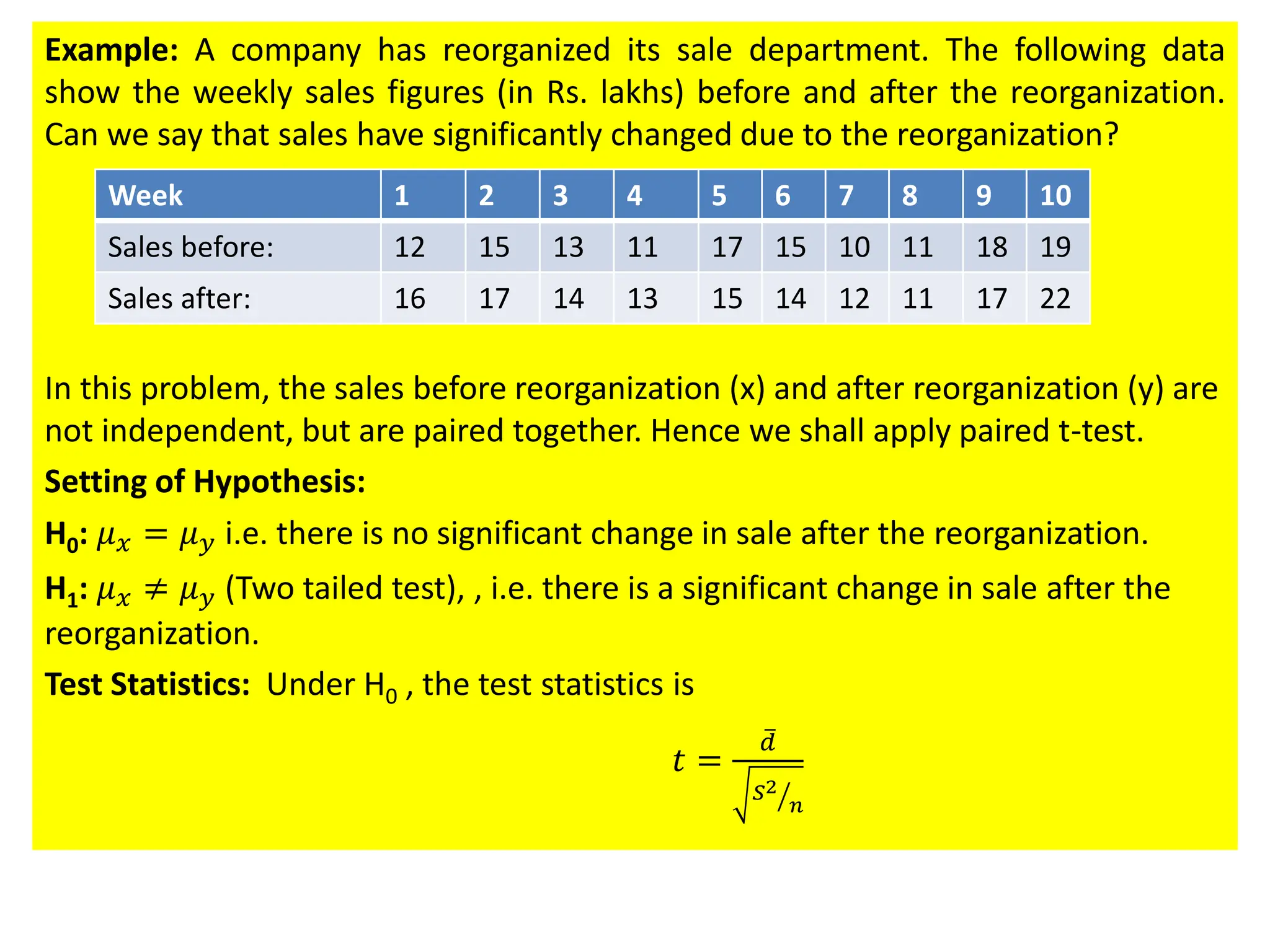
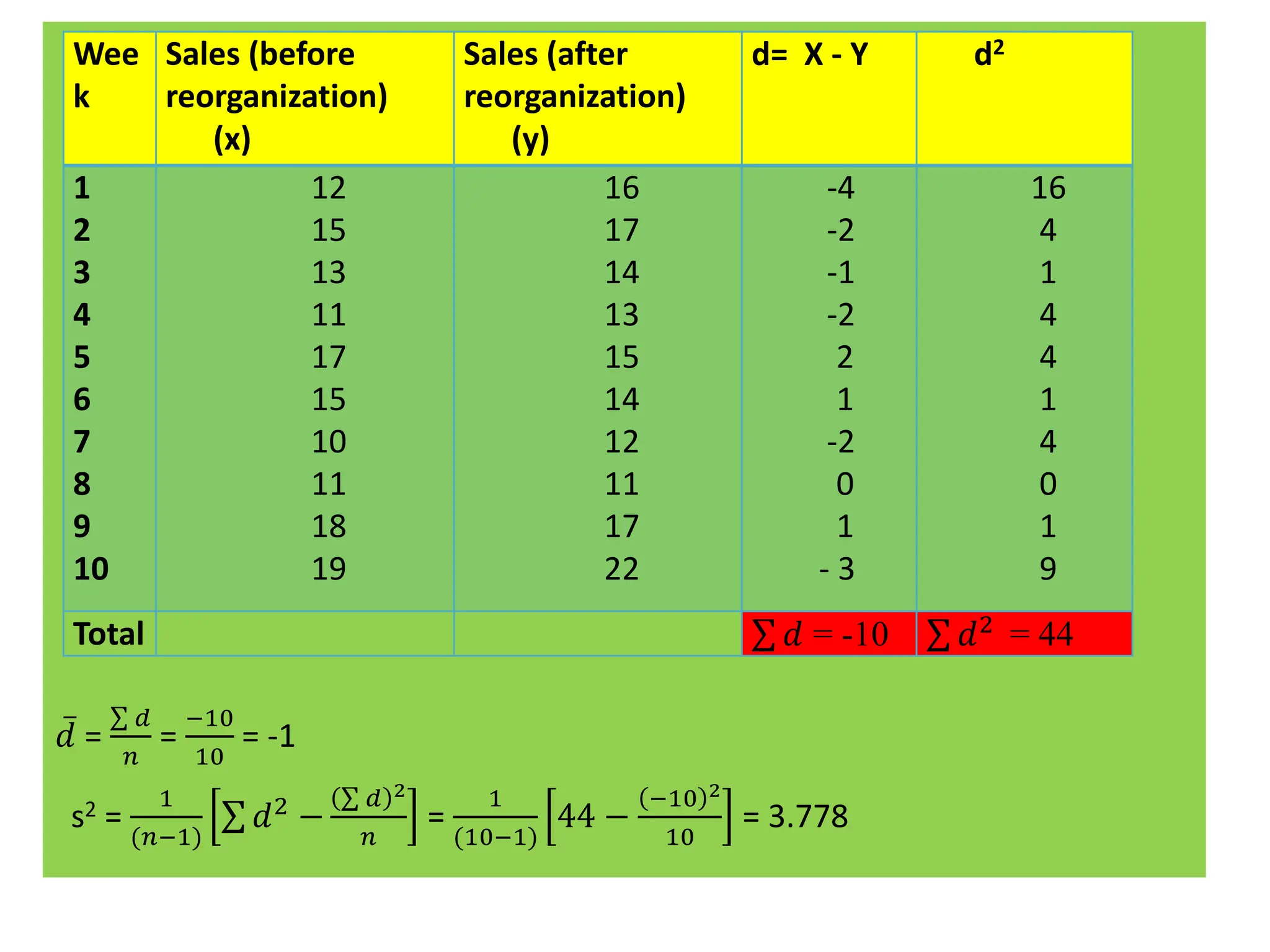
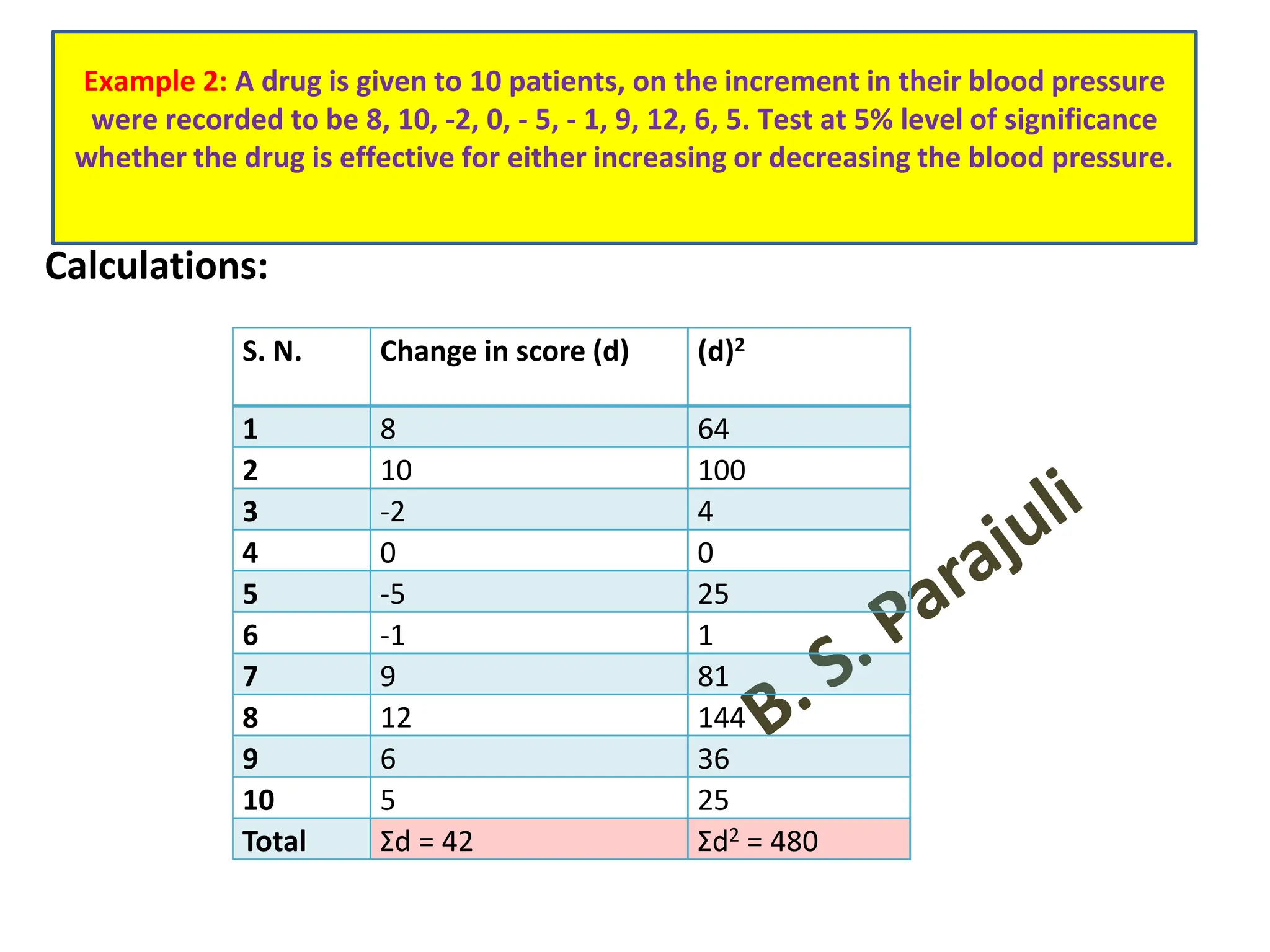
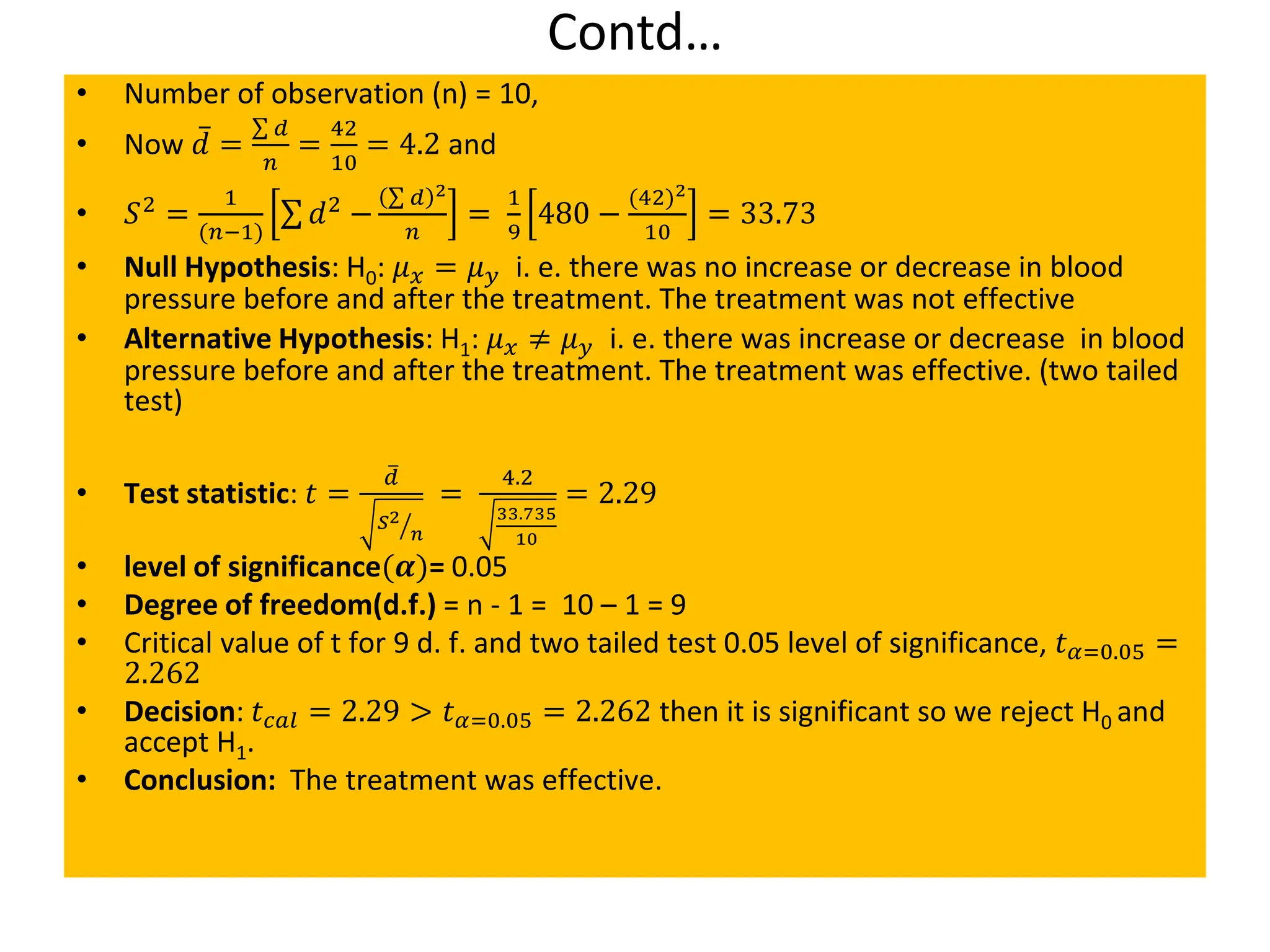
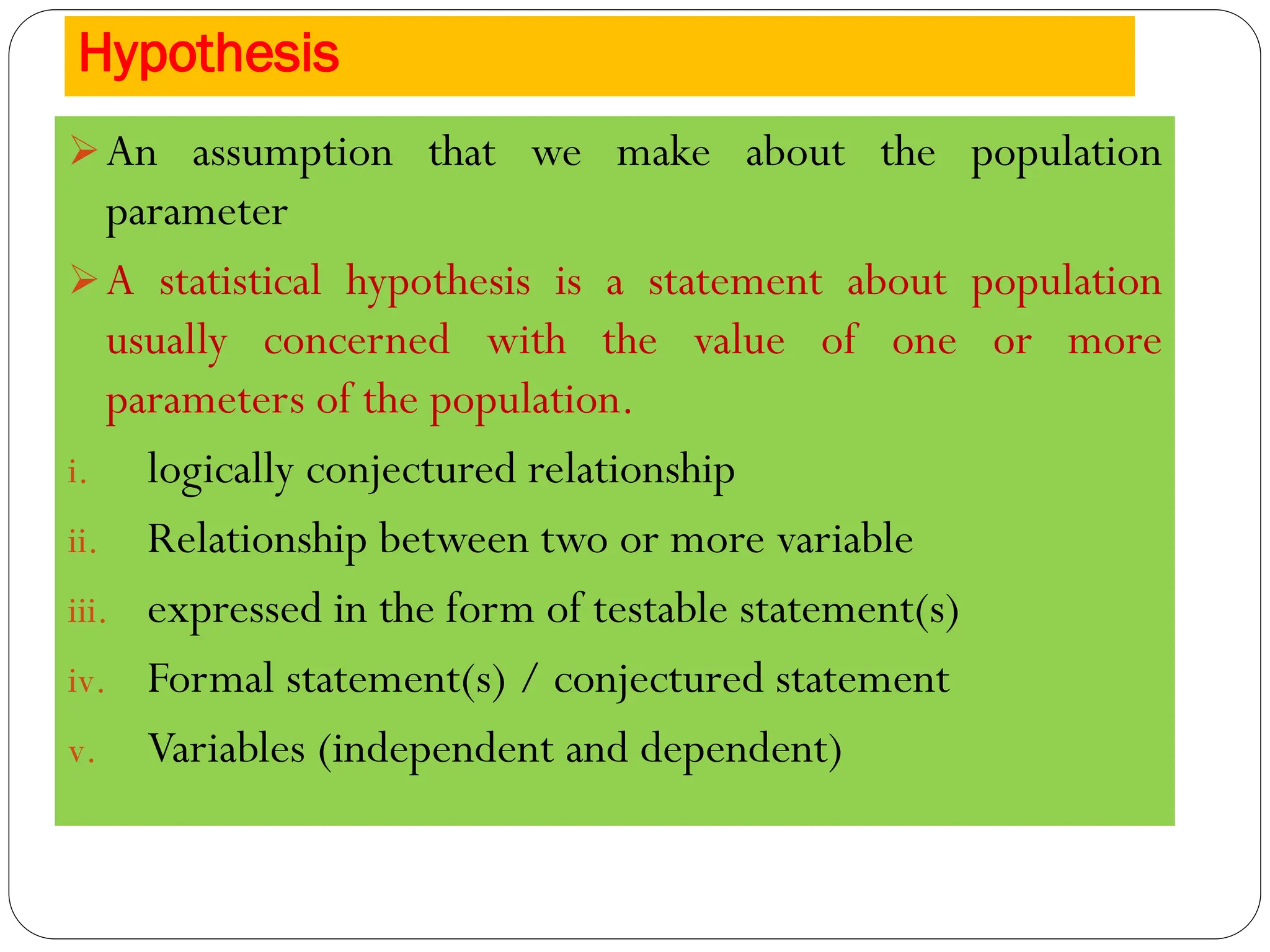
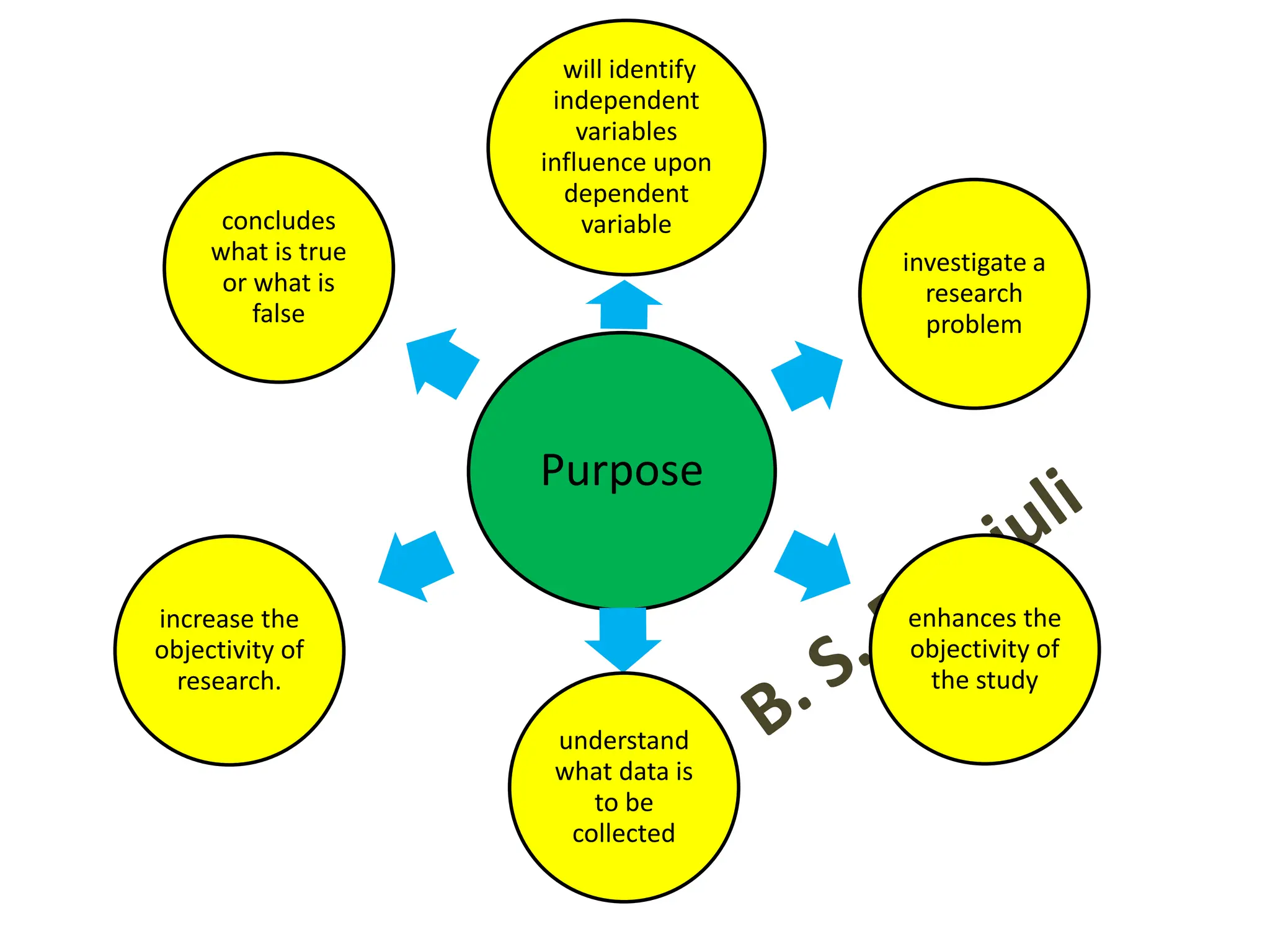
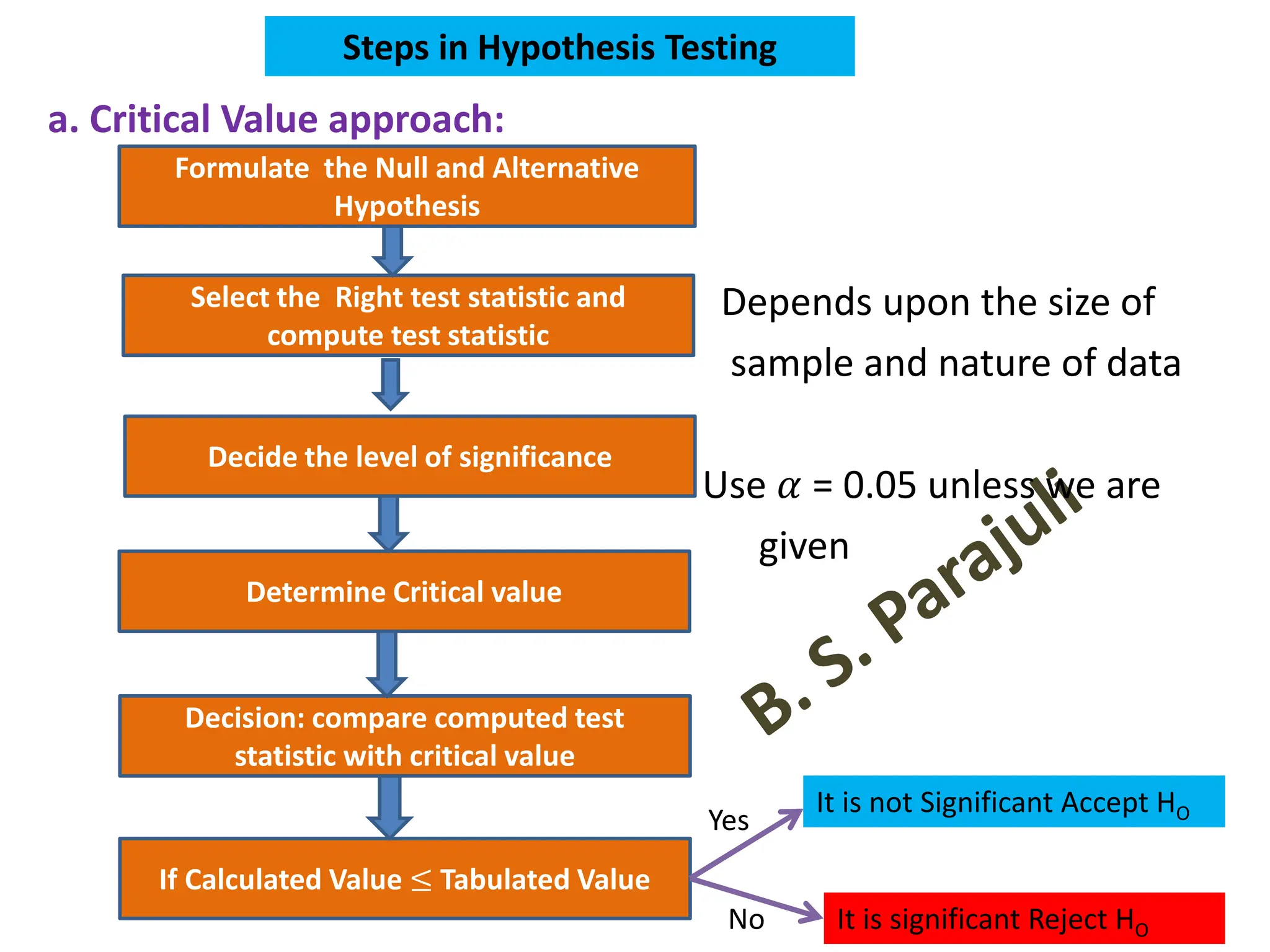
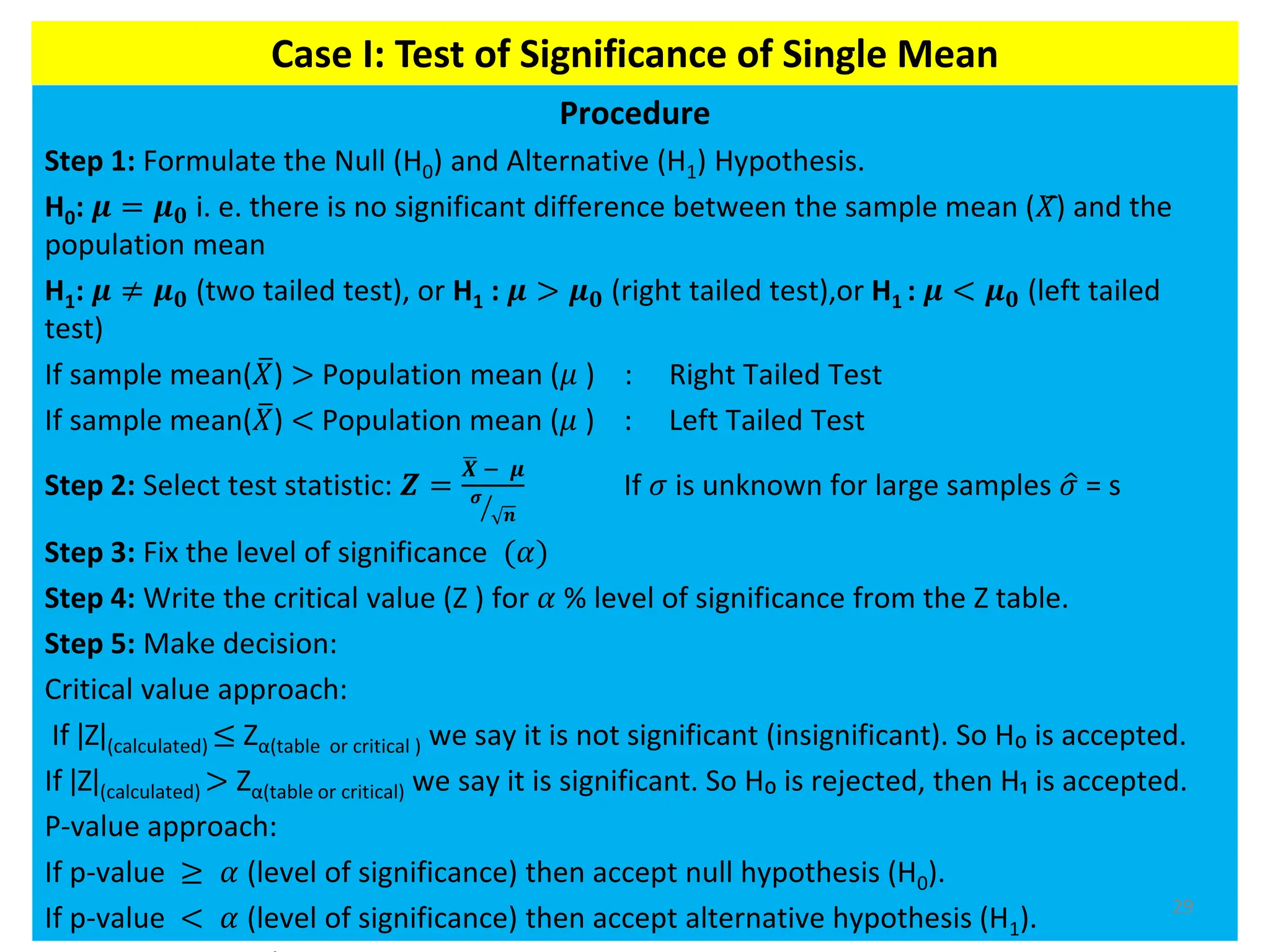
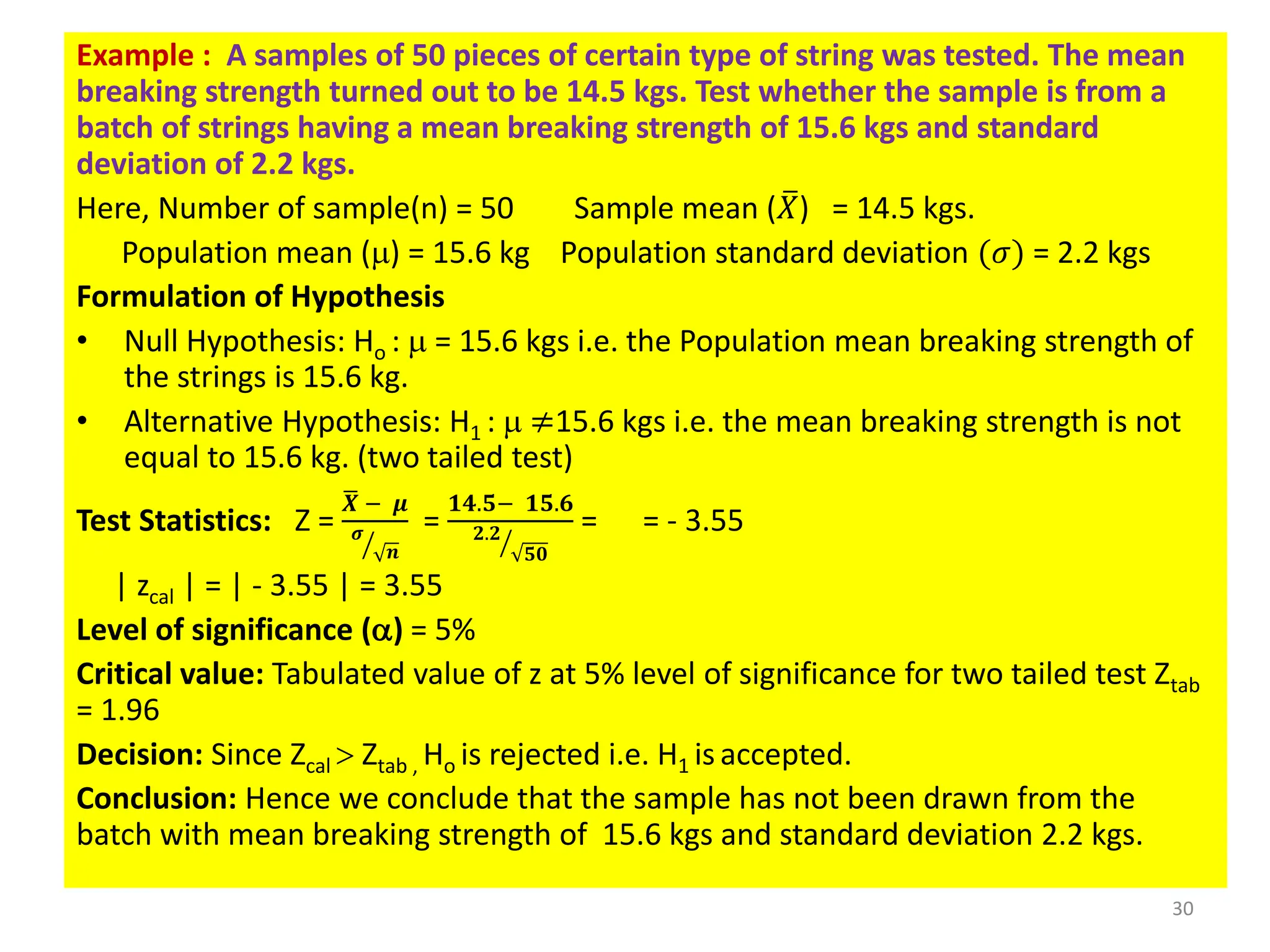
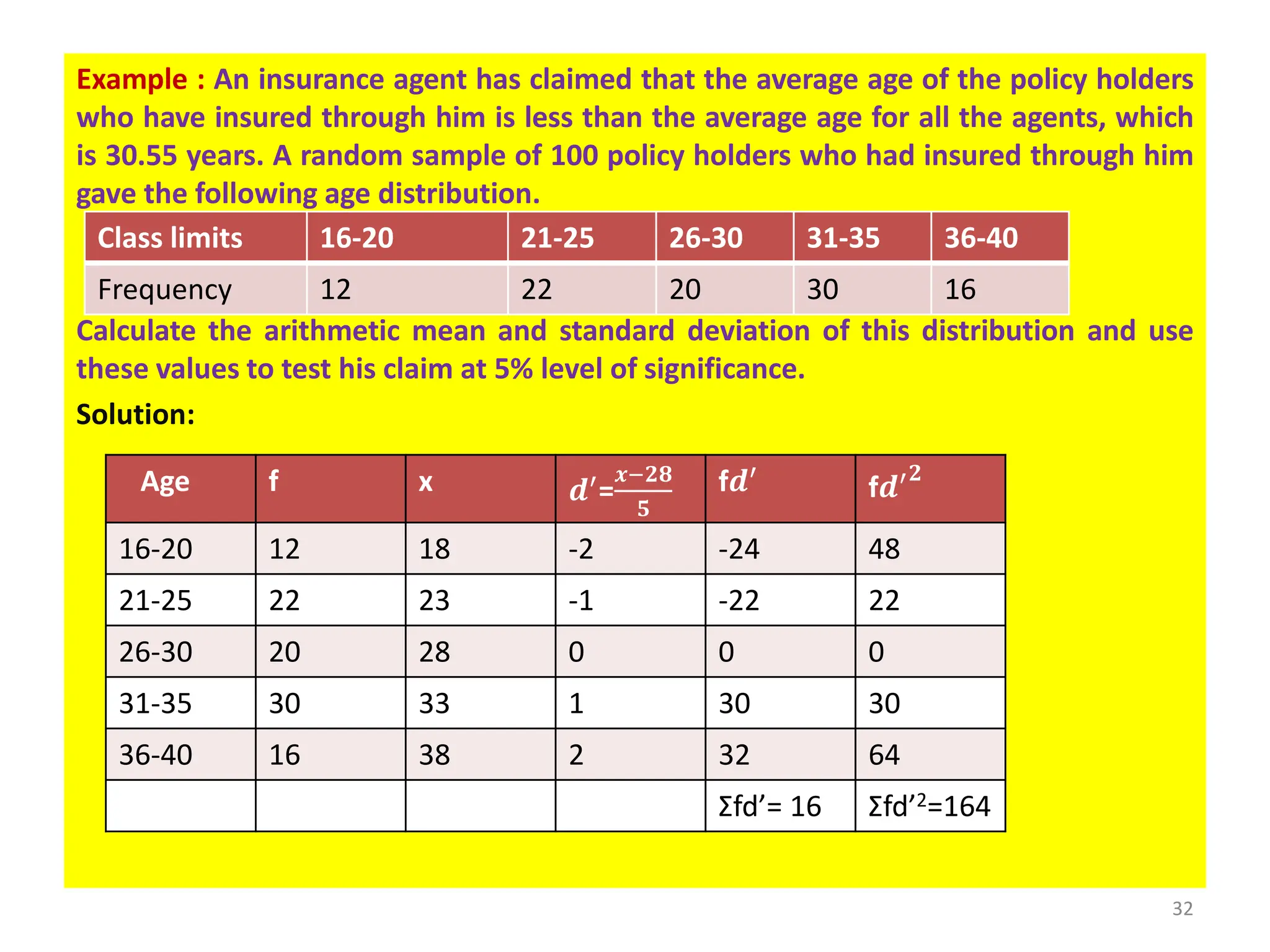
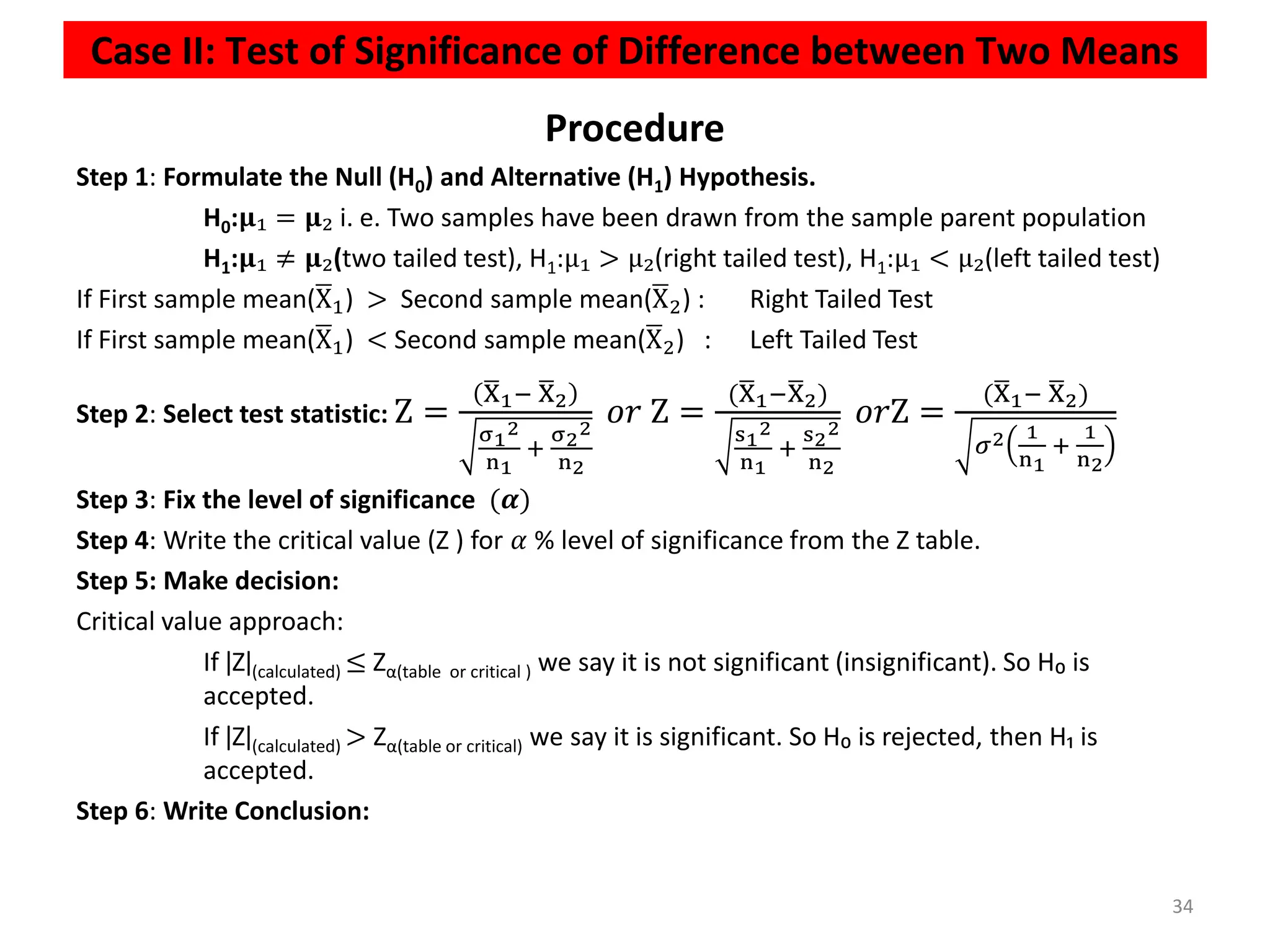
This document discusses hypothesis testing procedures. It defines a hypothesis as a statement about a population parameter that can be tested. The key points covered are:
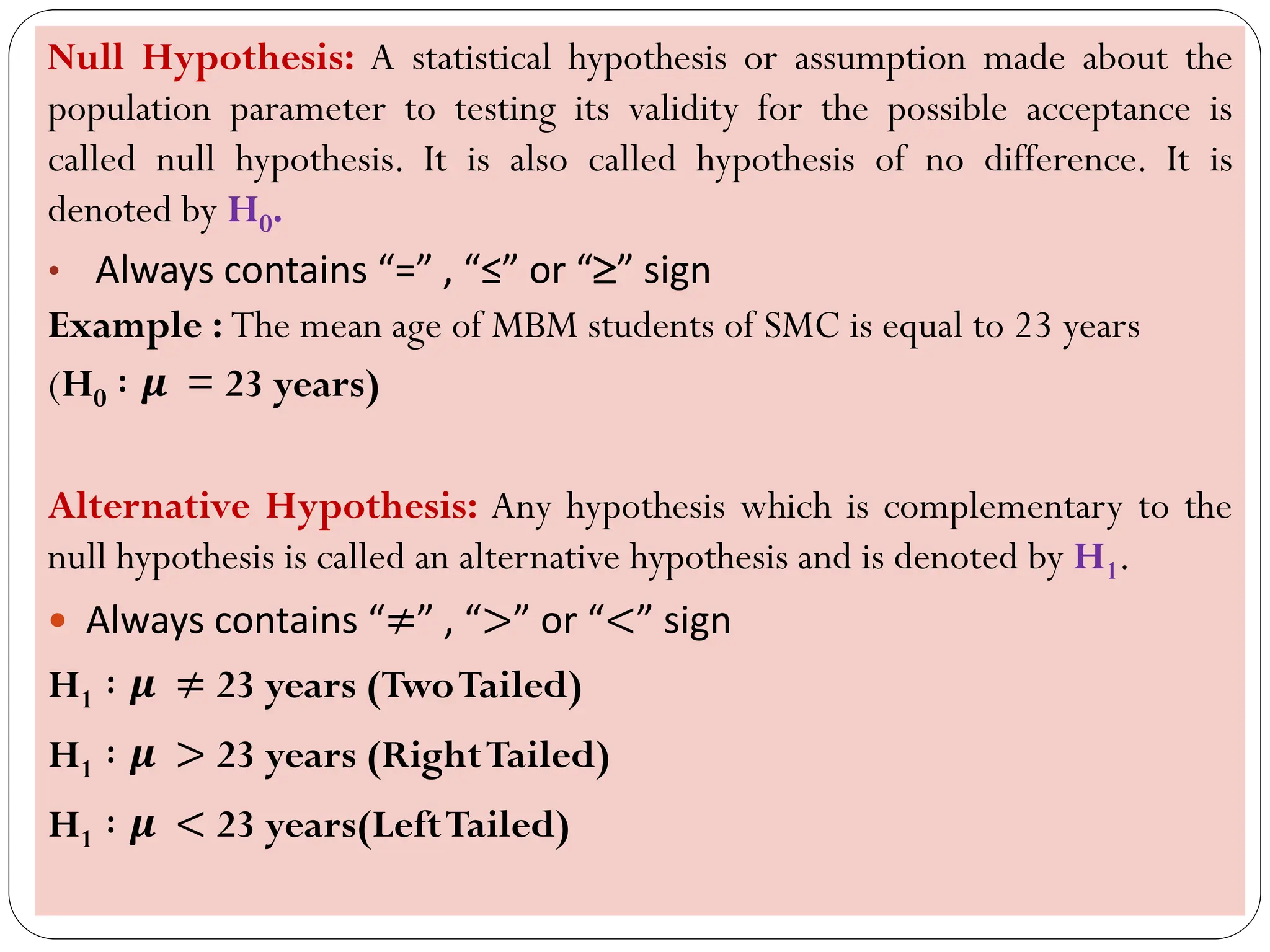
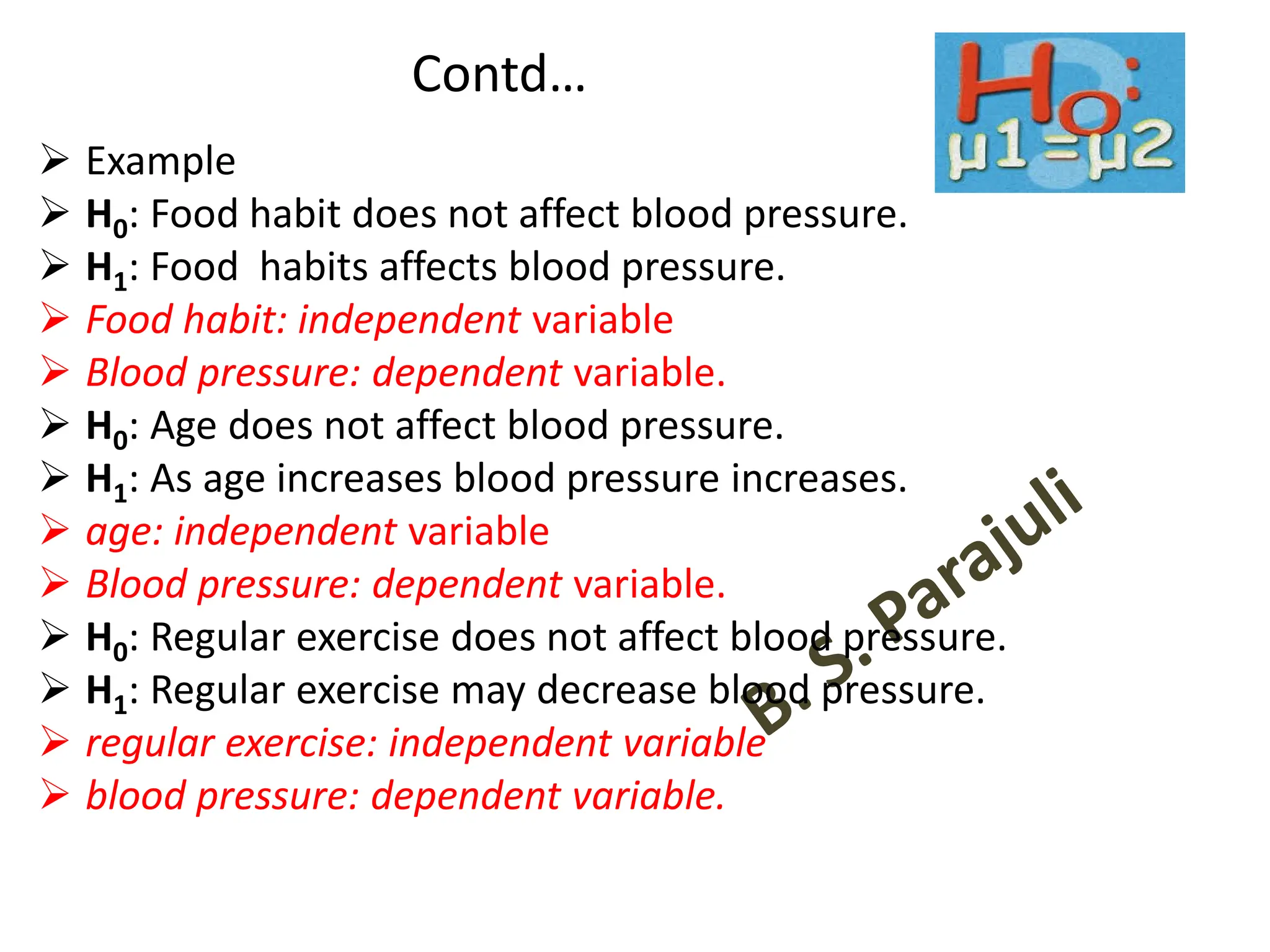
- Null and alternative hypotheses are defined, with the null hypothesis containing "=", "<", or ">" and the alternative containing "≠", "<", or ">"
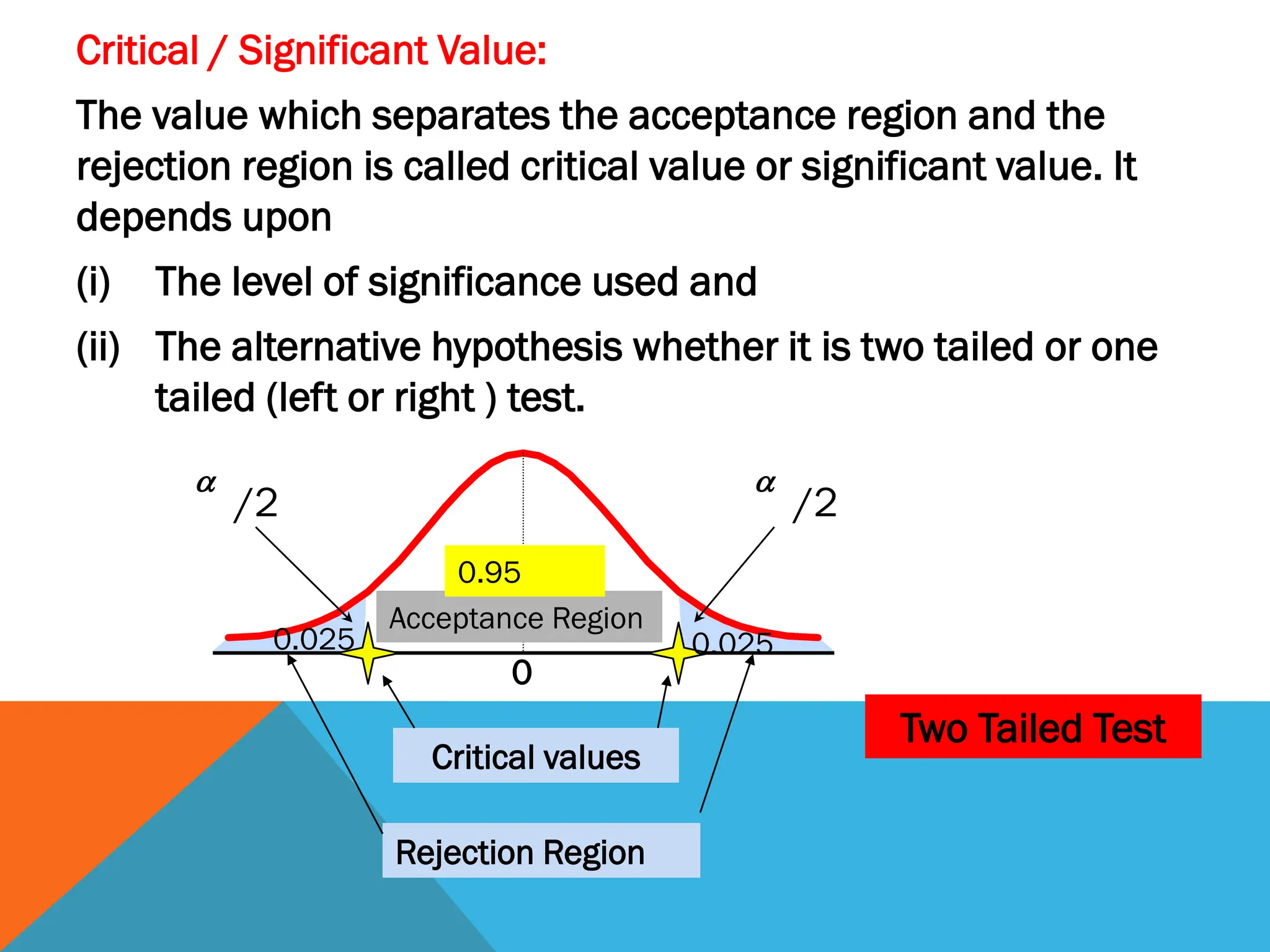
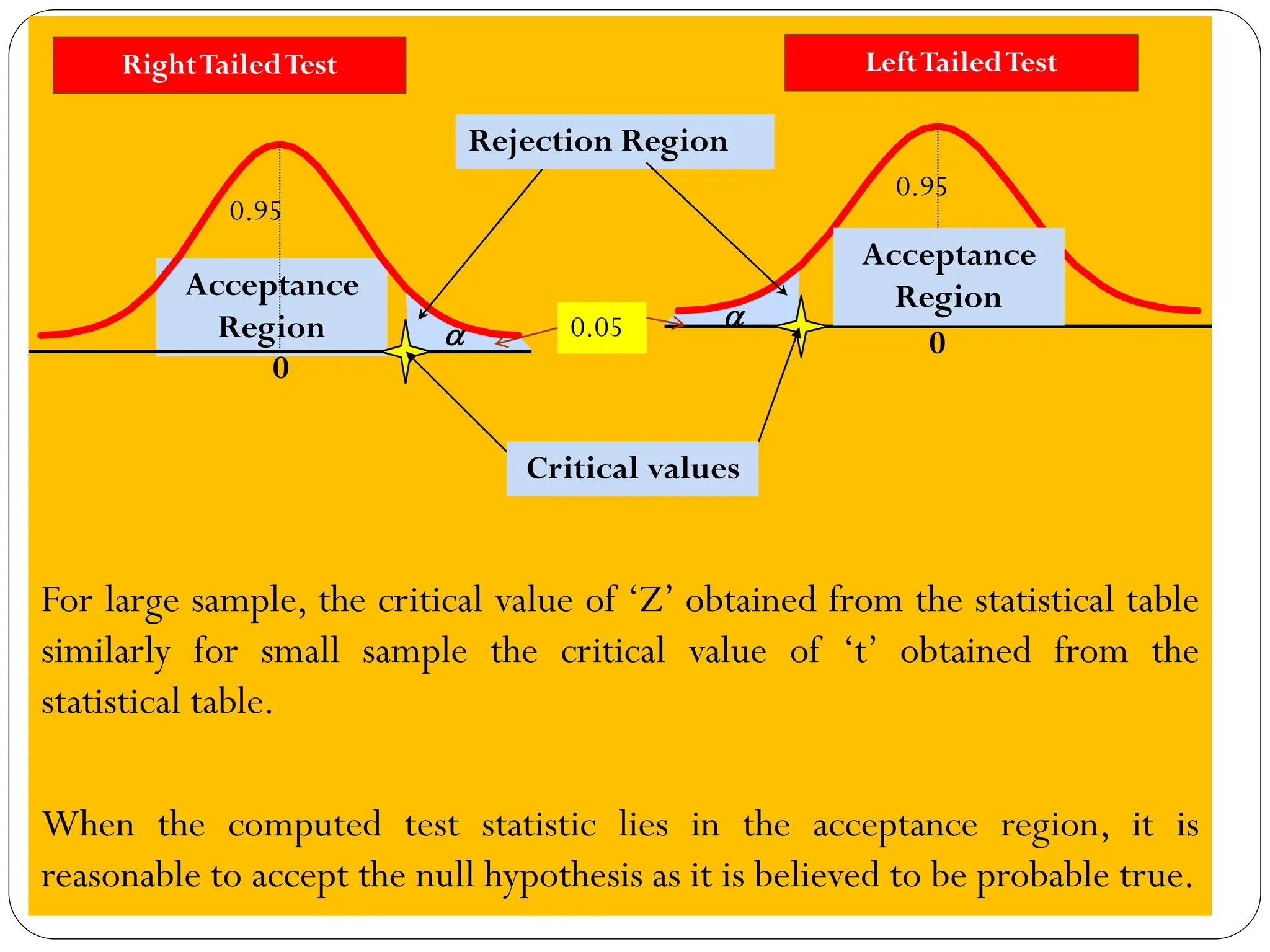
- Tests can be one-tailed or two-tailed depending on the alternative hypothesis
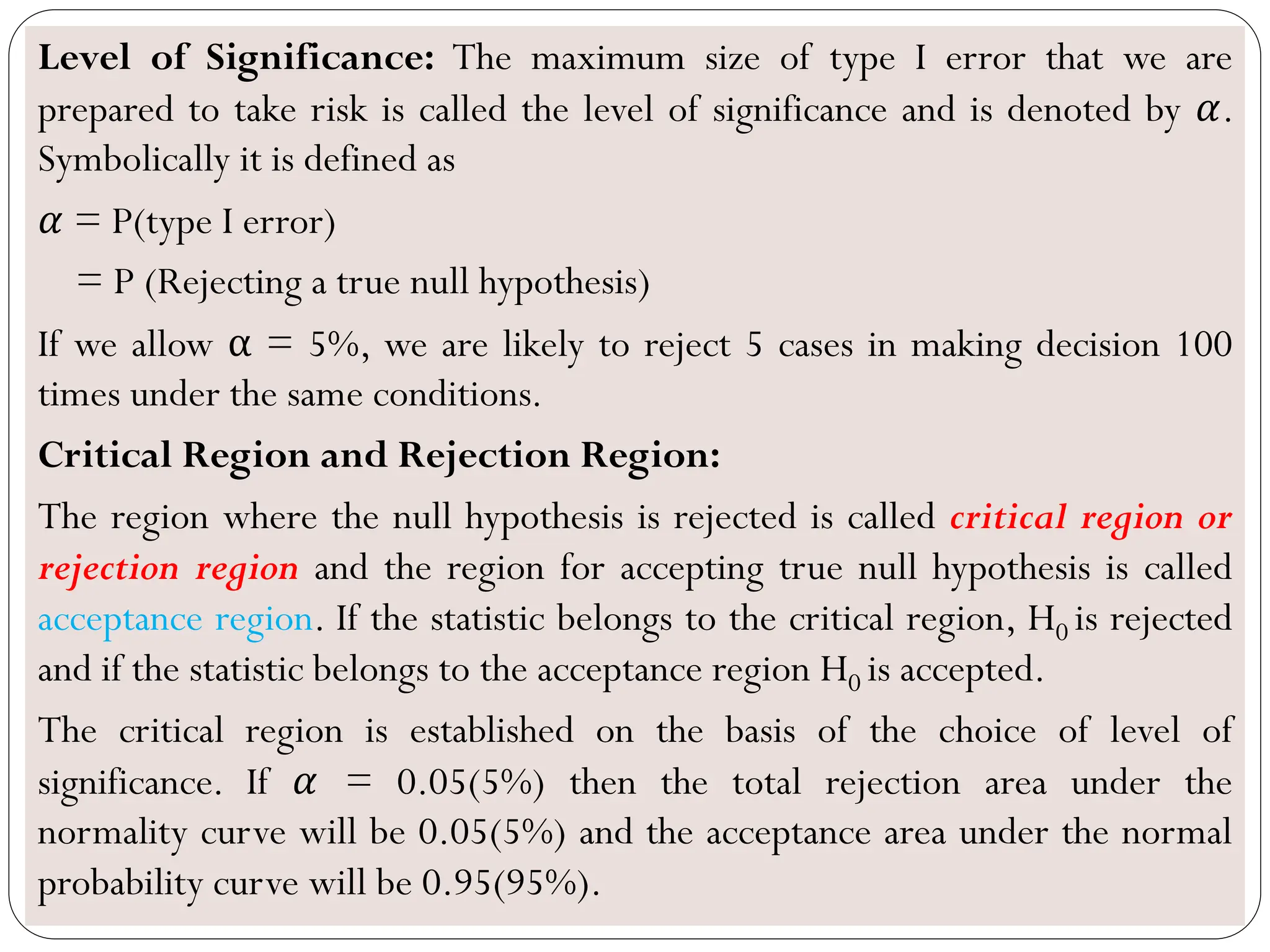
- The level of significance and critical values are used to determine whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis
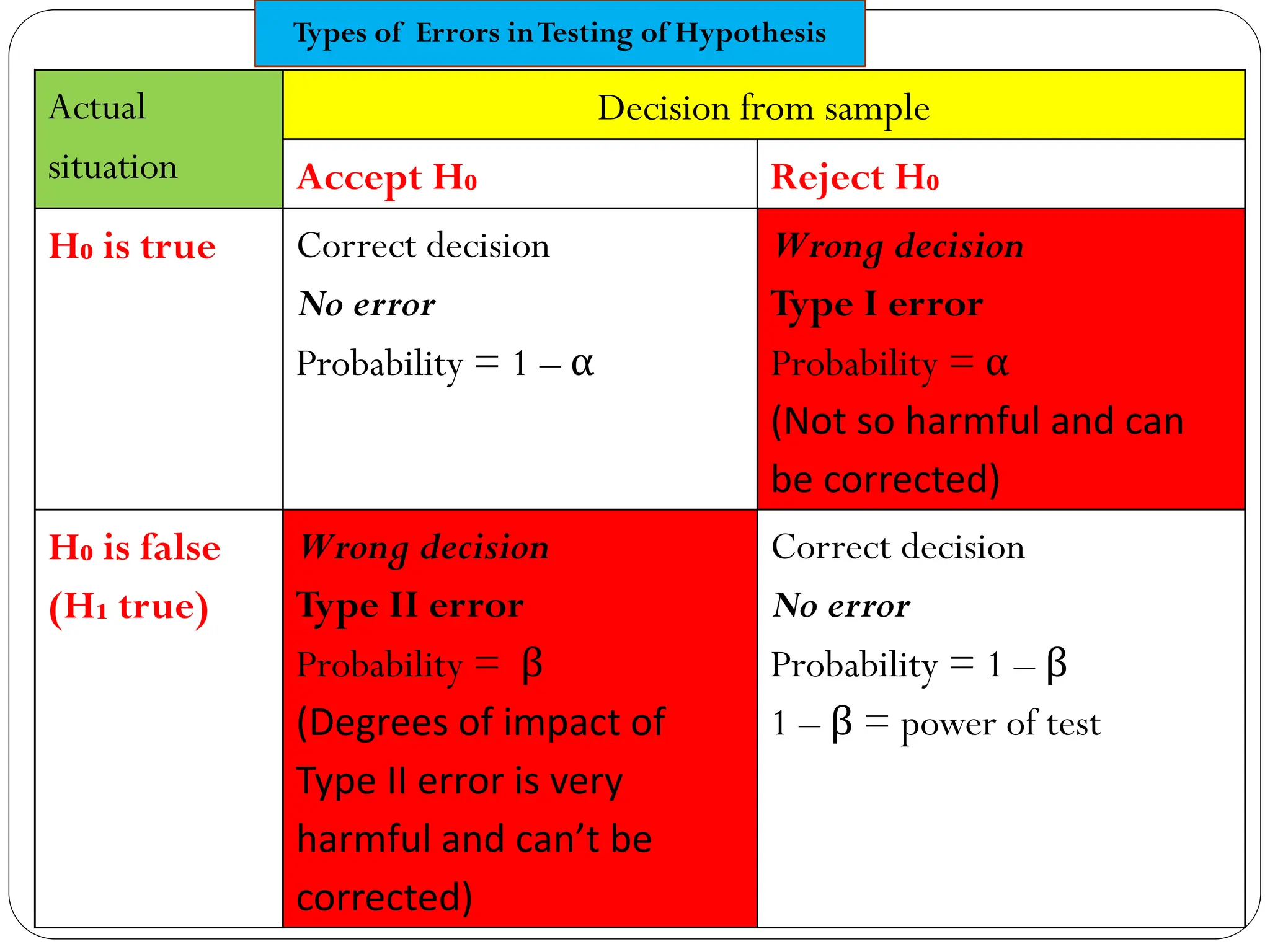
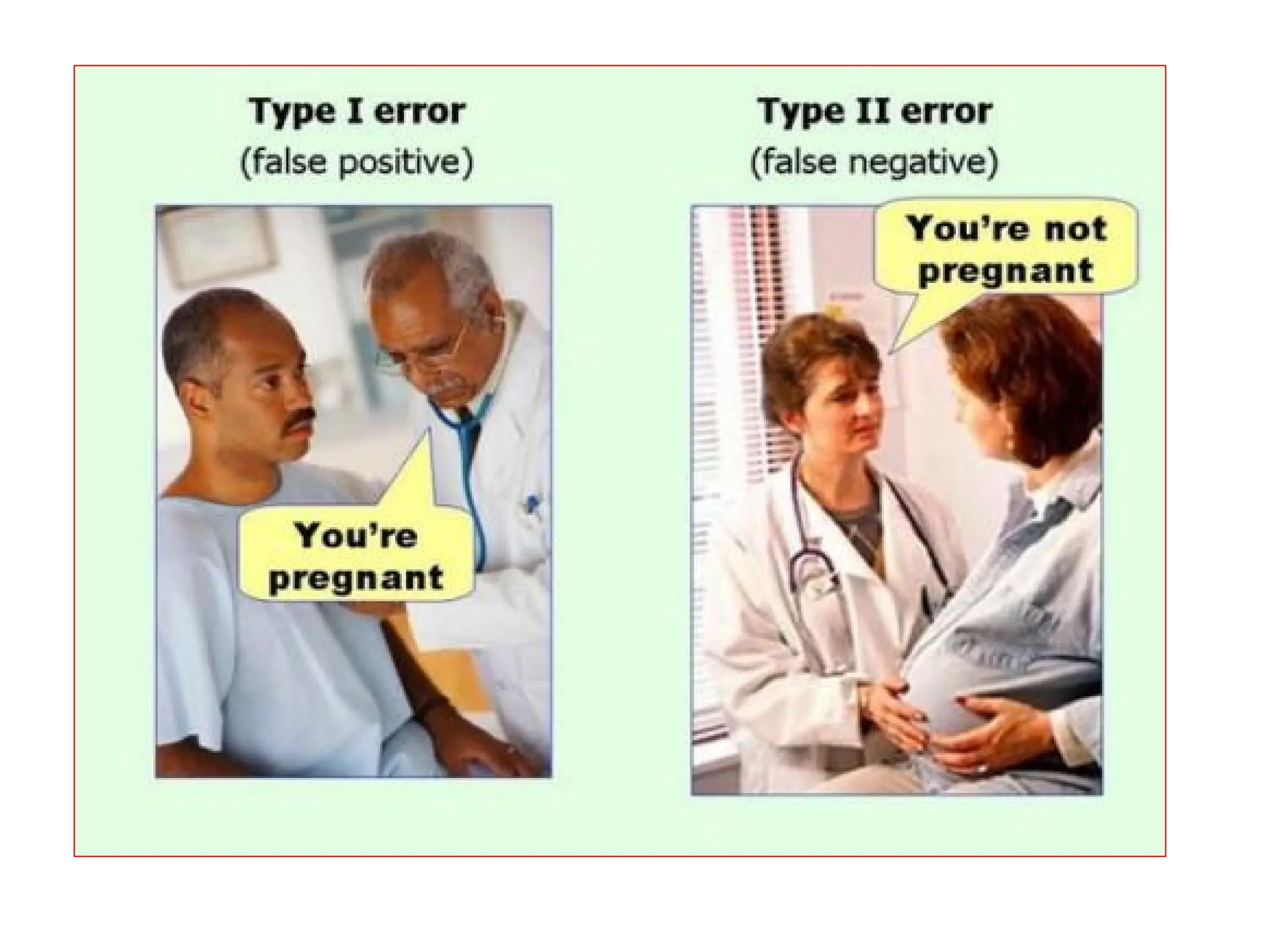
- Type I and type II errors are explained as incorrect rejections or failures to reject the null hypothesis
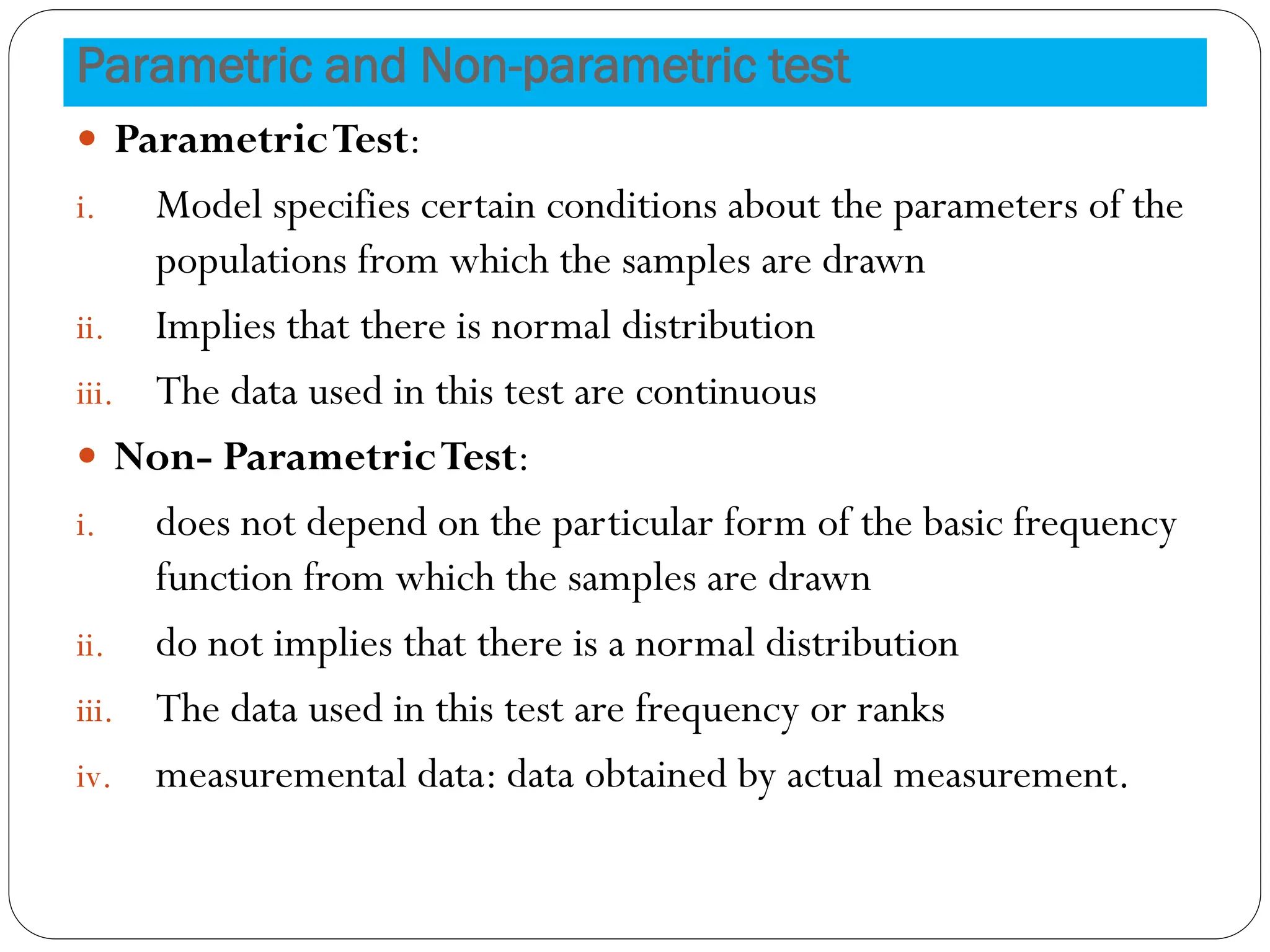
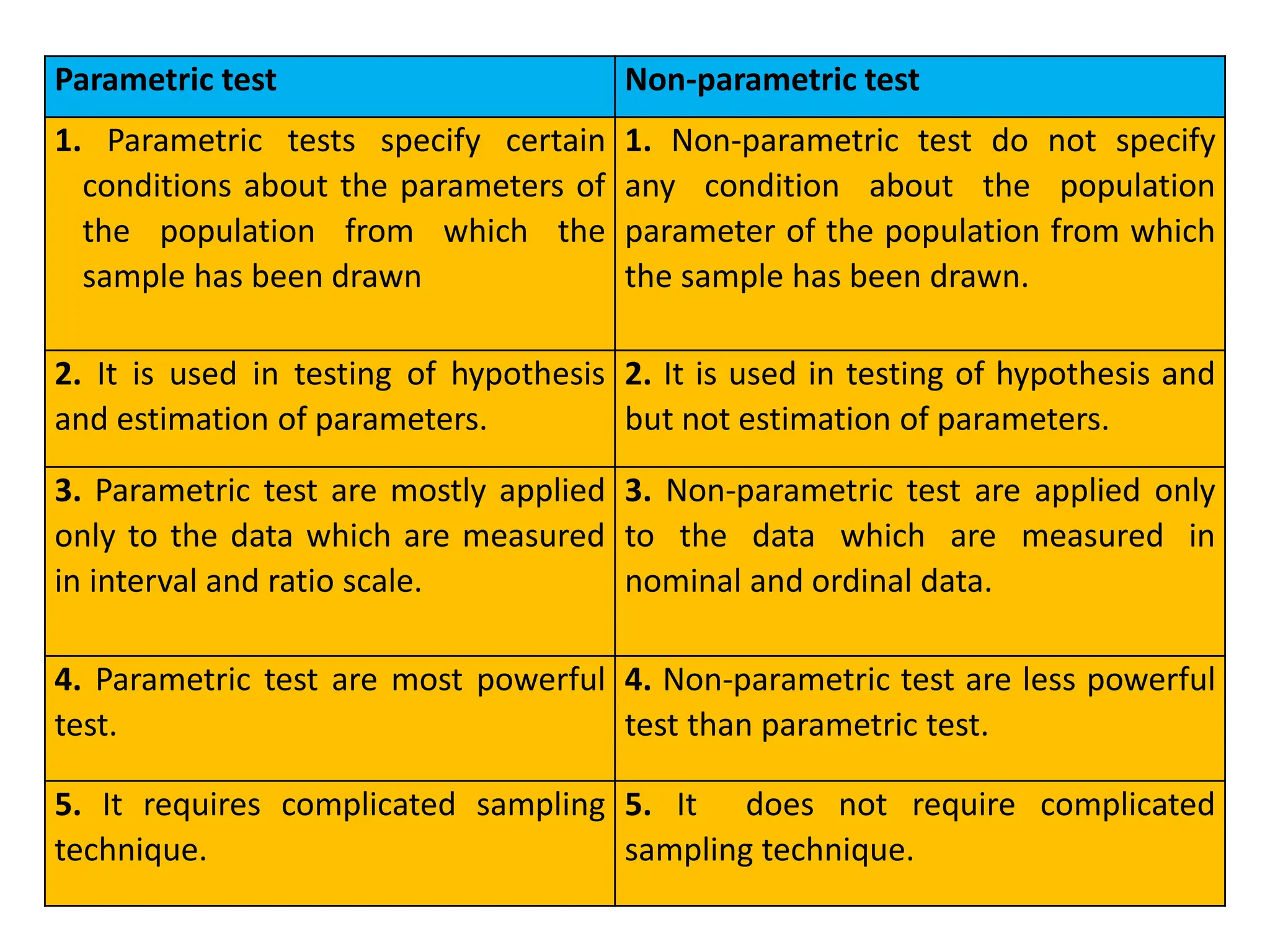
- Parametric and non-parametric tests are compared based on their data








![Finding p-value:
(i) For Left Tailed Test:
p = P( Z < Zcal)
= 0.5 – P(0 < Z < Z cal)
(ii) For Right Tailed Test
p = P( Z >Zcal)
= 0.5 – P(0 < Z < Z cal)
(iii) For Two Tailed Test:
p = P( Z < Zcal) + P( Z >Zcal)
= 2 P(Z >Zcal)
= 2[0.5 – P(0 < Z < Z cal)] Z = 0
Zcal
Zcal
Zcal
Zcal
Z = 0
Z = 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingofhypothesiscombined-240411050833-f40eac08/75/Testing-of-Hypothesis-combined-with-tests-pdf-24-2048.jpg)
![Two tailed test and Confidence interval
• If the reference value specified in H0 lies outside the
interval (that is, is less than the lower bound or
greater than the upper bound), you can reject H0.
• If the reference value specified in H0 lies within the
interval (that is, is not less than the lower bound or
greater than the upper bound), you fail to reject H0.
If hypothesis value 𝐻0: 𝜇 = 𝜇0lies within calculated
confidence interval estimate
[ ത
𝑋 − 𝑍 Τ
𝛼
2
𝑆. 𝐸. ( ത
𝑋) < 𝜇0 < ത
𝑋 − 𝑍 Τ
𝛼
2
𝑆. 𝐸. ( ത
𝑋)]
then null hypothesis is accepted otherwise rejected.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingofhypothesiscombined-240411050833-f40eac08/75/Testing-of-Hypothesis-combined-with-tests-pdf-25-2048.jpg)
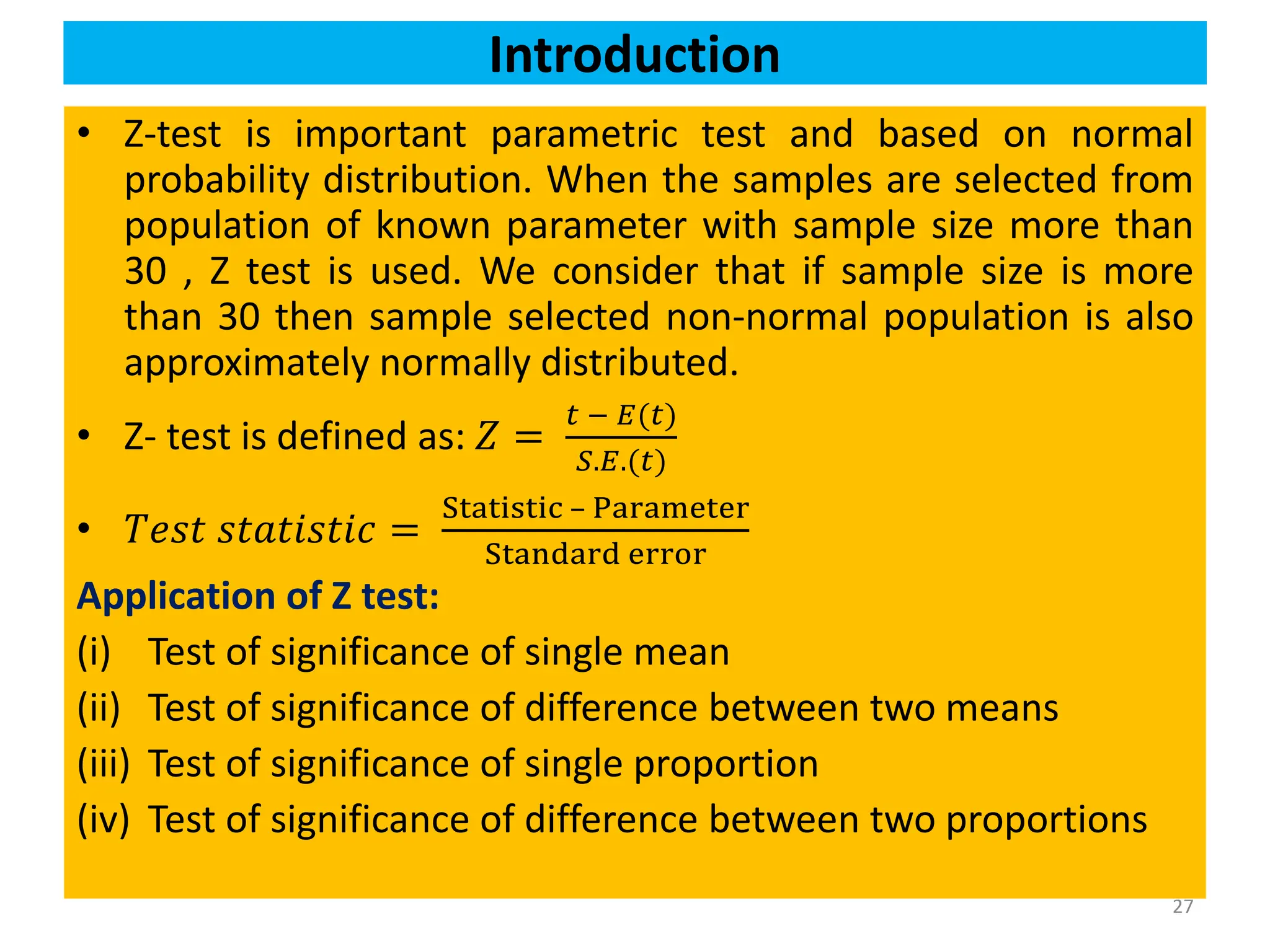




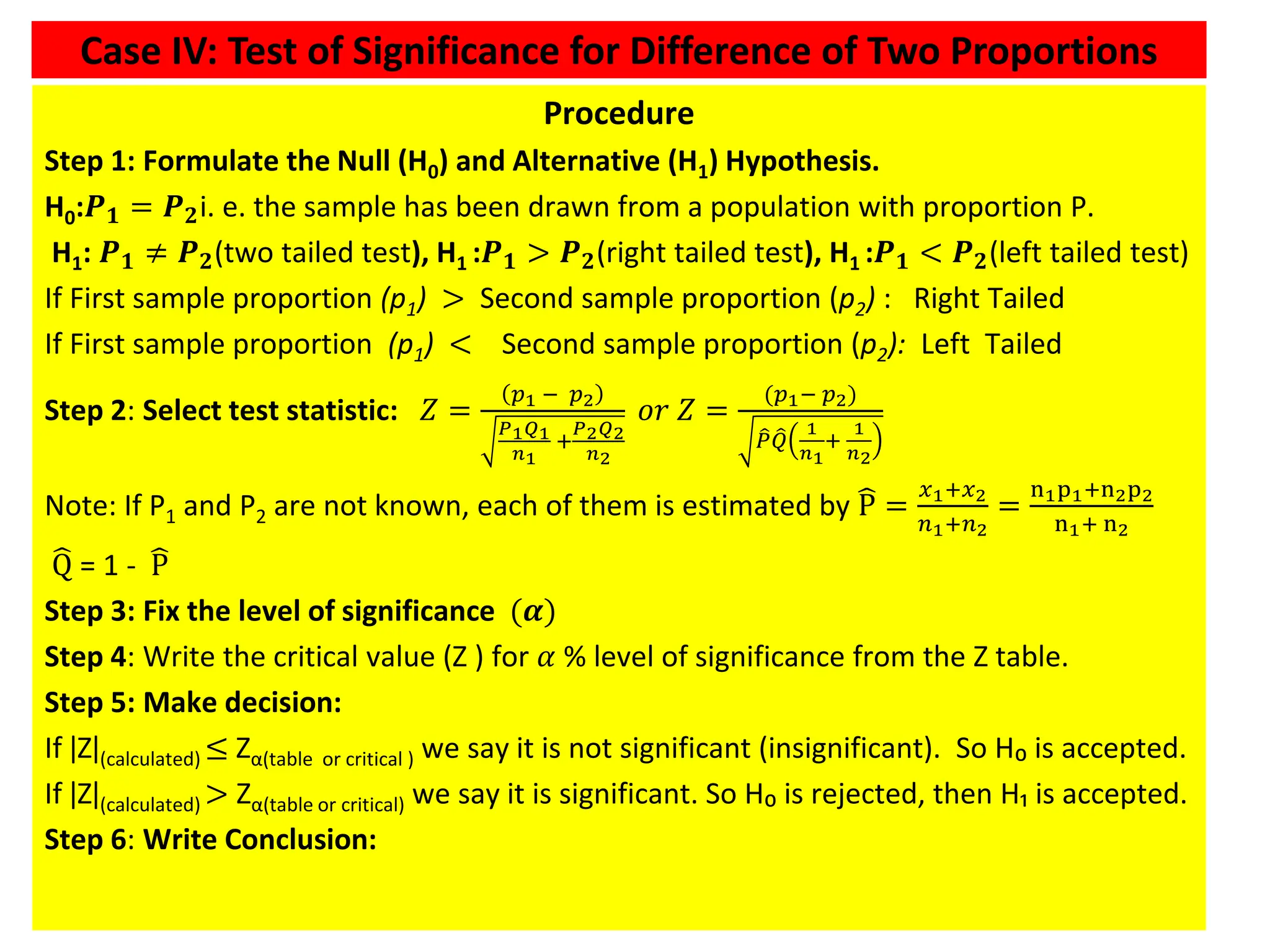
![Case III: Test of significance of Single Proportion
39
Procedure
Step 1: Formulate the Null (H0) and Alternative (H1) Hypothesis.
H0:P = 𝑃0i. e. the sample has been drawn from a population with proportion H1:P ≠
𝑃0(two tailed test), H1:P > 𝑃0(right tailed test), H1:𝑃 < 𝑃0(left tailed test)
If sample proportion(p) > Population Proportion(P) : Right Tailed Test
If Sample Proportion(p) < Population proportion(P) : Left tailed Test
Step 2: Select test statistic:𝑍 =
𝐷𝑖𝑓𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒
𝑆.𝐸.
=
𝑝 − 𝑃
𝑃𝑄
𝑛
[Note: if we have sampling from a
finite population of size N, then 𝑆. 𝐸. 𝑝 =
𝑁−𝑛
𝑁−1
𝑃(1−𝑃)
𝑛
=
𝑁−𝑛
𝑁−1
𝑃𝑄
𝑛
]
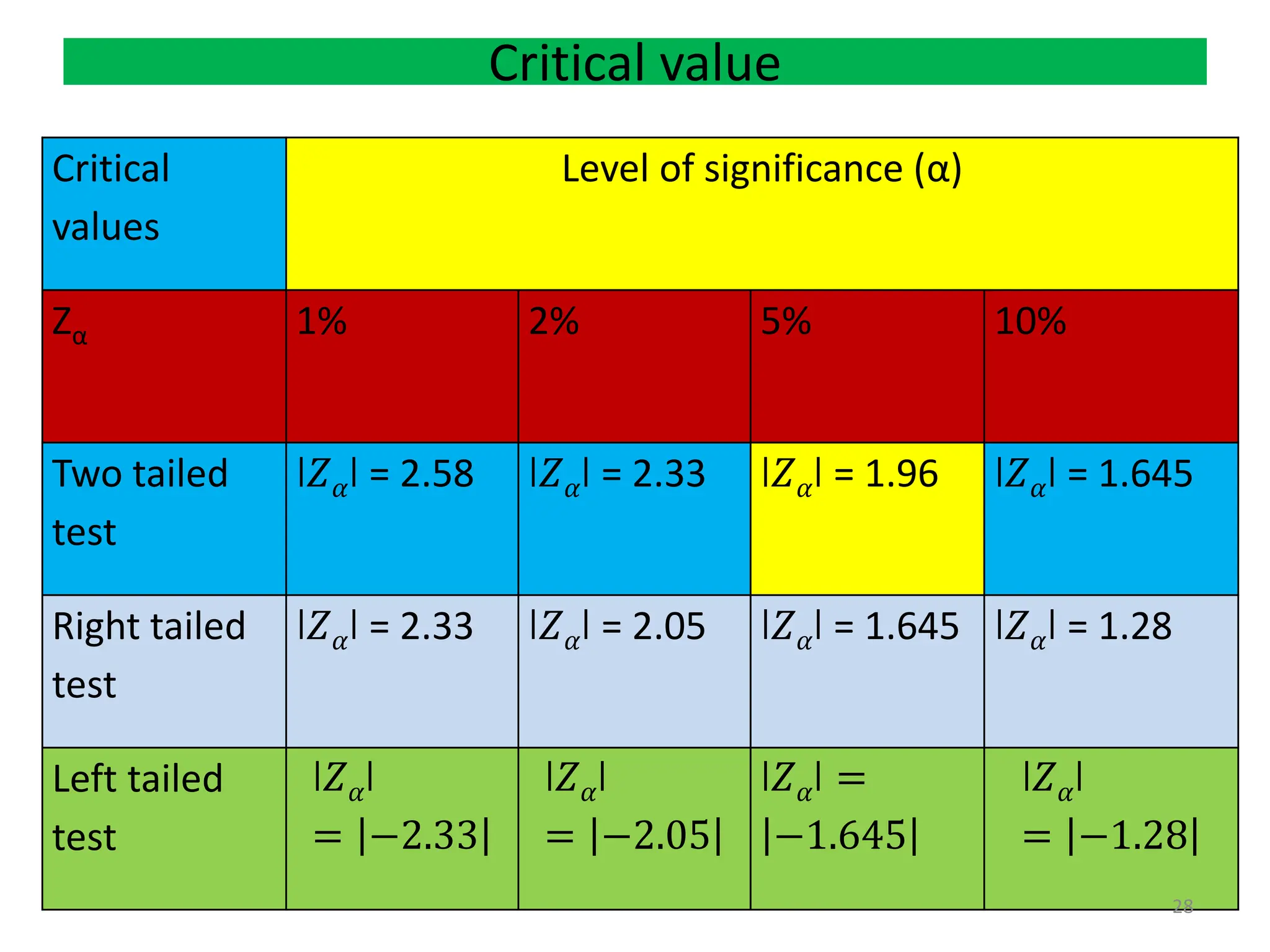
Step 3: Fix the level of significance (𝛼)
Step 4: Write the critical value (Z ) for 𝛼 % level of significance from the Z table.
Step 5: Make decision:
Critical value approach:
If ǀZǀ(calculated) ≤ Zα(table or critical ) we say it is not significant (insignificant).So H₀ is
accepted.
If ǀZǀ(calculated) > Zα(table or critical) we say it is significant. So H₀ is rejected, then H₁ is
accepted.
Step 6: Write Conclusion:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingofhypothesiscombined-240411050833-f40eac08/75/Testing-of-Hypothesis-combined-with-tests-pdf-39-2048.jpg)


Test Statistics: Zcal =
𝑝 − 𝑃
𝑃𝑄
𝑛
=
0.80−0.90
0.90 ×0.10
200
= -4.71 ǀZcalǀ = 4.71
Level of Significance(𝜶): 1%
Critical Value: Ztab = -2.33 ǀZtabǀ = 2.33
Decision: Since | zcal |> | ztab | So H0 is rejected and H1 is accepted.
Conclusion:
41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingofhypothesiscombined-240411050833-f40eac08/75/Testing-of-Hypothesis-combined-with-tests-pdf-41-2048.jpg)

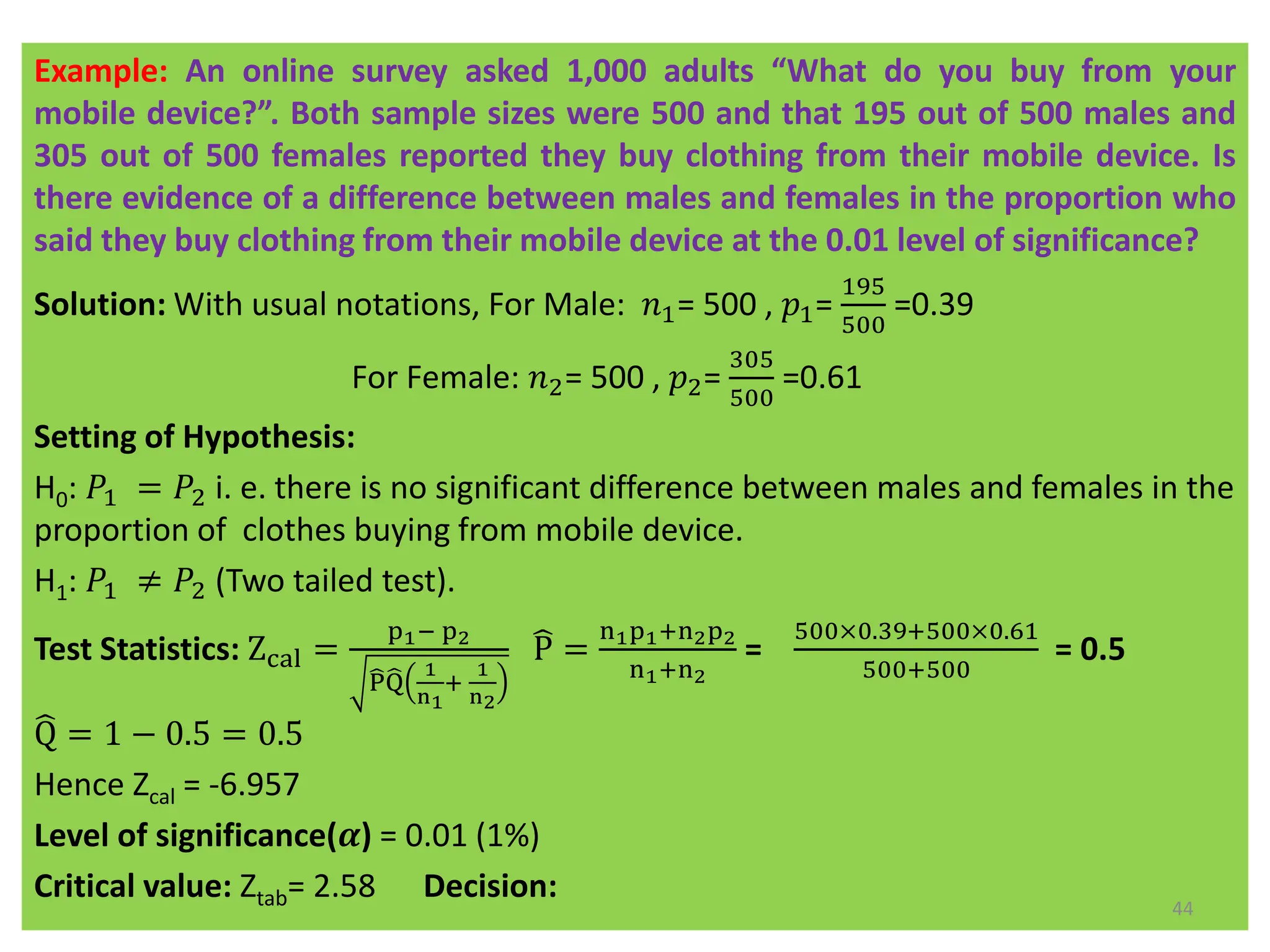
Test Statistics: Zcal =
𝑝 − 𝑃
𝑃𝑄
𝑛
=
0.27−0.20
0.20 ×0.80
500
= 3.91
Level of Significance(𝜶): 0.05
Critical value: Ztab = 1.645 Decision: Since Zcal > Ztab so H0 is rejected
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingofhypothesiscombined-240411050833-f40eac08/75/Testing-of-Hypothesis-combined-with-tests-pdf-42-2048.jpg)



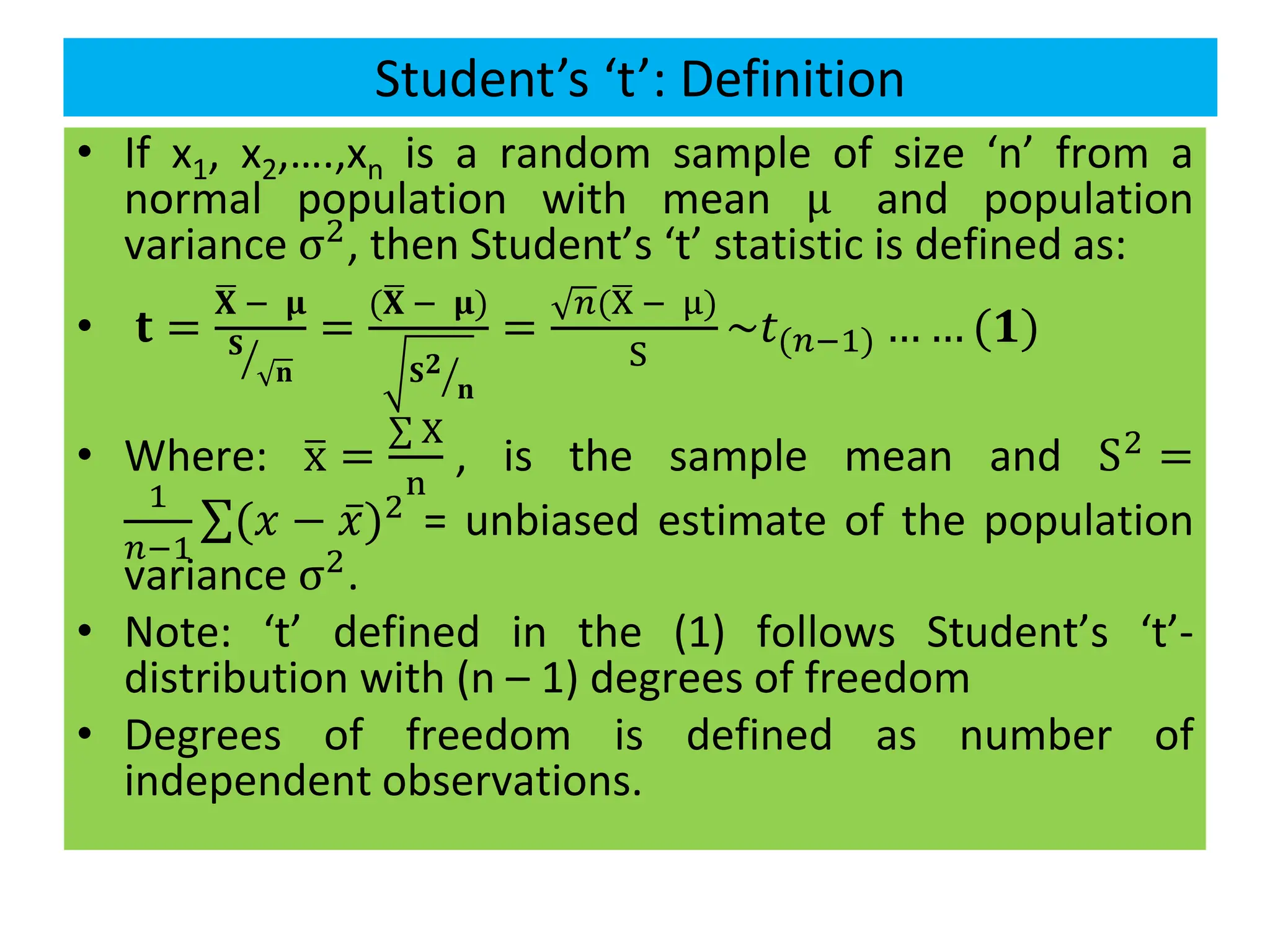
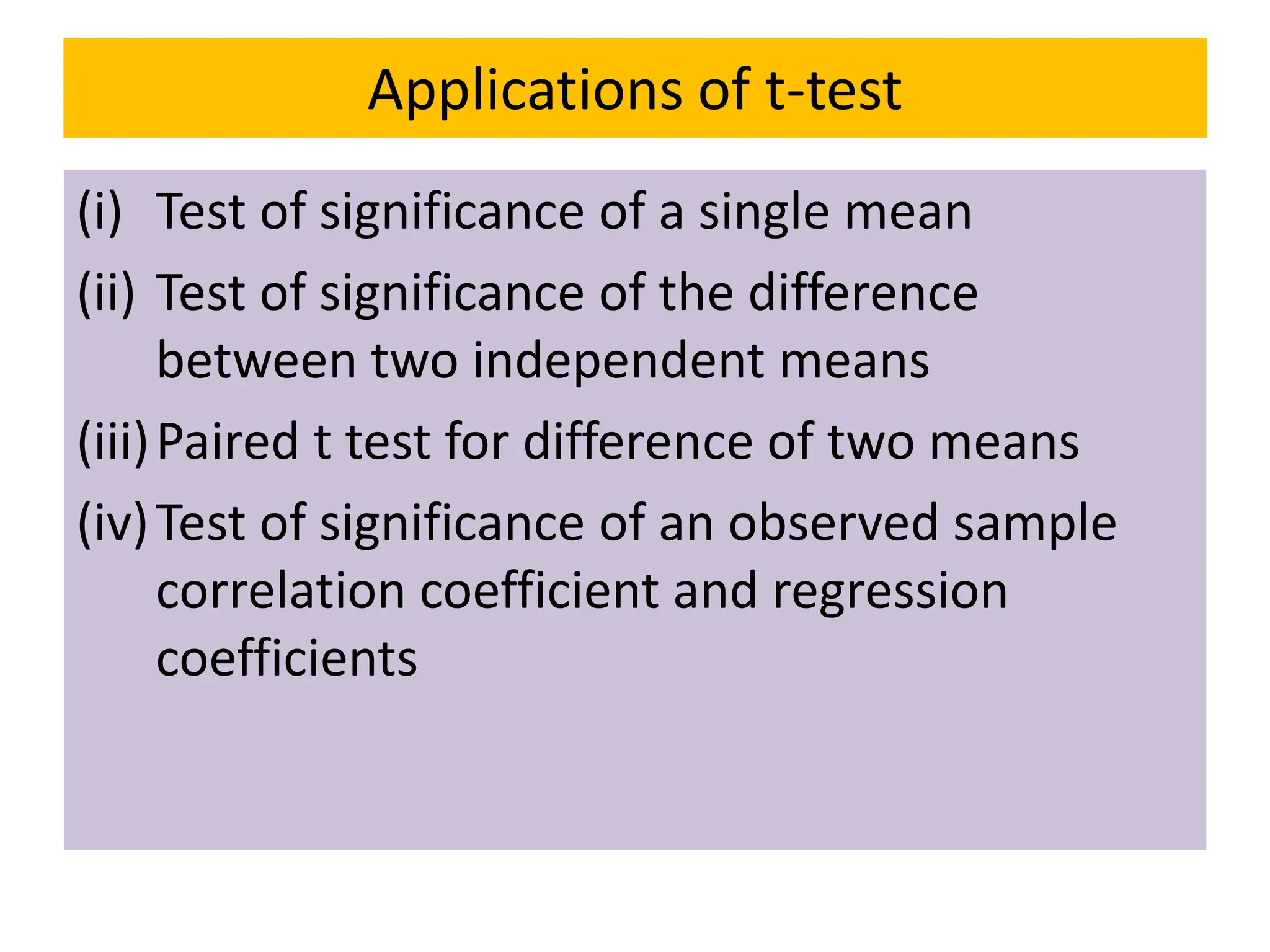
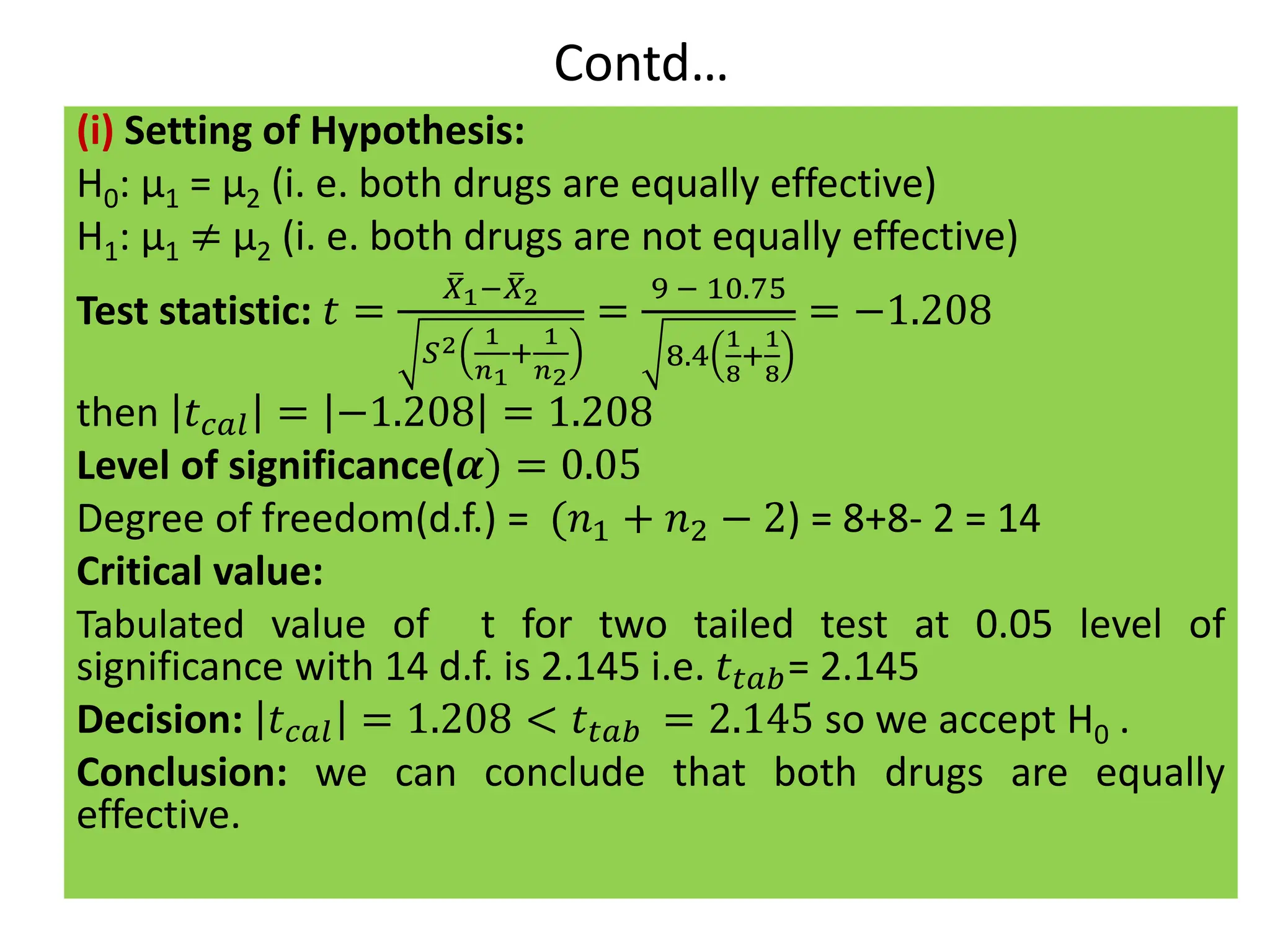
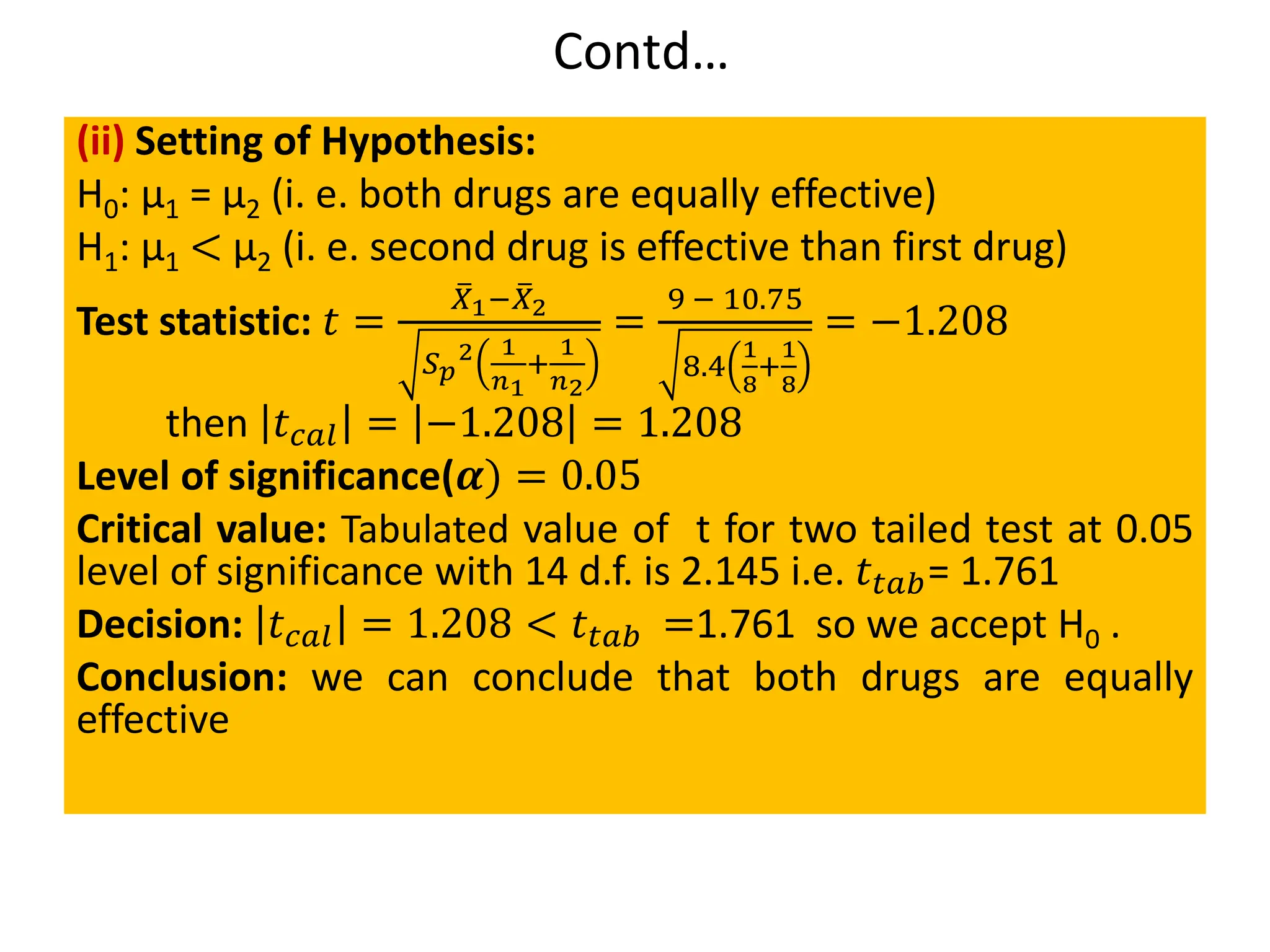
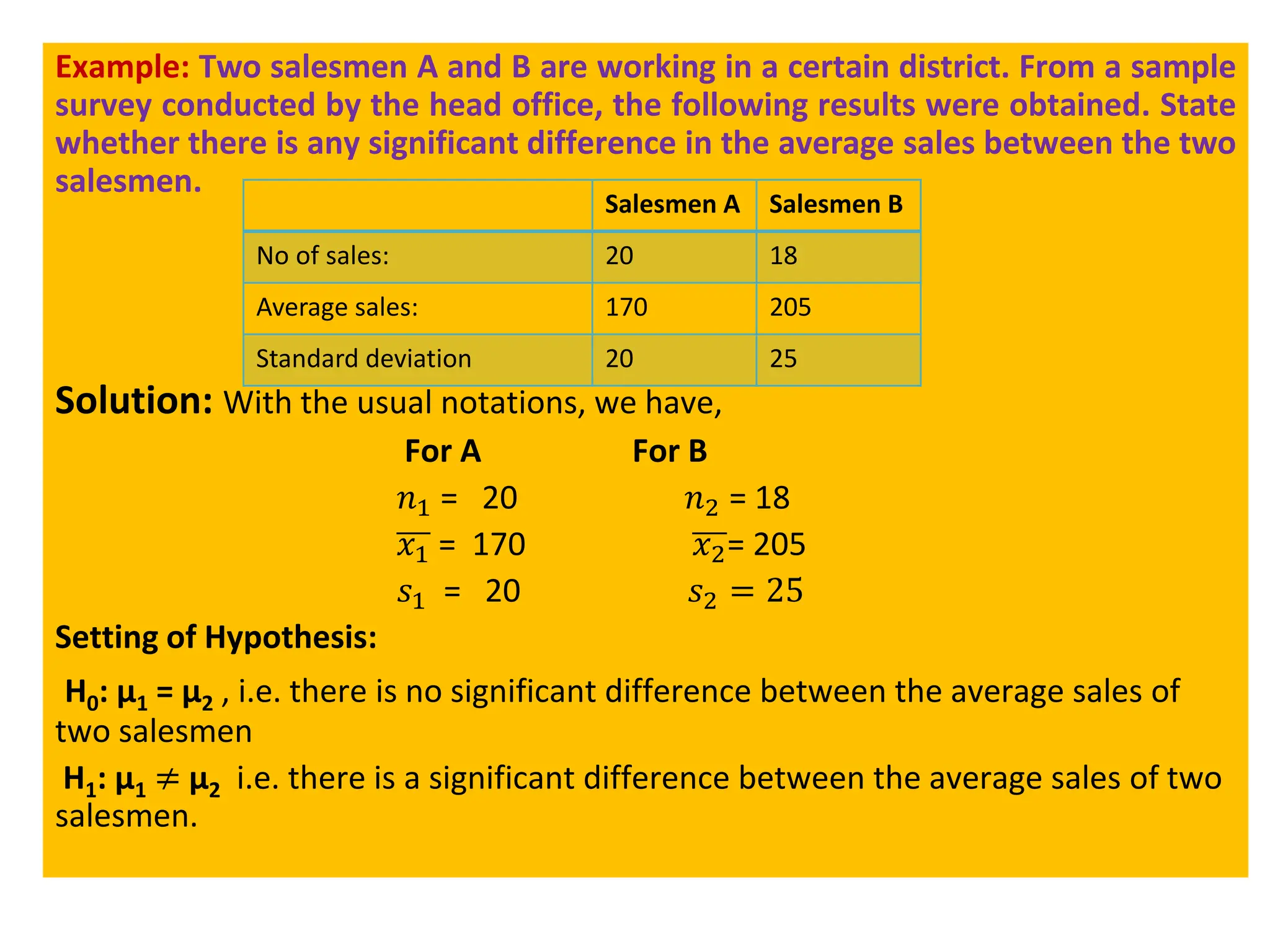
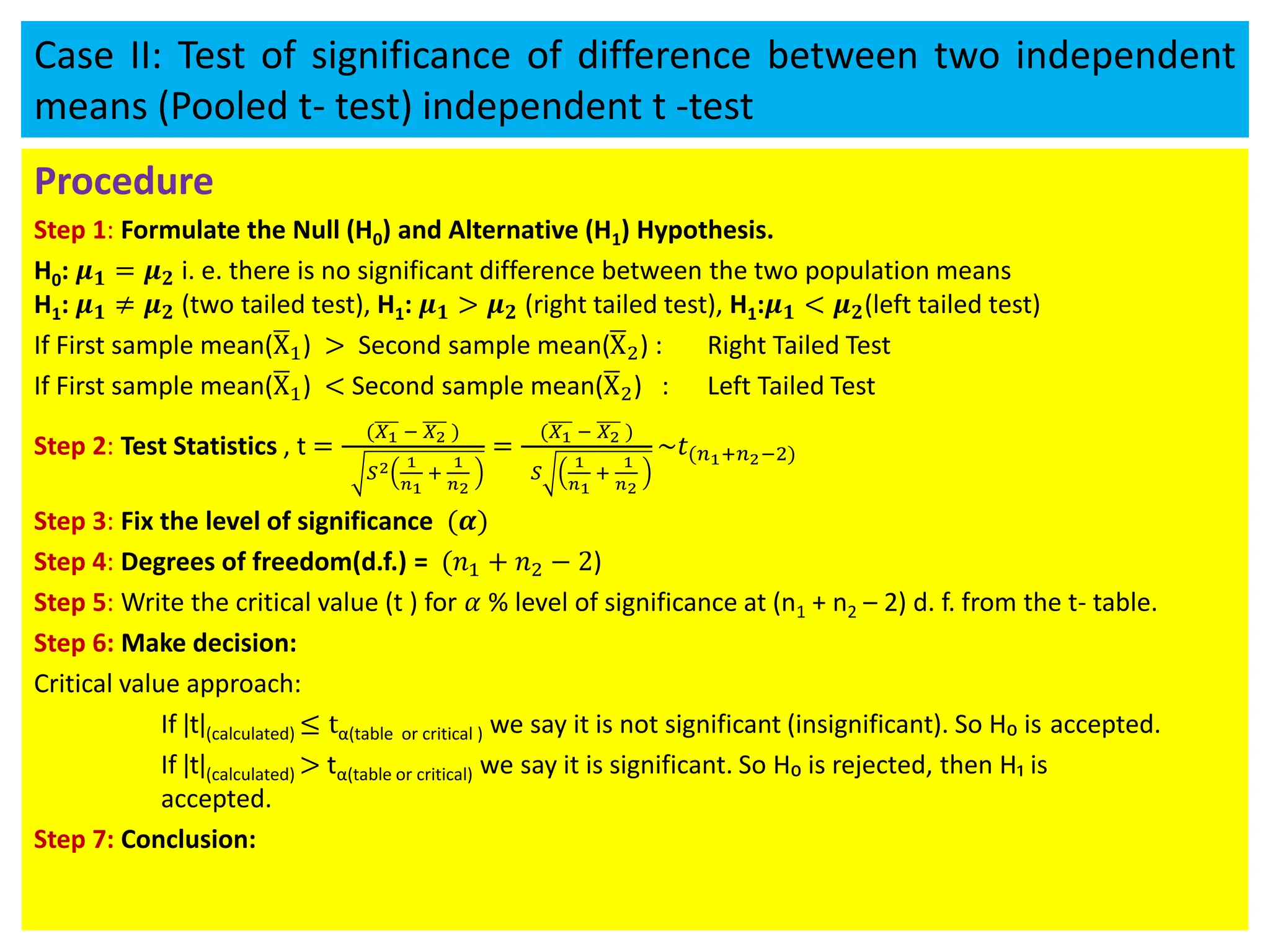
![Case I: Test of significance of a single mean
Procedure
Step 1: Formulate the Null (H0) and Alternative (H1) Hypothesis.
H0: 𝜇 = 𝜇0
H1: 𝜇 ≠ 𝜇0 (Two tailed test), : 𝜇 > 𝜇0 (Right tailed test), : 𝜇 < 𝜇0 (Left tailed test)
If sample mean ( ത
𝑋) > Population mean (𝜇) : Right Tailed Test
If sample mean ( ത
𝑋) < Population mean (𝜇) : Left Tailed Test
Step 2: Select test statistic:
t =
ഥ
X − μ
ൗ
S
n
=
n (ഥ
X − μ)
S
[𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑢𝑛𝑏𝑖𝑎𝑠𝑒𝑑( 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙 𝑑𝑎𝑡𝑎 𝑖𝑠 𝑔𝑖𝑣𝑒𝑛)]
t=
ഥ
X − μ
ൗ
s
n−1
=
(n−1) (ഥ
X − μ)
s
[𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑏𝑖𝑎𝑠𝑒𝑑 (𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒 𝑠. 𝑑. 𝑖𝑠 𝑔𝑖𝑣𝑒𝑛)]
Step 3: Fix the level of significance (𝜶)
Step 4: degrees of freedom(d.f.) = (n – 1)
Step 5: Write the critical value (t ) for 𝛼 % level of significance from the t- table.
Step 6: Make decision: Critical value approach:
If ǀtǀ(calculated) ≤ tα(table or critical ) : it is not significant (insignificant). So H₀ is accepted.
If ǀtǀ(calculated) > tα(table or critical) : it is significant. So H₀ is rejected, then H₁ is accepted.
Step 7: Write Conclusion:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingofhypothesiscombined-240411050833-f40eac08/75/Testing-of-Hypothesis-combined-with-tests-pdf-53-2048.jpg)
![Confidence intervals using ‘t’ or Confidence interval for
Small Samples
• Confidence intervals = estimator ± (reliability
constant) x (standard error of the estimate).
• Reliability coefficient is obtained from the table of t-
distribution.
• C. I. (μ) = ത
𝐱 ± 𝐭𝜶,𝒏−𝟏.
𝐒
𝐧
. [ For unbiased estimator,
When actual data is given]
• C. I. (μ) = ത
𝐱 ± 𝐭𝜶,𝒏−𝟏.
𝐬
𝐧−𝟏
. [ For biased estimator
when sample s.d. or variance is given]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingofhypothesiscombined-240411050833-f40eac08/75/Testing-of-Hypothesis-combined-with-tests-pdf-55-2048.jpg)
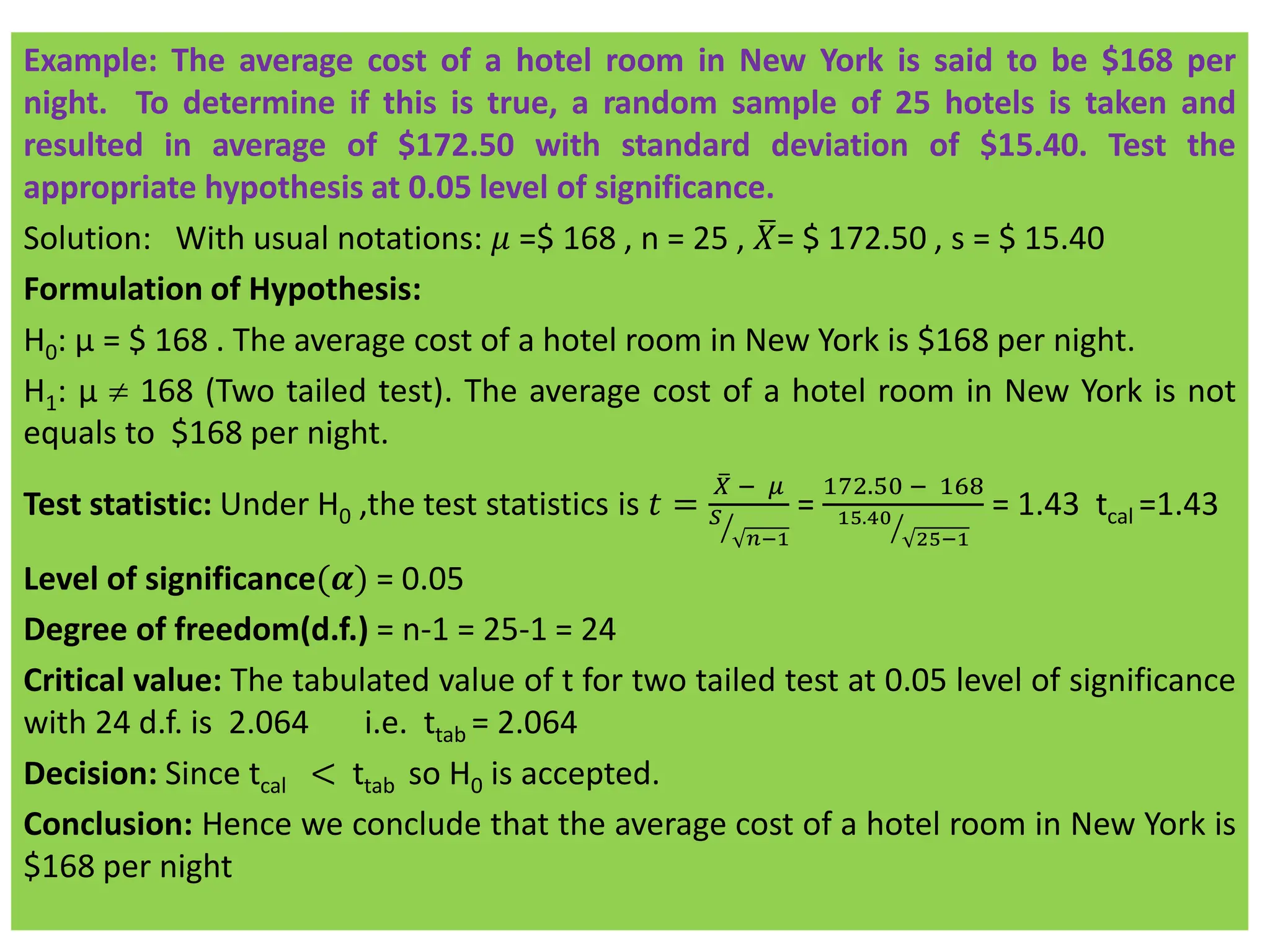

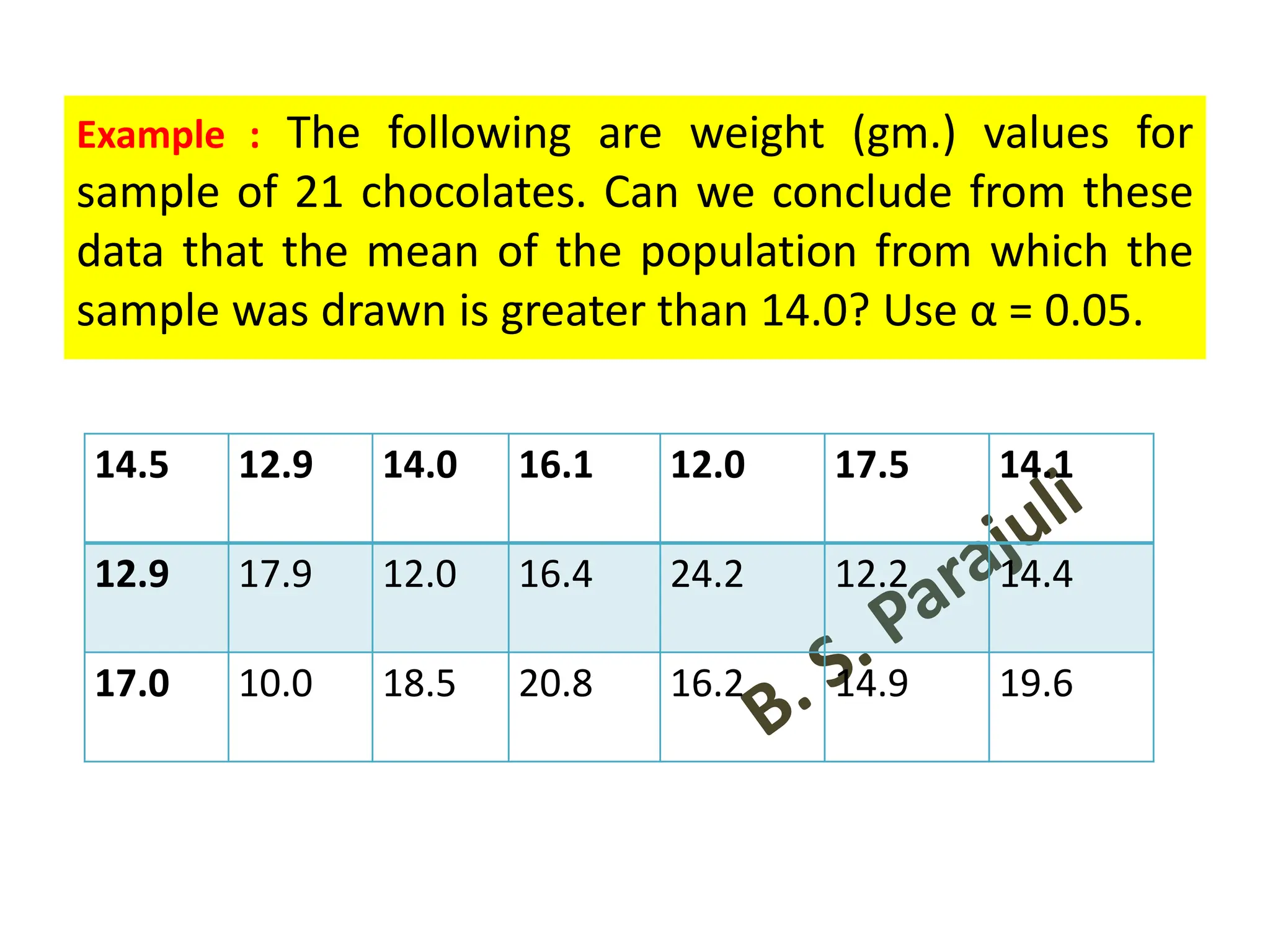
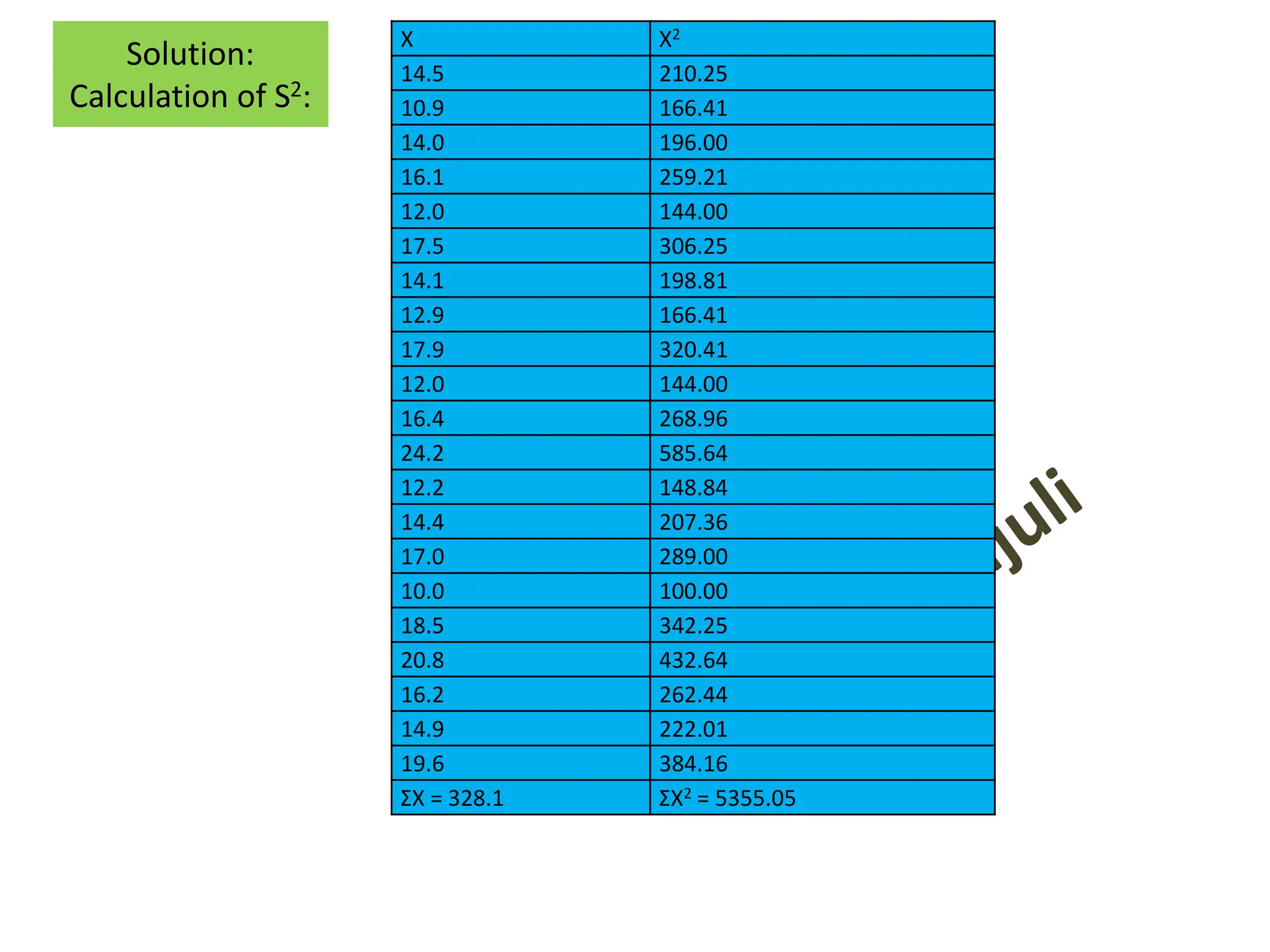
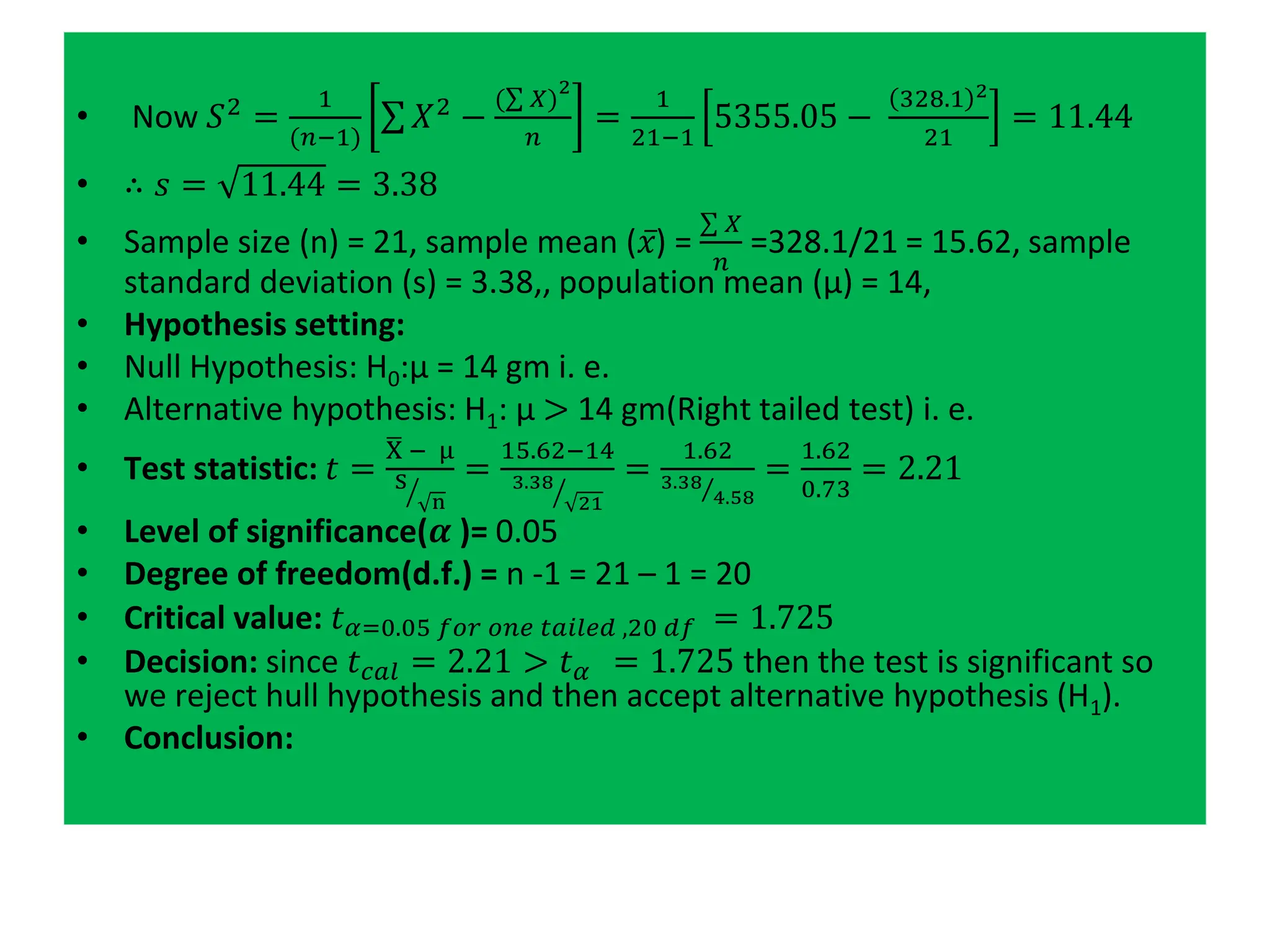
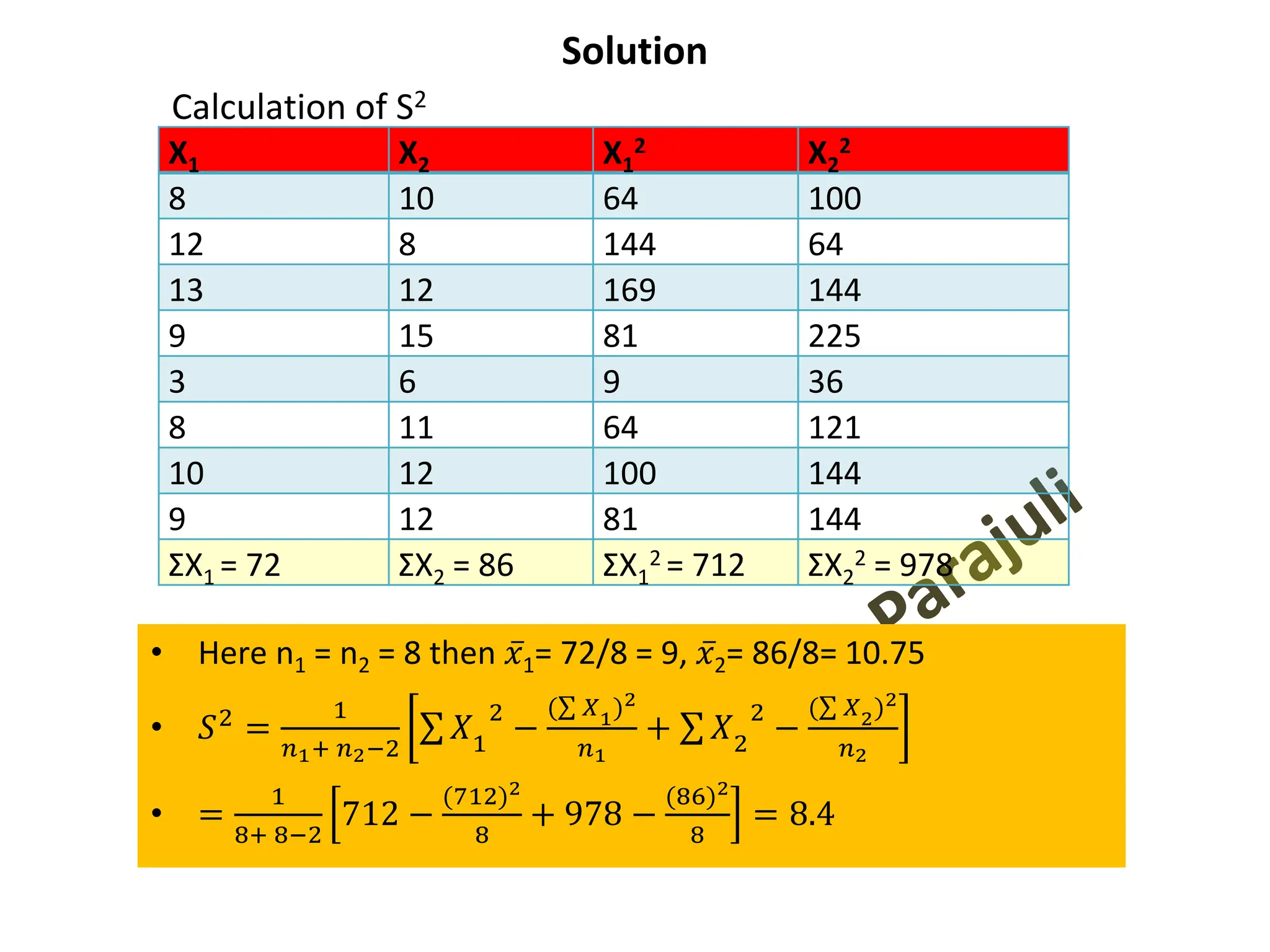
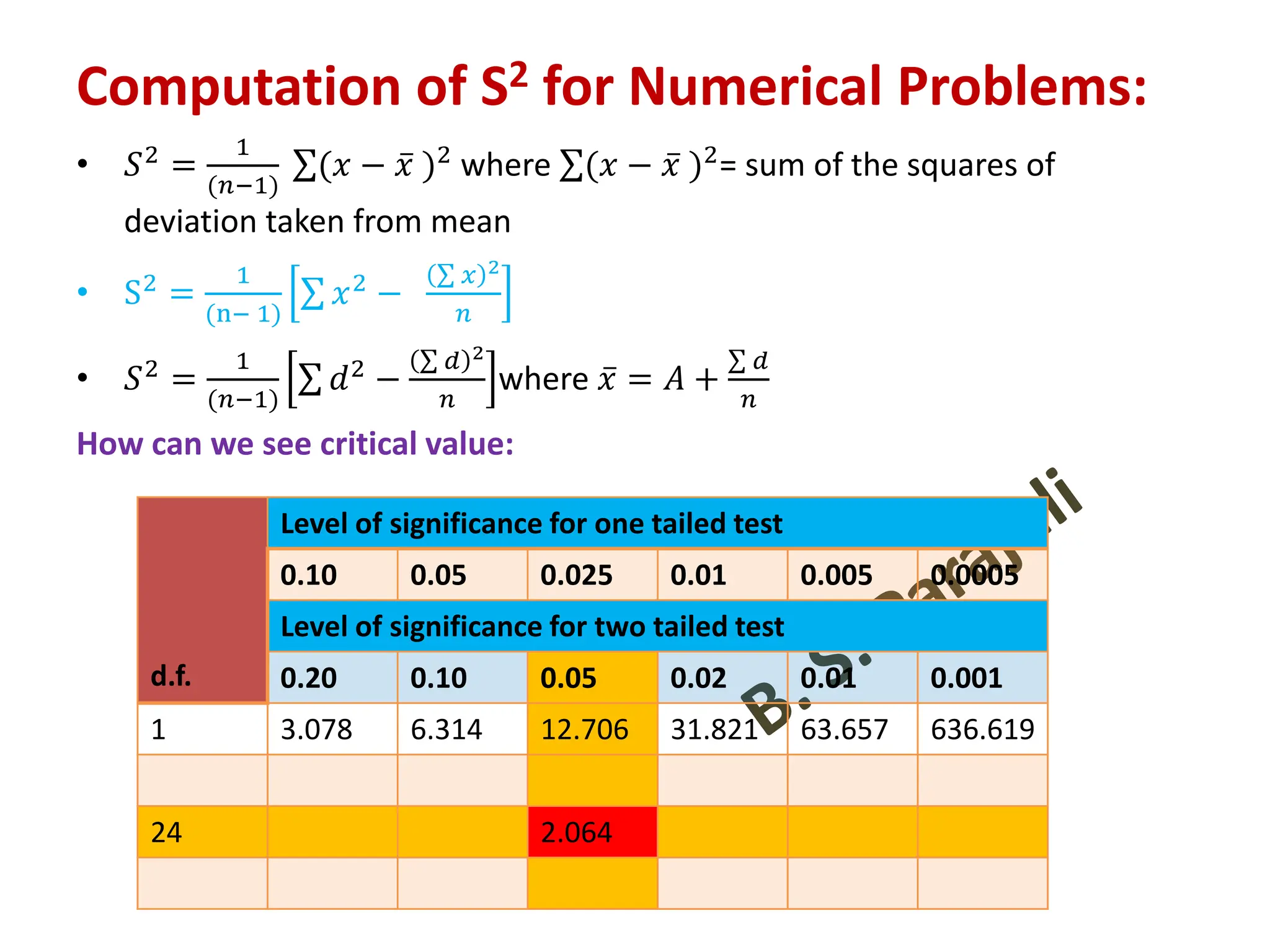
![Calculation of S2
• Actual mean method: 𝑆2
=
1
(𝑛1+ 𝑛2−2)
[σ(𝑋1 − 𝑋1)2
+ σ(𝑋2 − 𝑋2)2
]
• Direct method: 𝑆2 =
1
(𝑛1+ 𝑛2−2)
ቂ
ቃ
σ 𝑋1
2
−
σ 𝑋1
2
𝑛1
+ σ 𝑋2
2
−
σ 𝑋2
2
𝑛2
• Short cut method: 𝑆2
=
1
(𝑛1+ 𝑛2−2)
ቂ
ቃ
σ 𝑑1
2
−
σ 𝑑1
2
𝑛1
+
σ 𝑑2
2
−
σ 𝑑2
2
𝑛2
• Where d1 = X – A, d2 = X – B, A = assumed mean of series X,
B = assumed mean of series Y.
• 𝑺𝟐
=
𝒏𝟏.𝒔𝟏
𝟐+ 𝒏𝟐.𝒔𝟐
𝟐
(𝒏𝟏+ 𝒏𝟐−𝟐)
[ when the sample variance (or sample
standard deviation) i. e. biased estimates are given]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingofhypothesiscombined-240411050833-f40eac08/75/Testing-of-Hypothesis-combined-with-tests-pdf-62-2048.jpg)