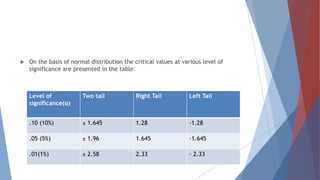
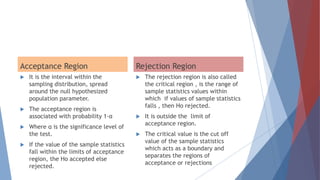
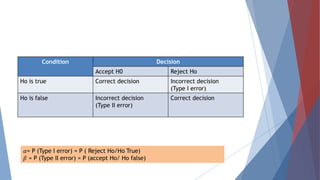
The document discusses testing of hypotheses. It defines a hypothesis as a tentative prediction about the relationship between variables. Good hypotheses are precise, testable, and consistent with known facts. Hypothesis testing involves formulating a null hypothesis (Ho) and an alternative hypothesis (H1). A significance level such as 5% is chosen. If the test statistic falls within the critical region, Ho is rejected. Type I error rejects a true Ho, while Type II error accepts a false Ho. Power refers to correctly rejecting a false Ho. The testing process determines test statistics, critical regions, and interprets results to draw conclusions.