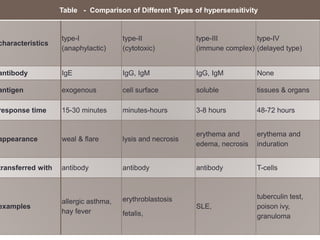
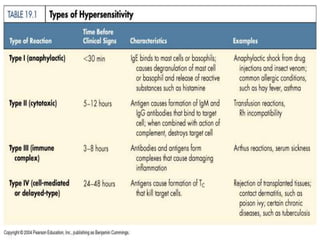
Hypersensitivity refers to excessive or harmful immune reactions. There are four main types:
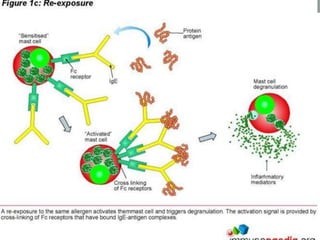
I. Type I is an immediate reaction mediated by IgE antibodies binding to mast cells. Common examples include allergic reactions.
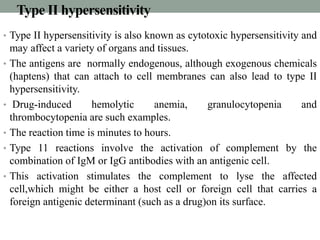
II. Type II involves IgG or IgM binding to cells, activating complement and causing cell lysis. Examples include hemolytic anemia.
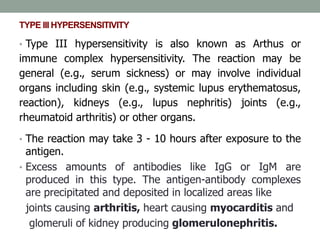
III. Type III occurs when antigen-antibody complexes are deposited in tissues, activating complement and attracting inflammatory cells. Examples include serum sickness.
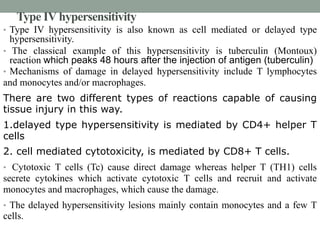
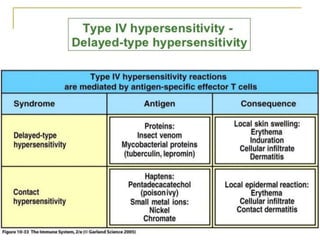
IV. Type IV is delayed hypersensitivity mediated by T cells. The tuberculin skin test detects exposure to tuberculosis bacteria.