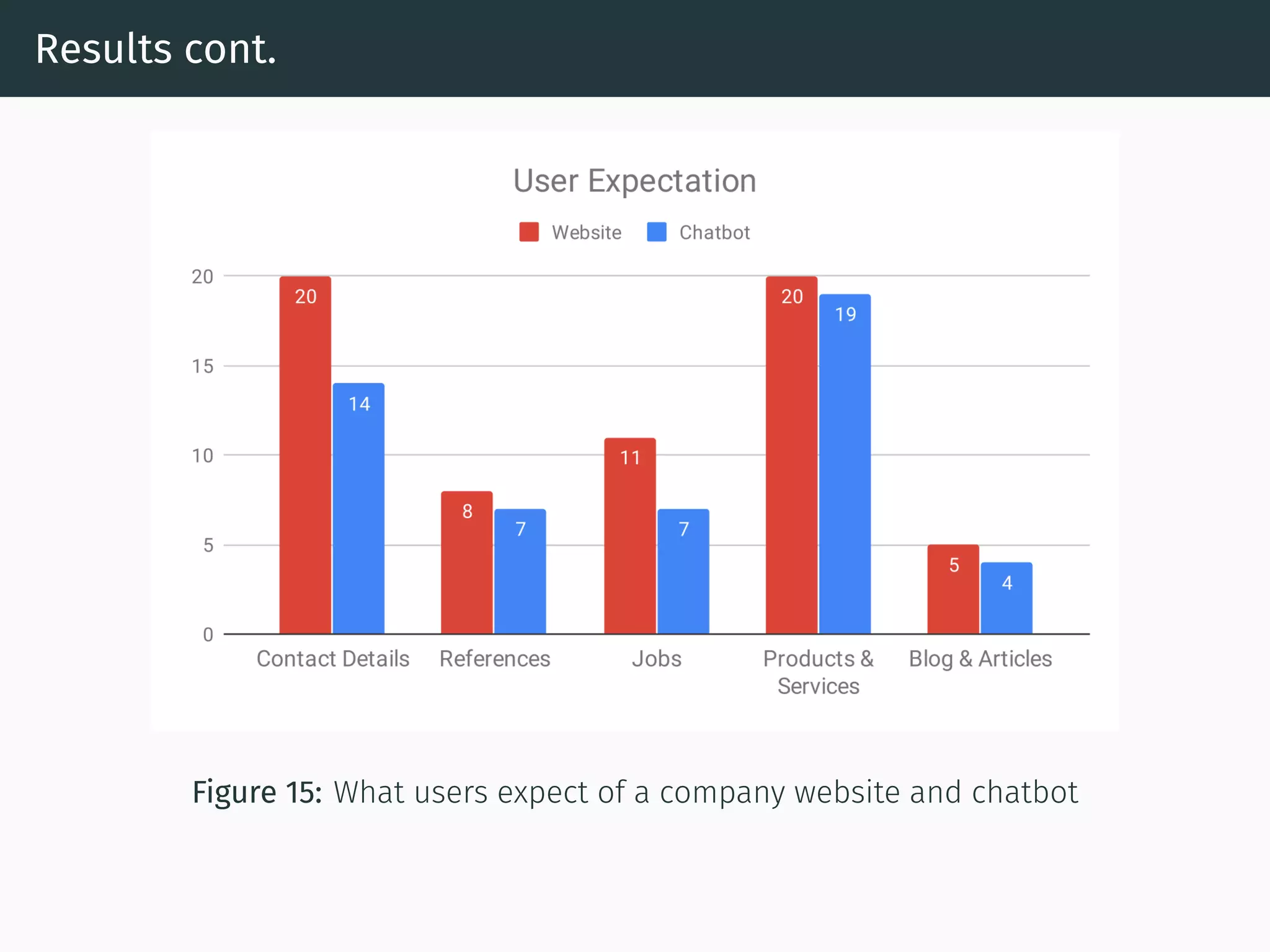
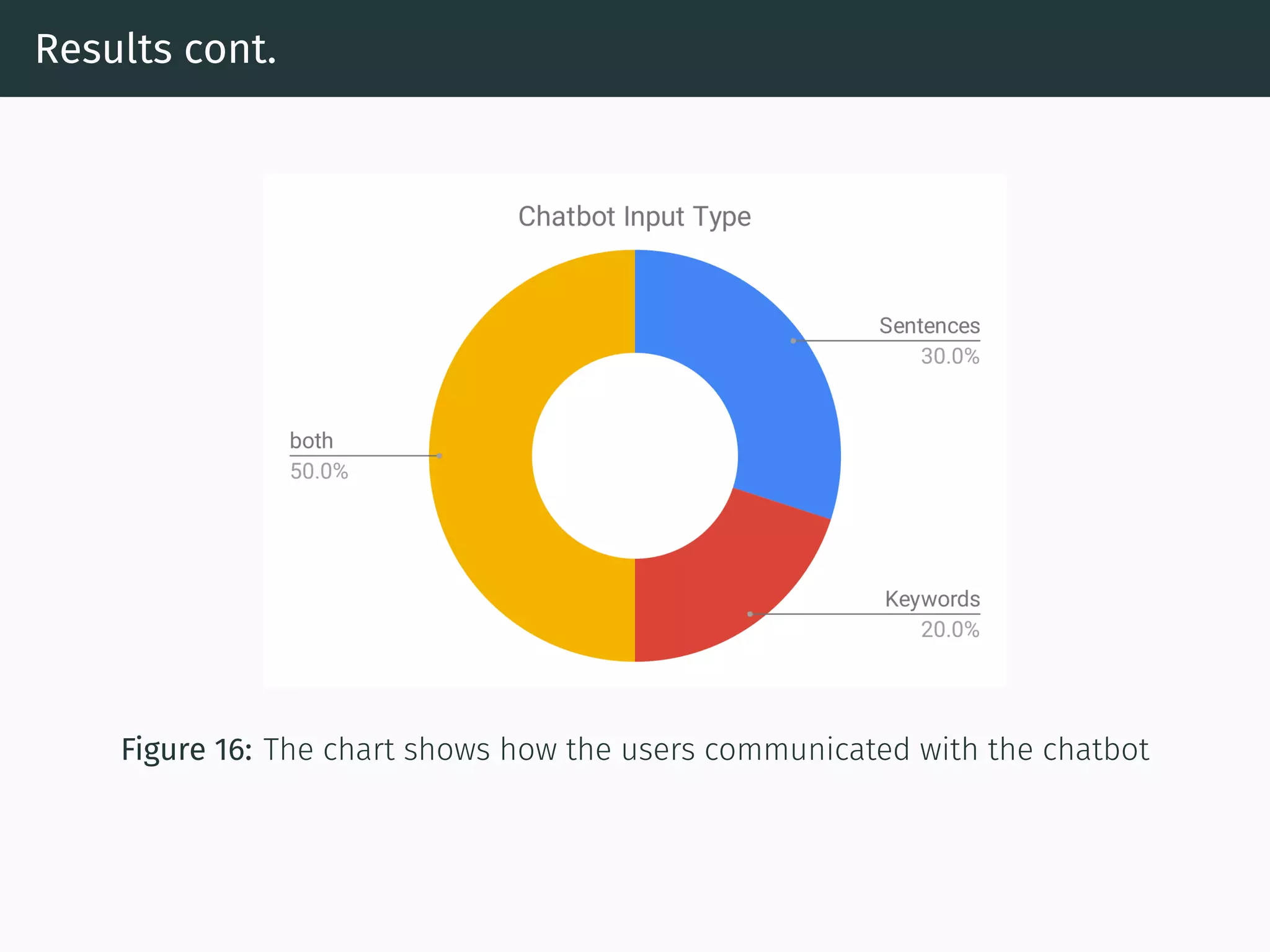
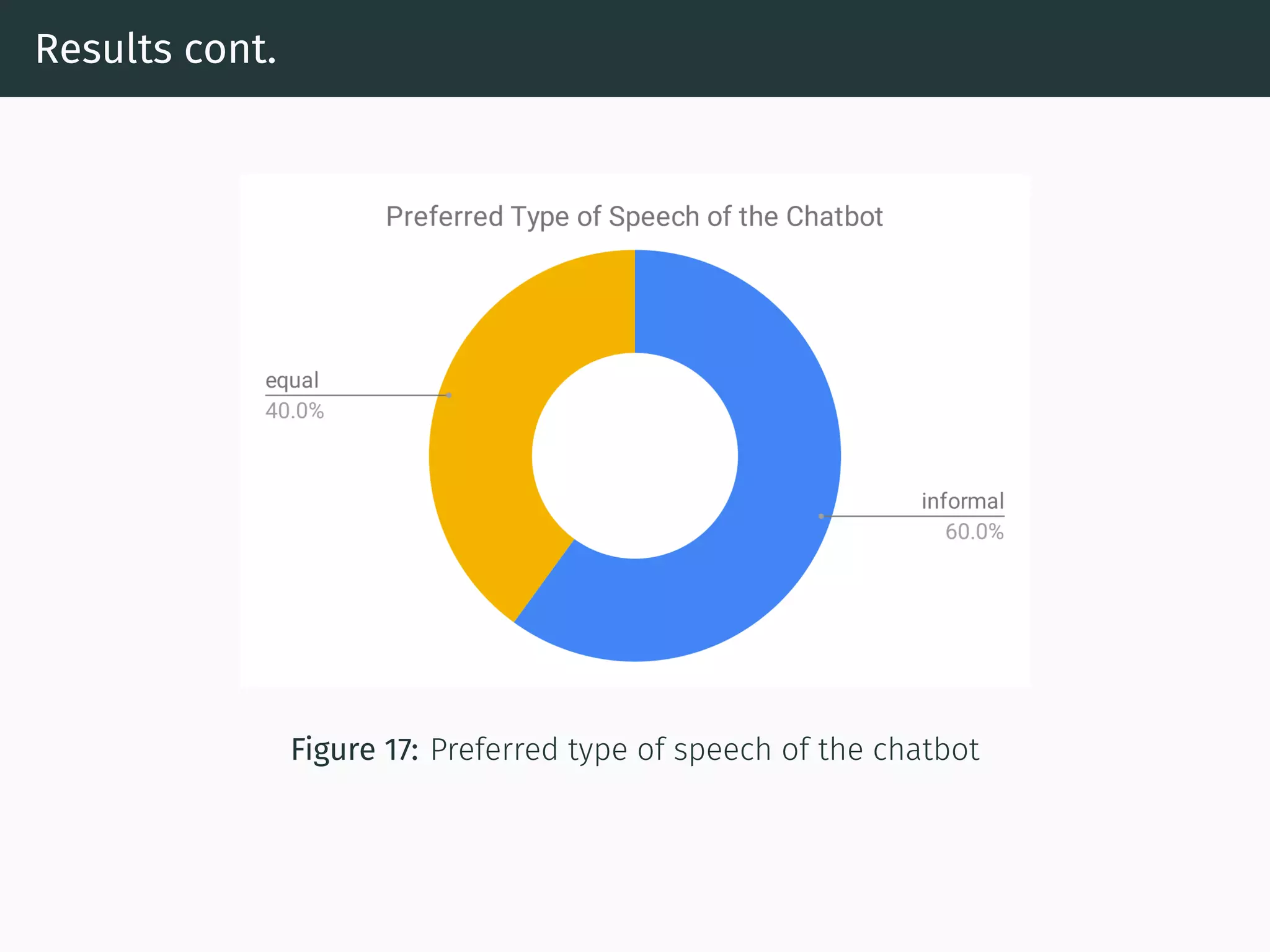
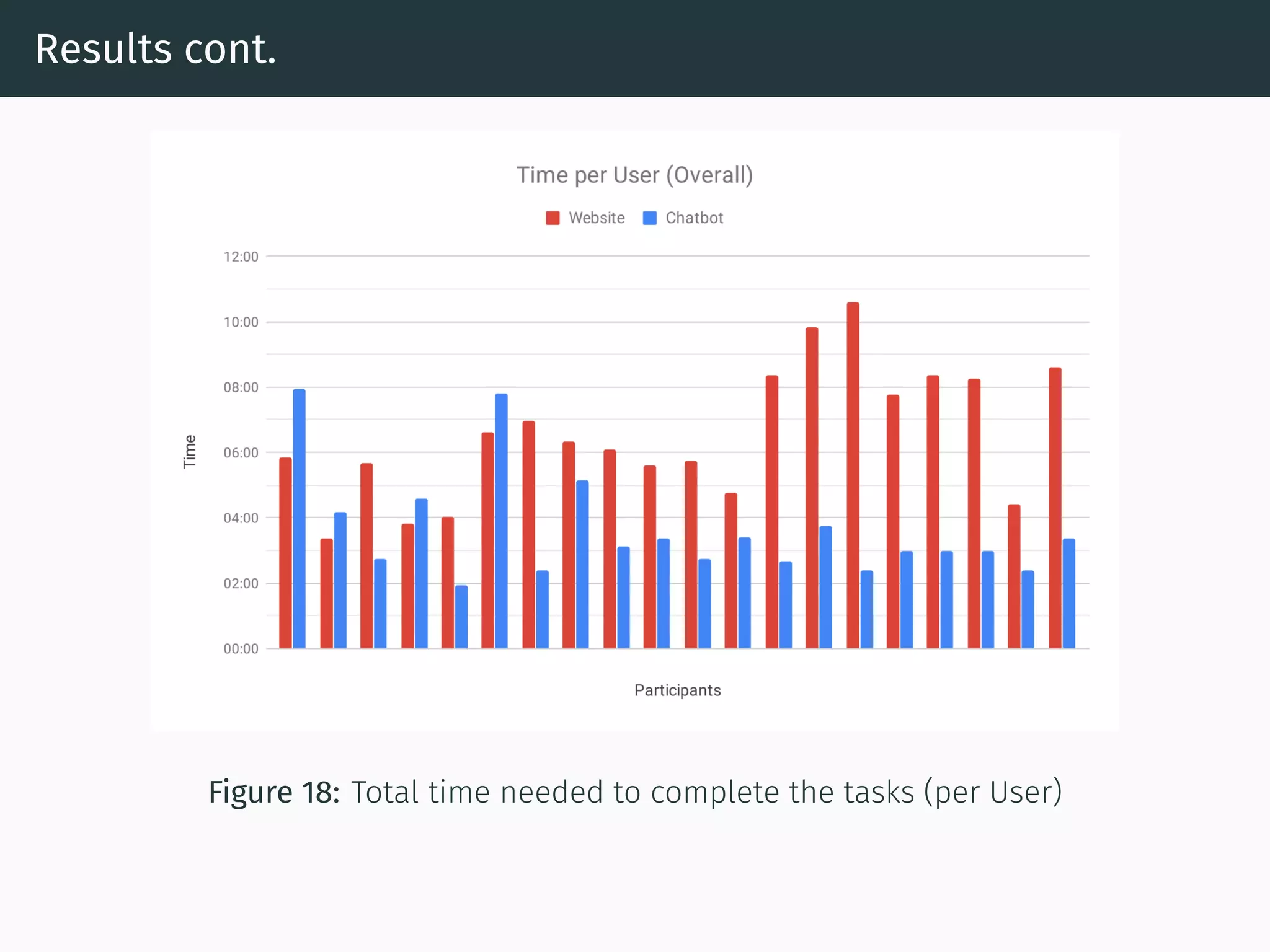
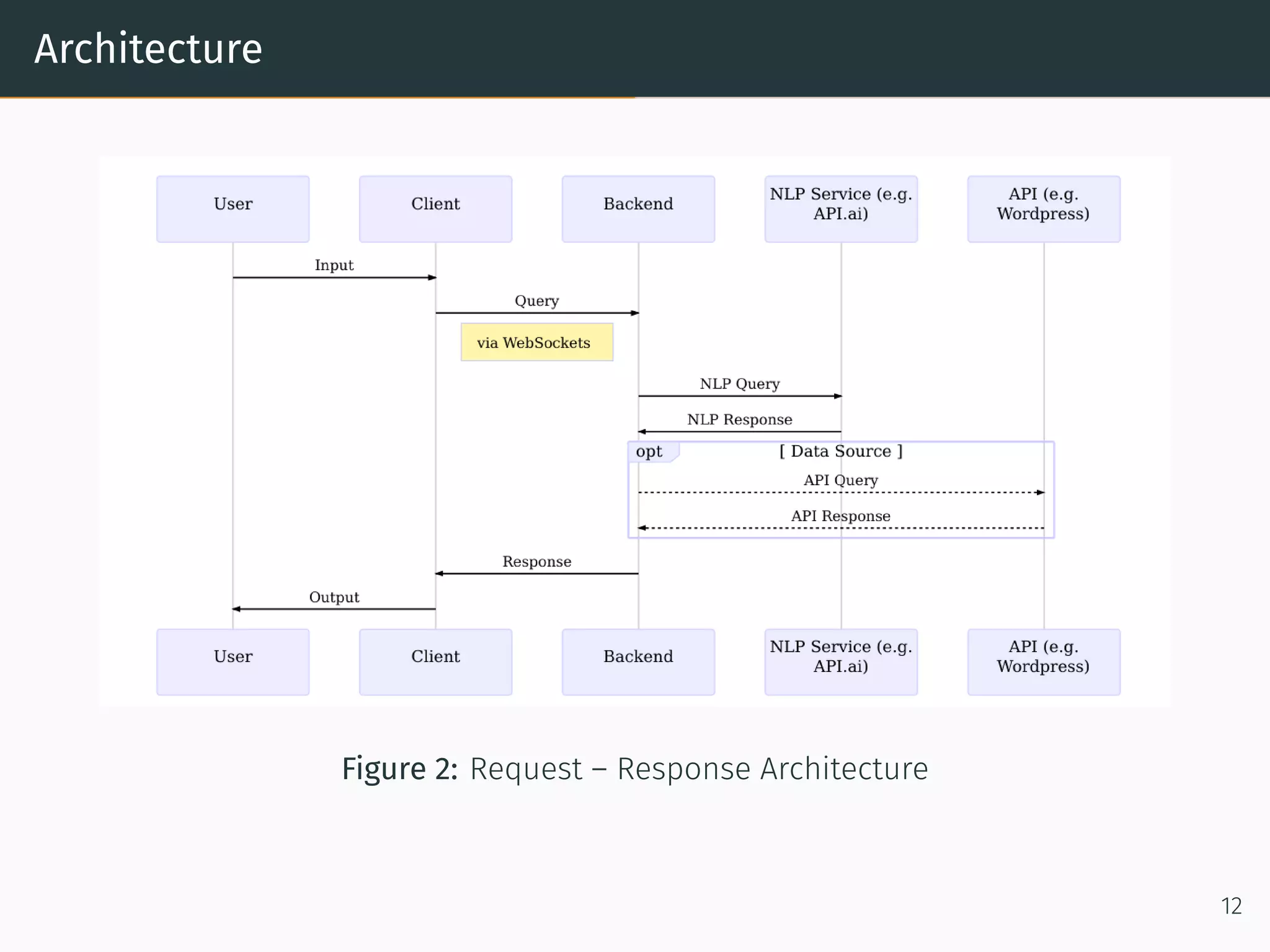
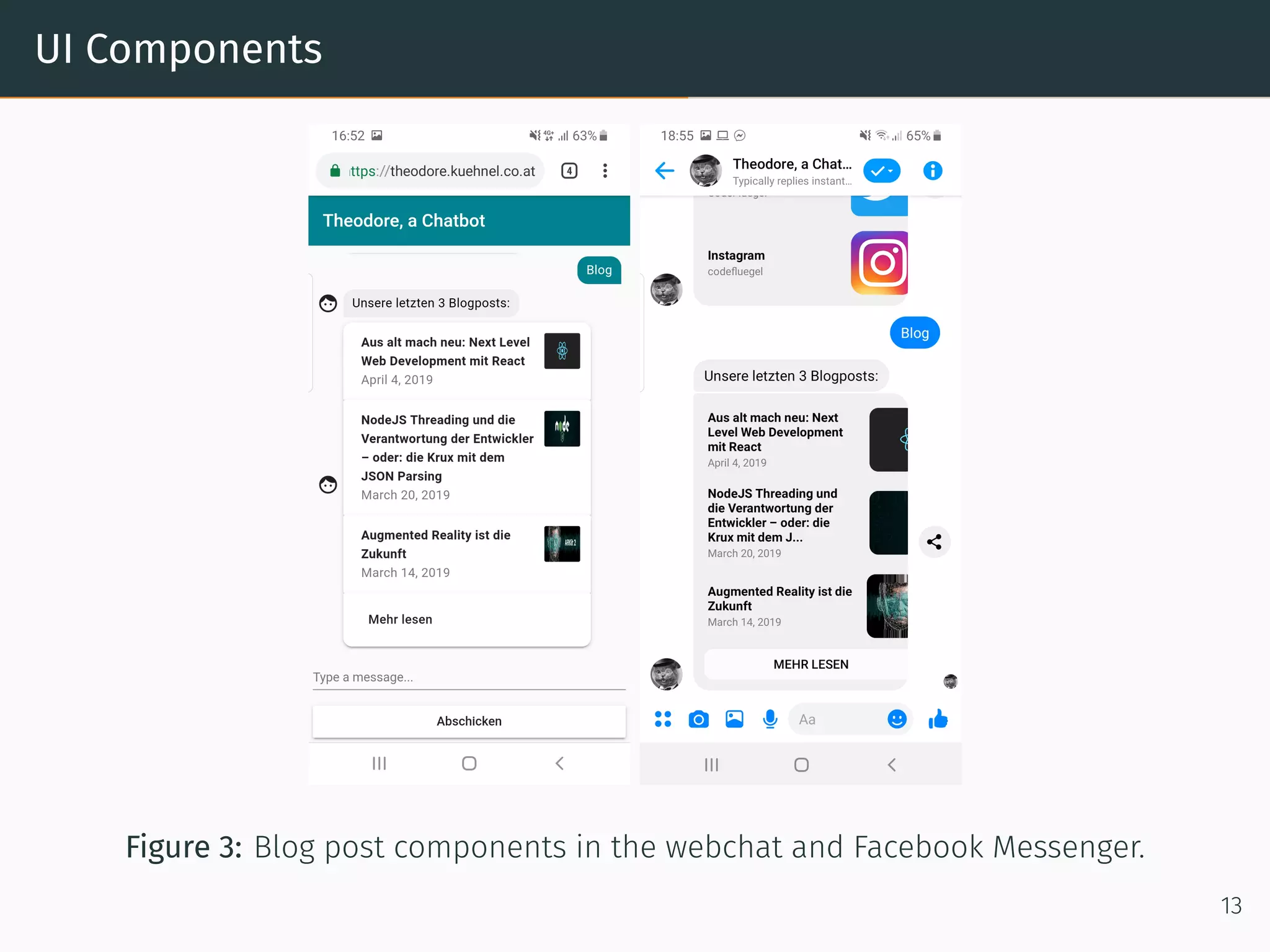
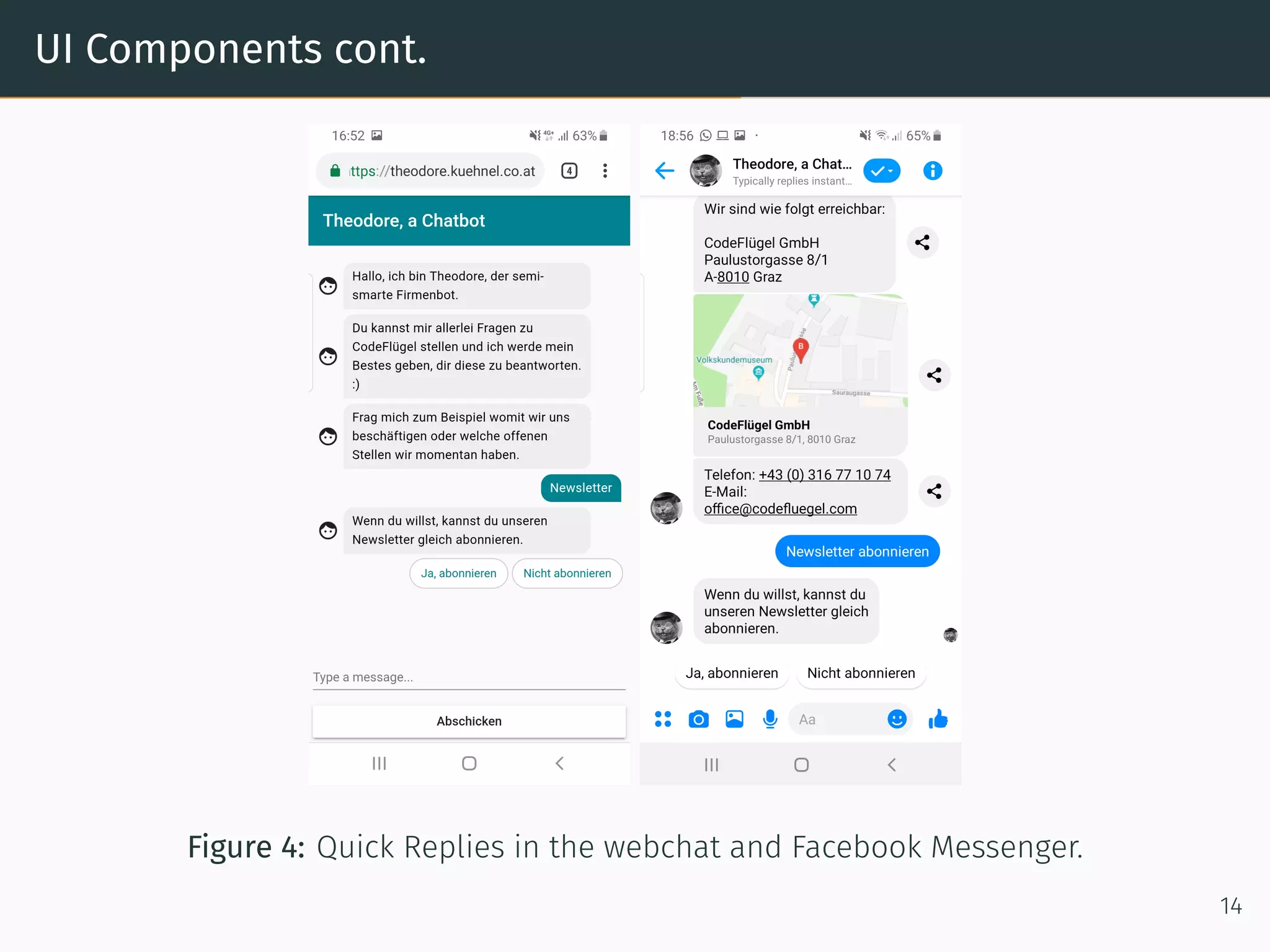
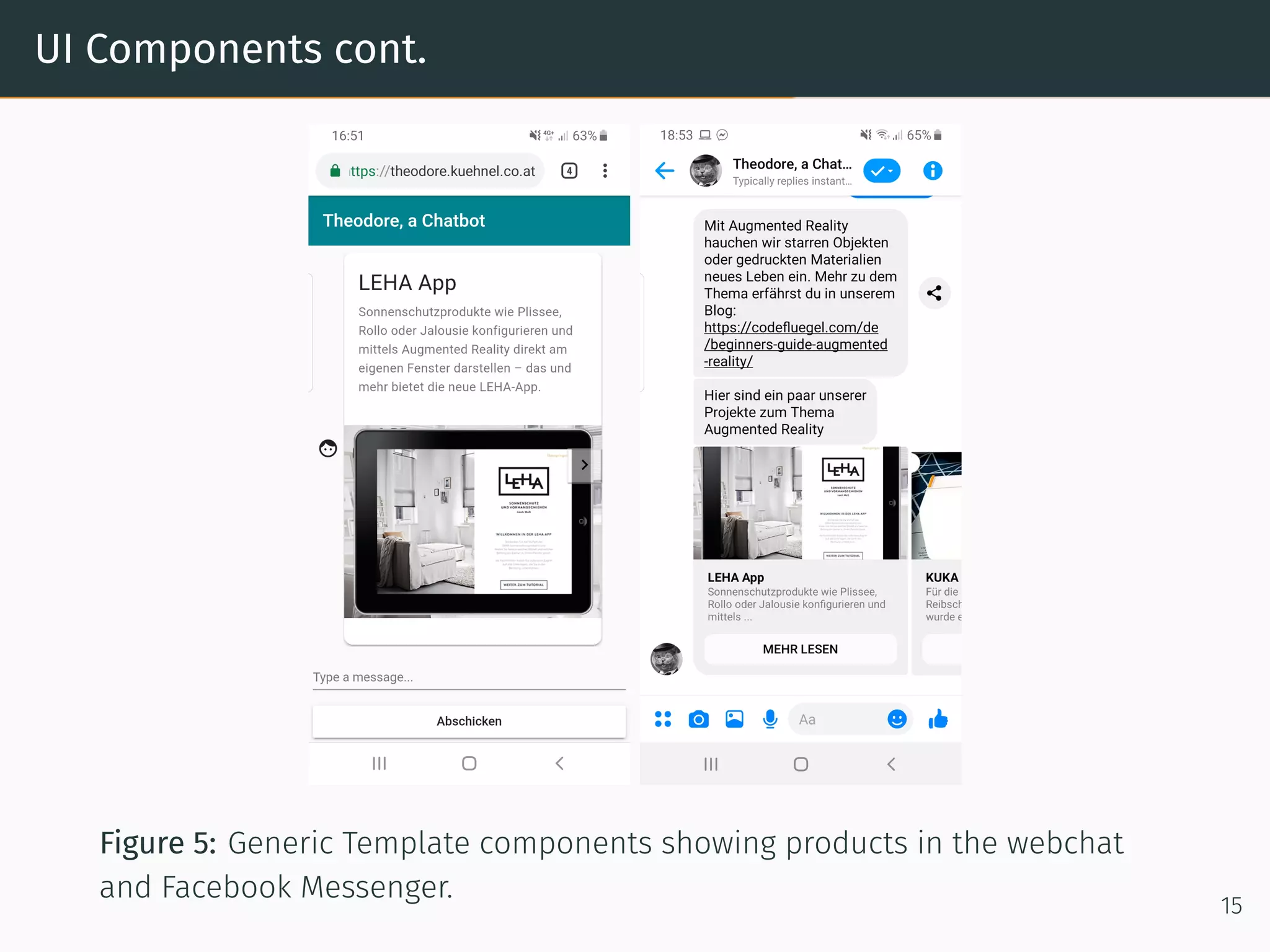
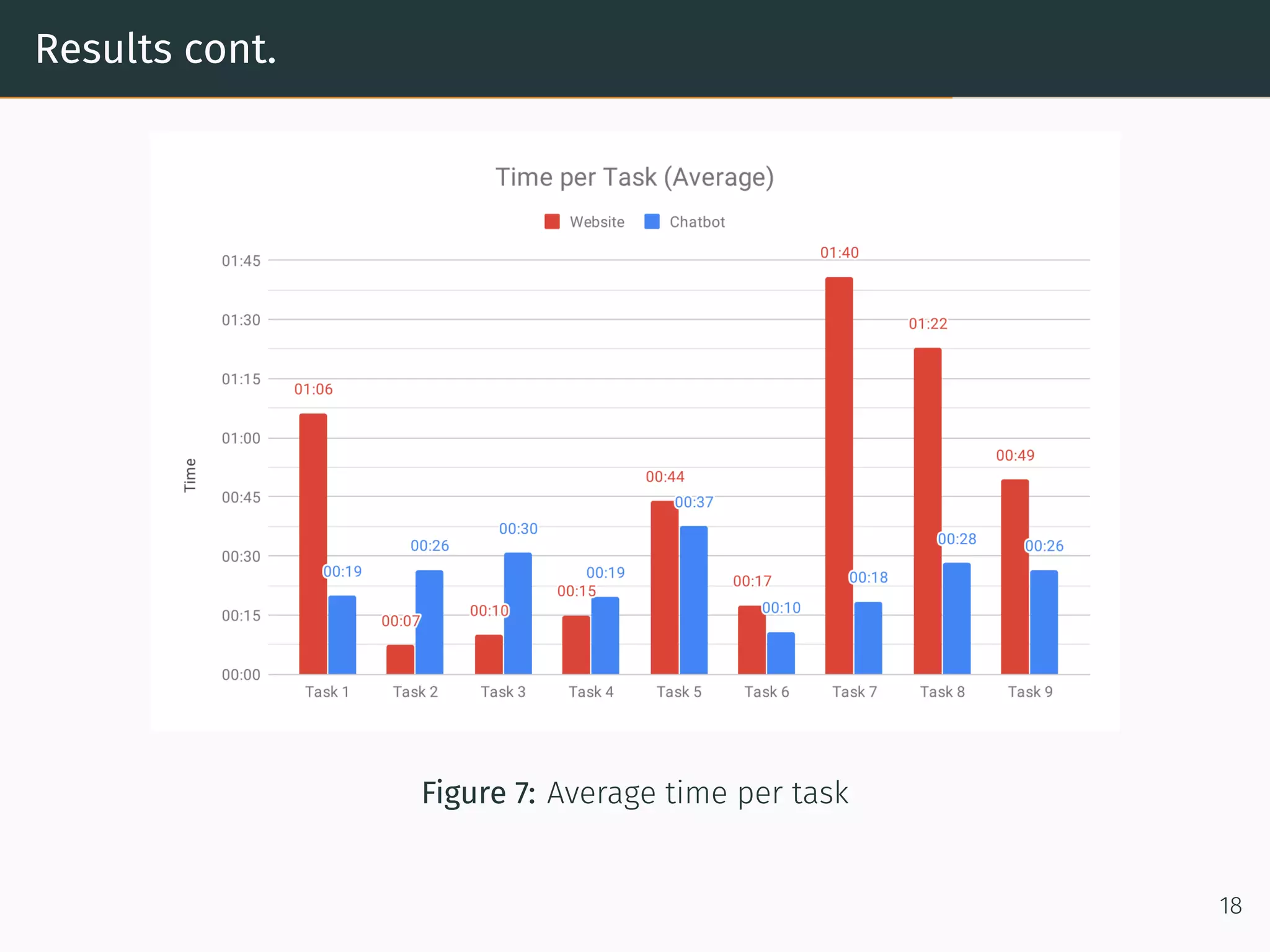
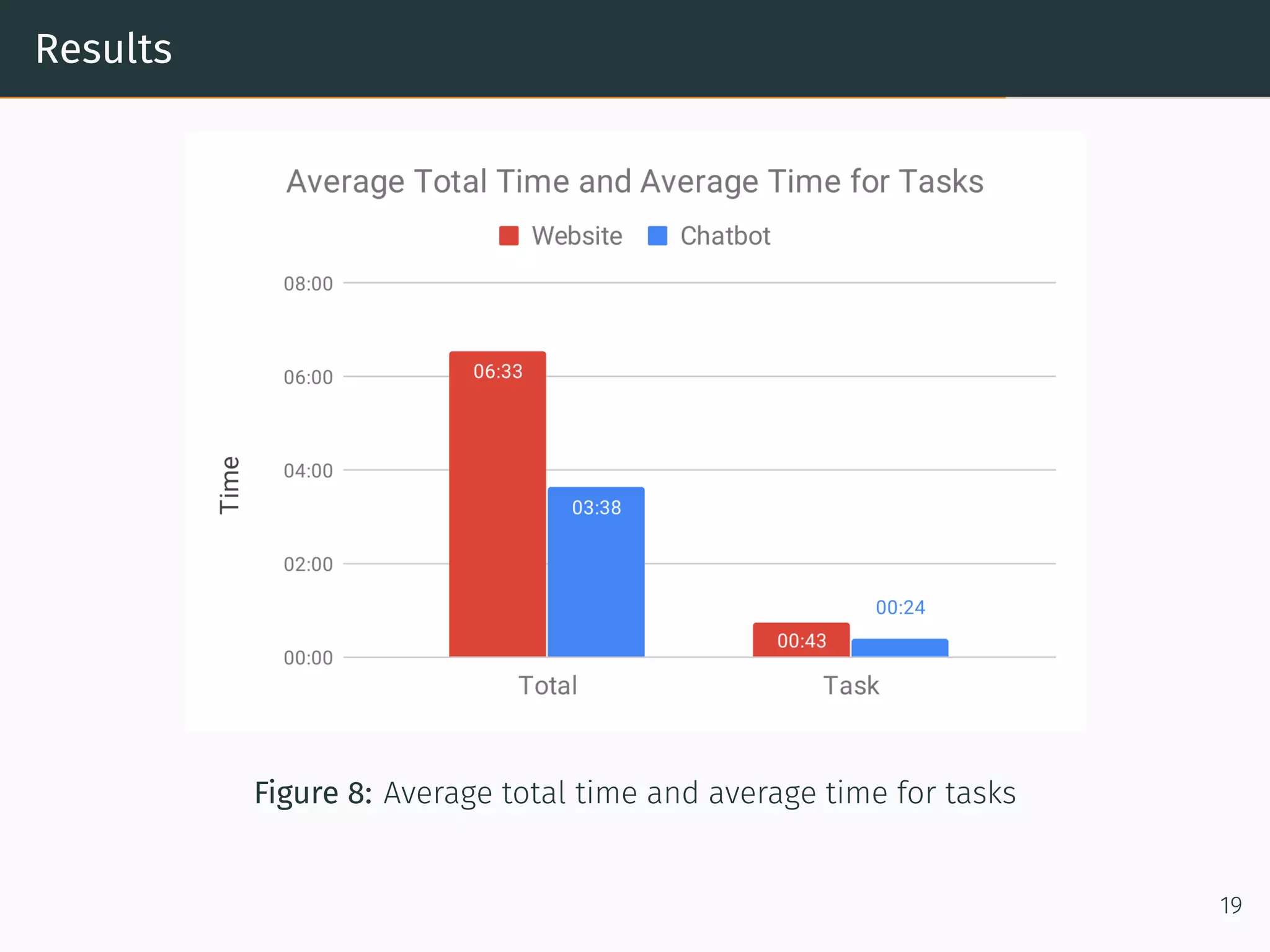
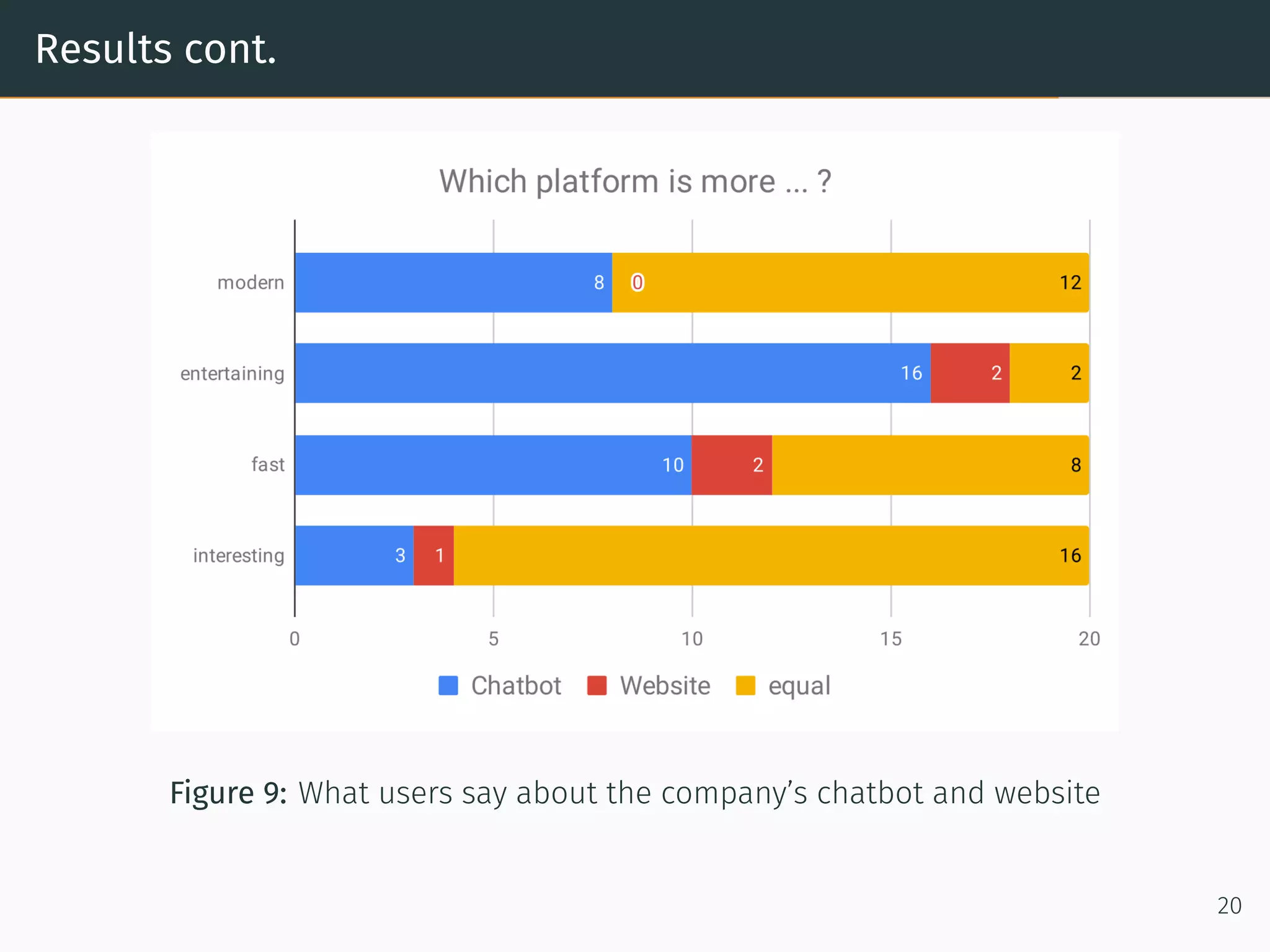
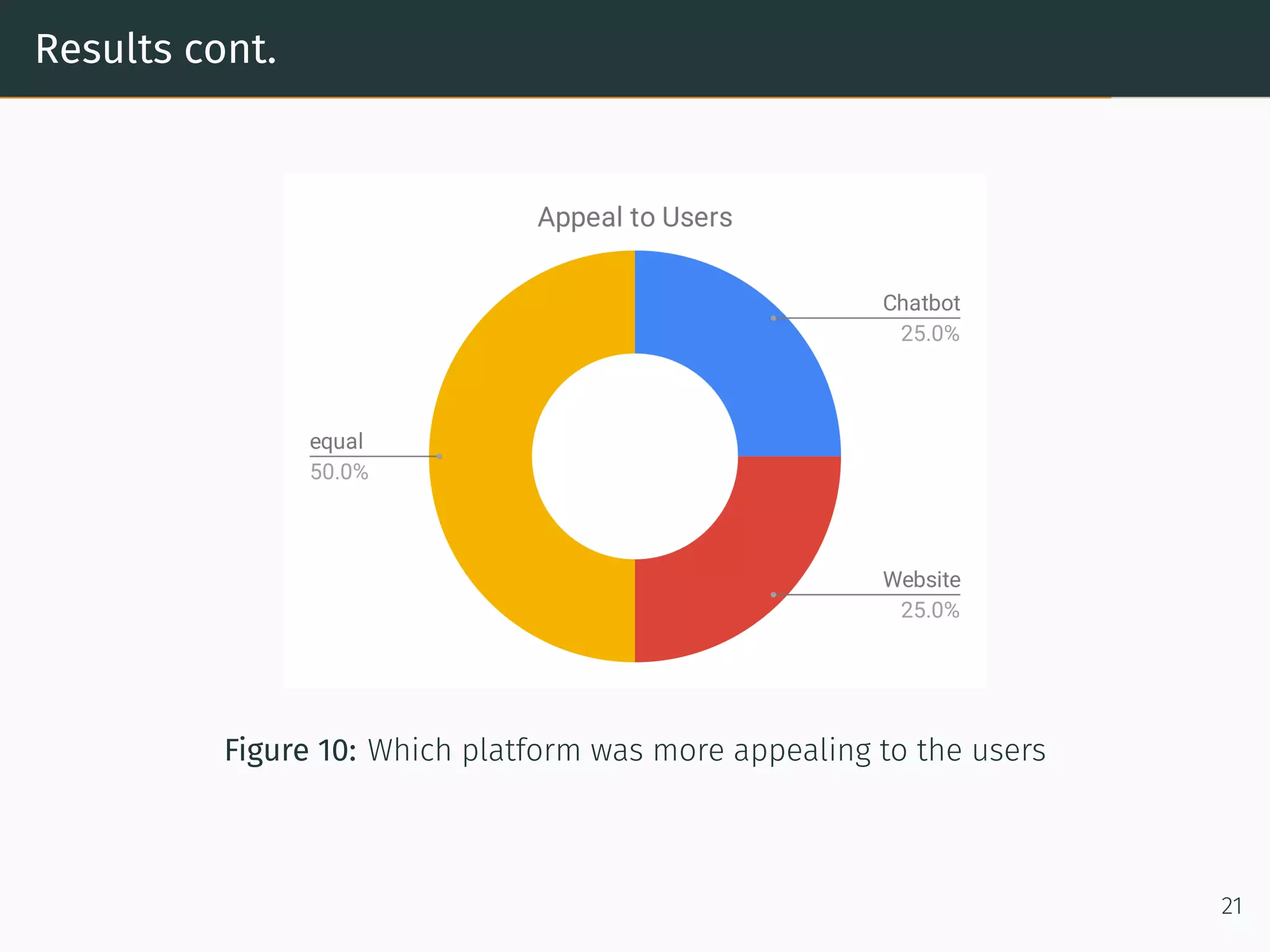
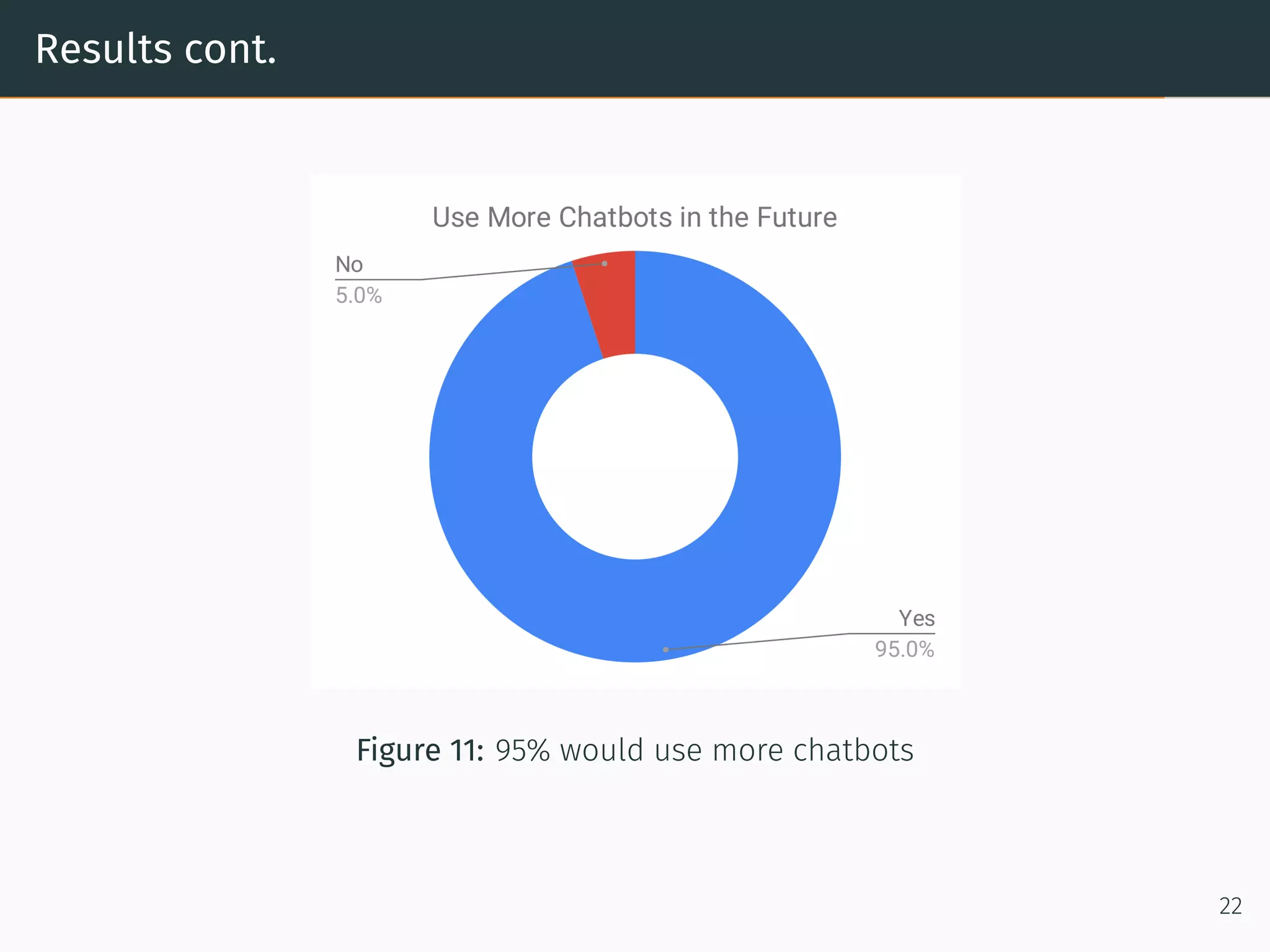
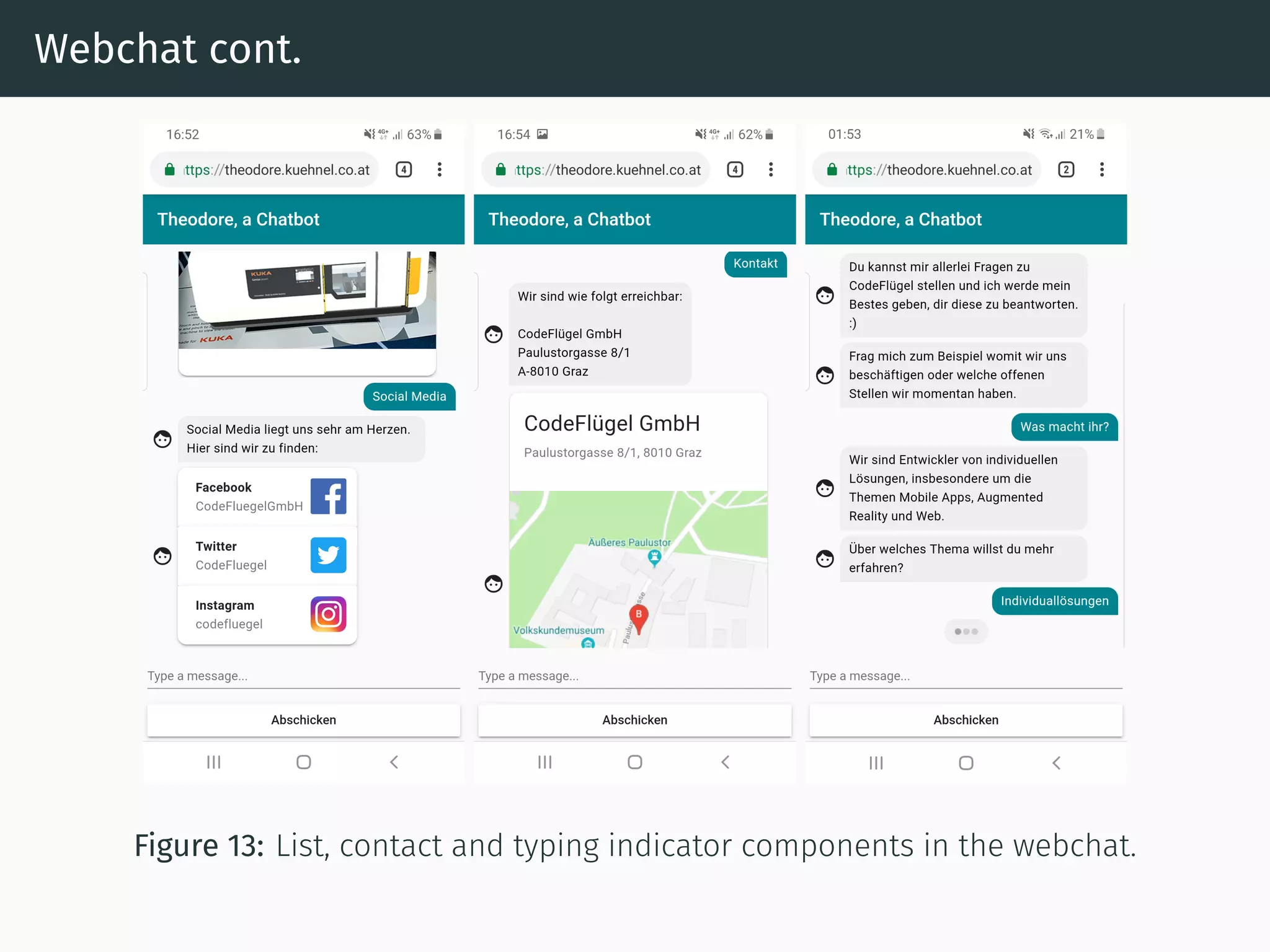
The document presents research on comparing chatbots to traditional websites for brand representation. It describes creating a chatbot named Theodore to represent a software company. A user study was conducted where participants completed tasks on both the chatbot and website. Results showed the chatbot was faster for specific information while the website was better for exploration. Users also found the chatbot more entertaining and had high acceptance of it. However, the chatbot needed improved intent matching. Overall, feedback on the chatbot was positive.





















![Message Format - Details
{
"message" : {
"attachment" : {
"type" : "template" ,
"payload" : {
"template_type" : "generic" ,
"elements" : [
{
"title" : "<TITLE_TEXT>" ,
"image_url" : "<IMAGE_URL_TO_DISPLAY>" ,
"subtitle" : "<SUBTITLE_TEXT>" ,
"default_action" : {
"type" : "web_url" ,
"url" : "<DEFAULT_URL_TO_OPEN>" ,
"messenger_extensions" : <TRUE | FALSE > ,
"webview_height_ratio" : "<COMPACT | TALL | FULL>"
} ,
"buttons" : [ < BUTTON_OBJECT > , . . . ]
} ,
. . .
]
}
}
}
}
Listing 1: A generic template JSON message in Facebook Messenger’s
format.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masterthesispresentation-200529064209/75/Chatbots-for-Brand-Representation-in-Comparison-with-Traditional-Websites-45-2048.jpg)