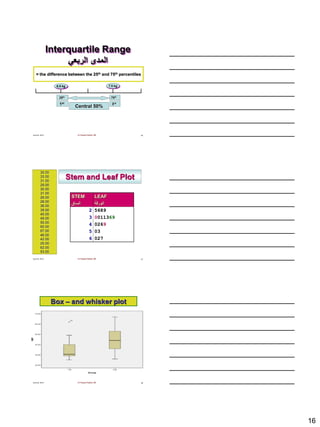
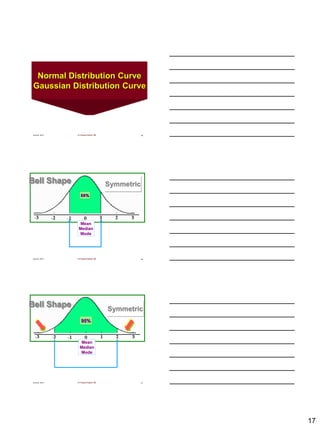
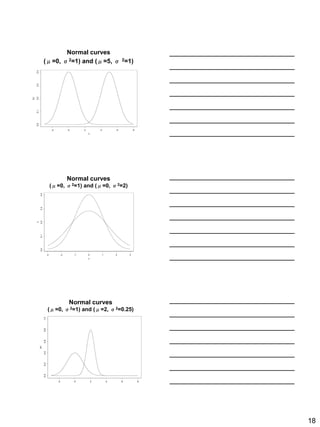
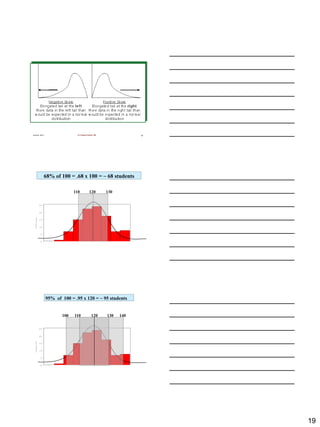
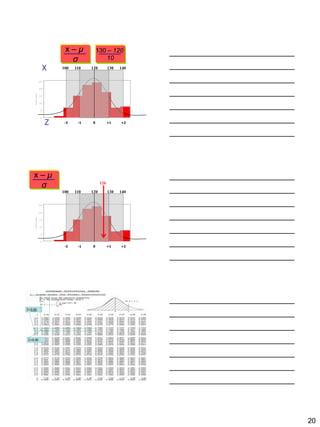
The document discusses the importance of descriptive statistics in public health, particularly in infection prevention and control. It covers the various types of data, measurement scales, and methods for organizing and summarizing data, including the use of frequency tables, graphs, and measures of central tendency. Additionally, it explores different types of variables, their categorization, and the application of statistical concepts in healthcare settings.









![13
June 22, 2013 Dr Fayssal Farahat, MD 37
Arithmetic Mean
ExtremesHR
variation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
19.2
51.9
33.1
86.7
29.1
45.3
16.4
85.7
18.9
42.6
42.9
32.1
Consider each variable
X
June 22, 2013 Dr Fayssal Farahat, MD 38
Weighted Mean
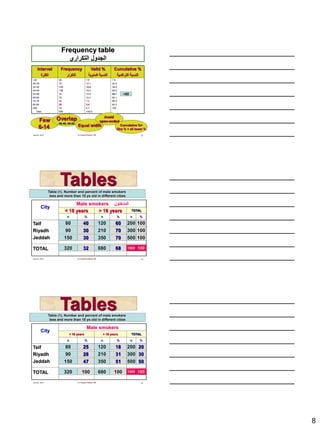
Interval Frequency Valid % Cumulative %
2-20
21-30
31-40
41-50
51-60
61-70
71-80
81-90
>90
Total
46
70
108
106
74
72
42
29
33
580
7.9
12.1
18.6
18.3
12.8
12.4
7.2
5.0
5.7
100.0
7.9
20.0
38.6
56.9
69.7
82.1
89.3
94.3
100
[(11 x 46) + (25 x 70) + ….+ (85 x 29) + (100 x 33)] / 580 = 49.1
X
?
June 22, 2013 Dr Fayssal Farahat, MD 39
Median
Middle observation
Odd Even
Extremes
Consider each variable
Ordinal data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontobiostatisticsi-220613-130622082221-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-biostatistics-13-320.jpg)