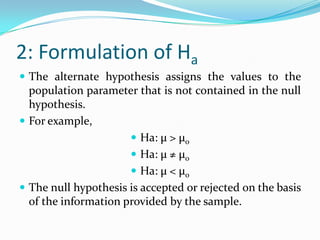
This document discusses key concepts in hypothesis testing, including:
- The null hypothesis states the assumption to be tested, while the alternative hypothesis is the opposite.
- Type I errors occur when a true null hypothesis is rejected, while type II errors occur when a false null hypothesis is accepted.
- One-tailed tests check for deviations in one direction, while two-tailed tests check both directions.
- The five steps of hypothesis testing are: formulating hypotheses, defining a test statistic, determining the statistic's distribution, defining a critical region, and making a decision using a p-value or test statistic.