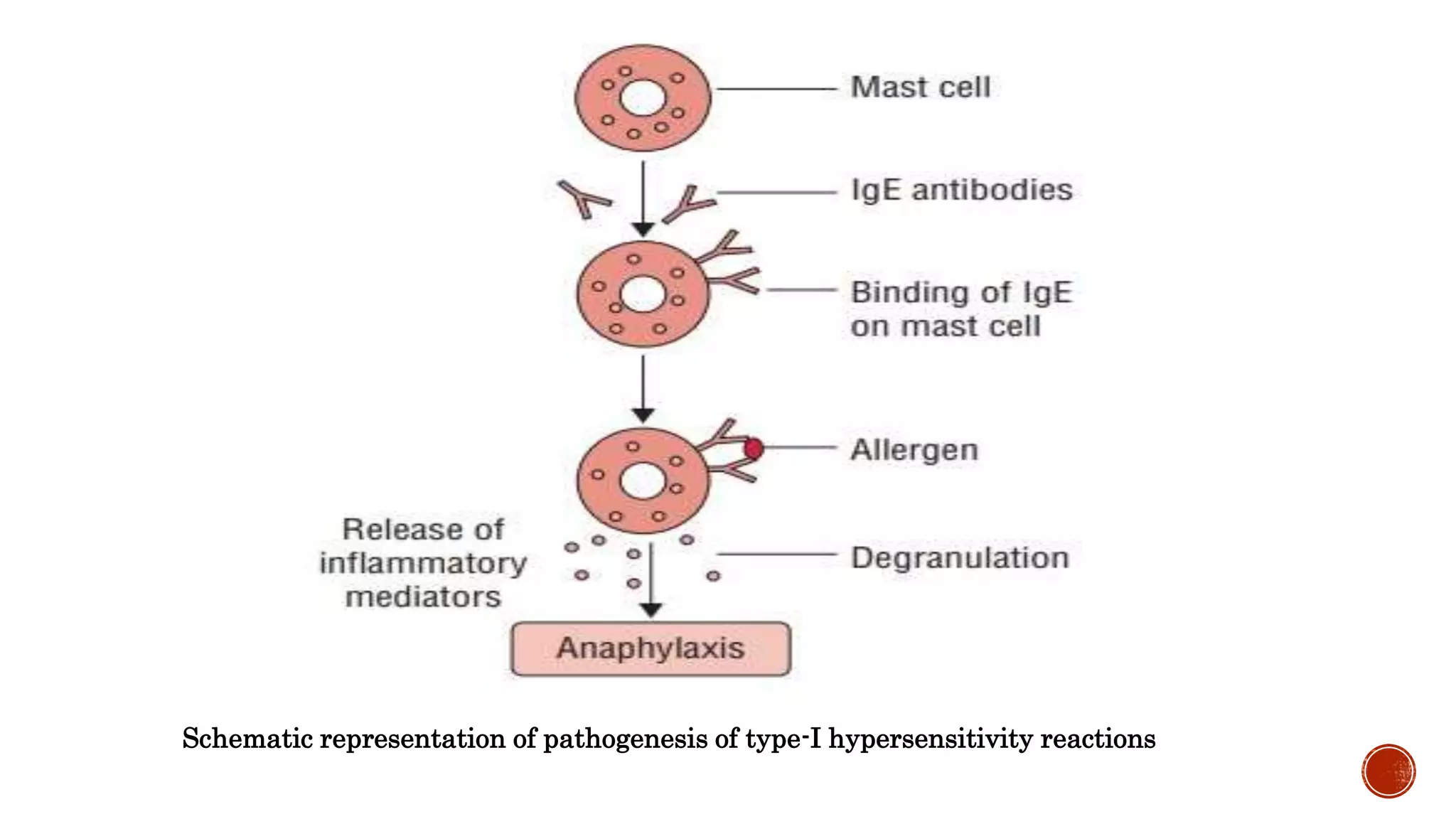
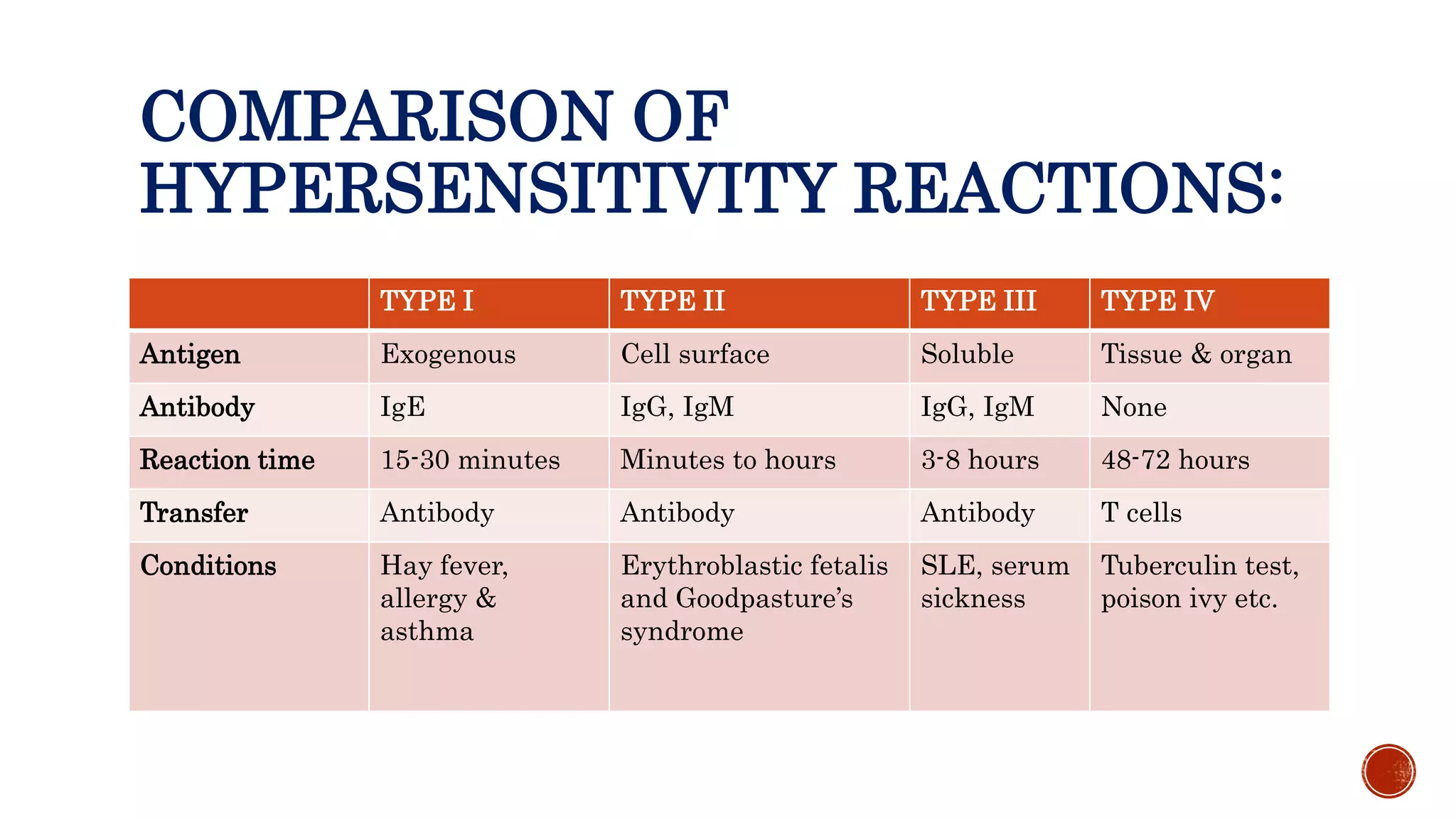
This document discusses the four types of hypersensitivity reactions: Type I (immediate hypersensitivity/anaphylactic), Type II (cytotoxic), Type III (immune complex-mediated), and Type IV (delayed hypersensitivity). It provides details on the definition, etiology, pathogenesis, and examples of each type of reaction. Type I involves IgE antibodies and mast cell/basophil degranulation. Type II involves IgG/IgM antibodies binding to cell surfaces and complement-mediated cell lysis. Type III occurs when antigen-antibody complexes are deposited in tissues. Type IV is T cell-mediated and has a delayed onset.