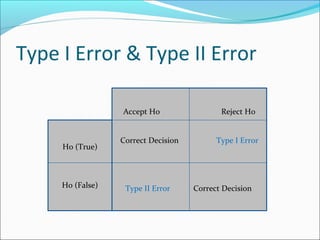
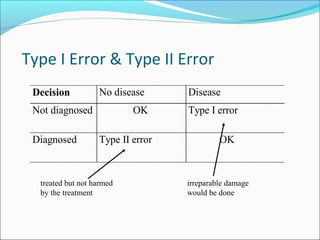
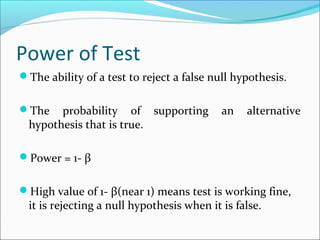
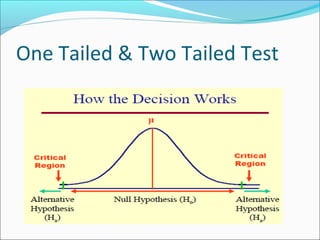
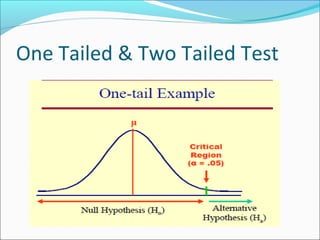
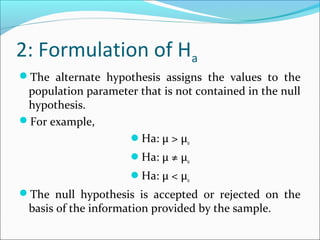
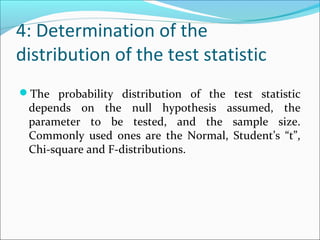
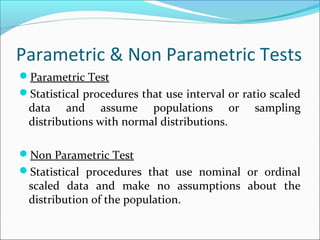
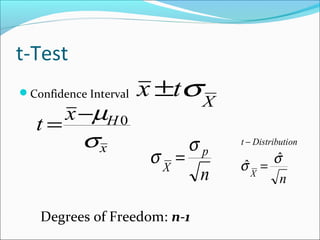
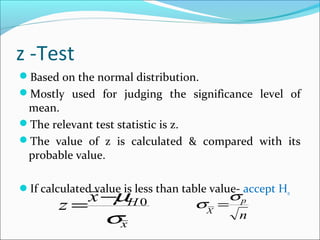
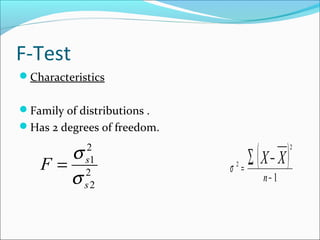
This document provides an overview of key concepts related to formulating and testing hypotheses. It defines a hypothesis as a proposition or claim about a population that can be empirically tested. Hypothesis testing involves examining two opposing hypotheses: the null hypothesis (H0) and alternative hypothesis (Ha). It describes the basic steps of hypothesis testing as formulating the hypotheses, defining a test statistic, determining the distribution of the test statistic, defining the critical region, and making a decision to accept or reject the null hypothesis. Key concepts like type I and type II errors, significance levels, critical values, and one-tailed vs two-tailed tests are also explained. Parametric tests like the z-test, t-test, and