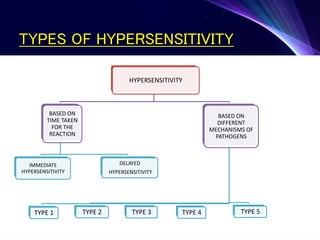
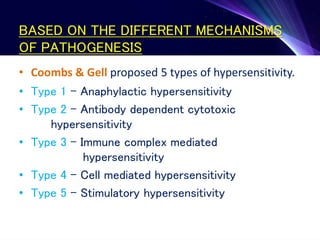
Hypersensitivity refers to excessive or inappropriate immune responses that are harmful to the body. There are four main types of hypersensitivity reactions based on their pathogenic mechanisms:
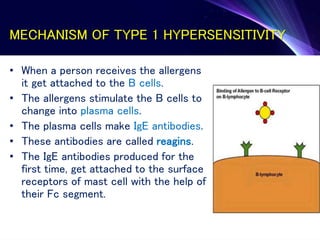
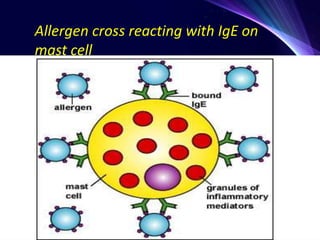
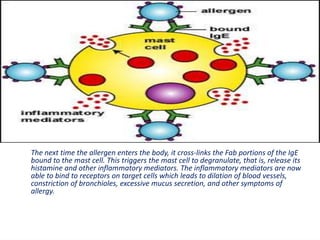
1. Type I reactions are immediate or anaphylactic and mediated by IgE antibodies, causing release of inflammatory mediators from mast cells.
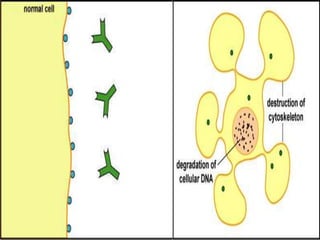
2. Type II reactions are antibody-dependent cytotoxic reactions, where antibodies bind to antigens on self cells leading to complement activation and cell lysis.
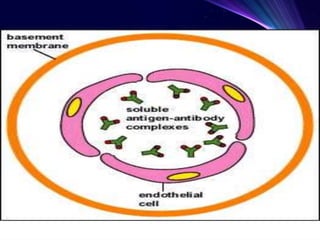
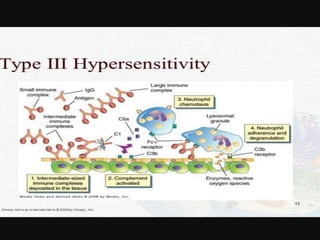
3. Type III reactions are immune complex-mediated, where circulating antigen-antibody complexes deposit in tissues and activate complement, causing inflammation.
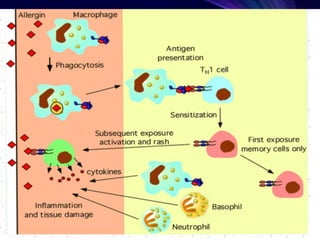
4. Type IV reactions are cell-mediated and involve activation of sensitized T cells by antigens,