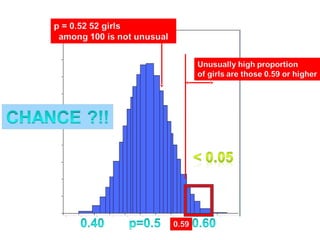
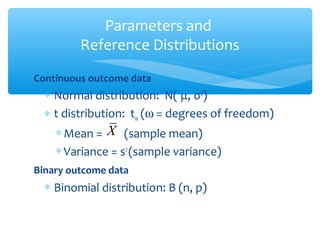
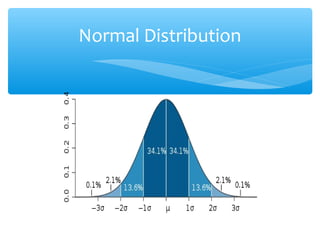
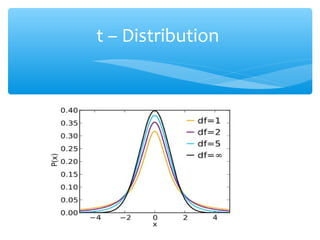
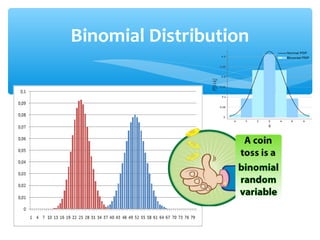
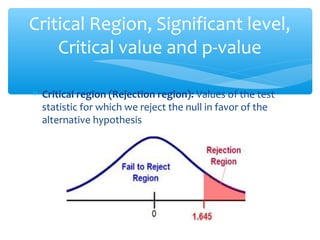
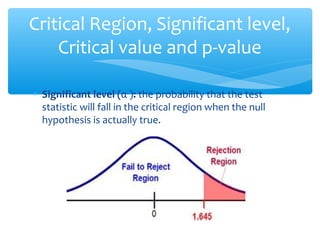
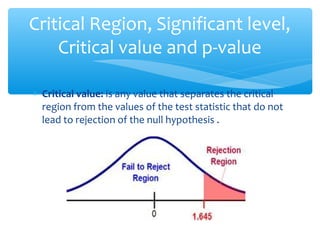
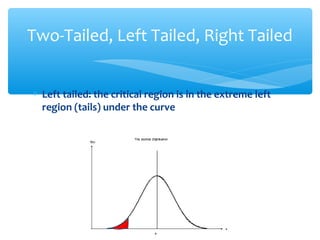
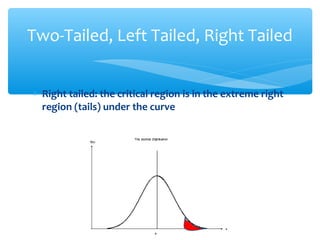
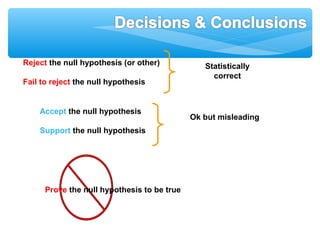
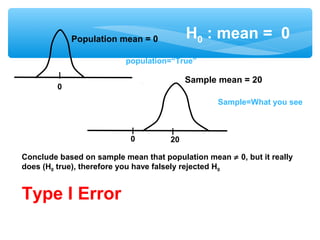
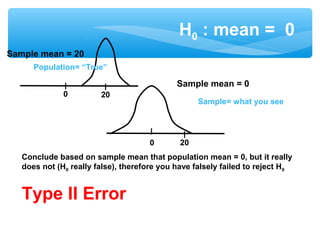
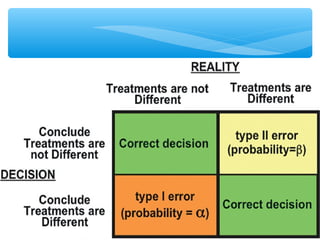
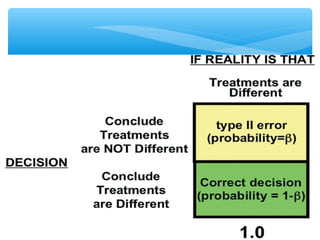
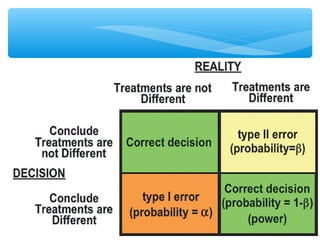
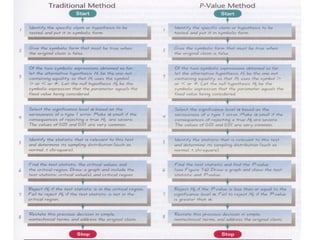
This document discusses hypothesis testing, which involves drawing inferences about a population based on a sample from that population. It outlines the key elements of a hypothesis test, including the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistics, critical regions, significance levels, critical values, and p-values. Type I and Type II errors are explained, where a Type I error involves rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, and a Type II error involves failing to reject the null when it is false. The power of a hypothesis test is defined as the probability of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis when it is false. Controlling type I and II errors involves considering the significance level, sample size, and population parameters in the null and alternative hypotheses.