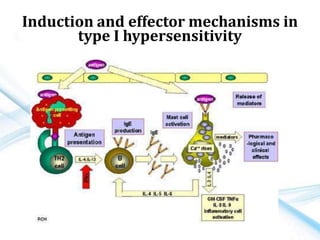
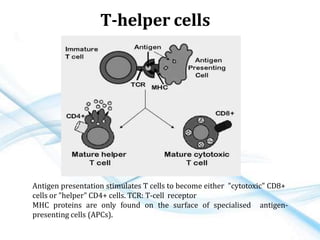
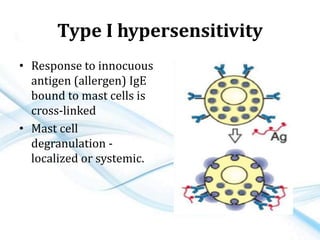
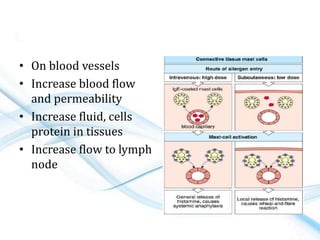
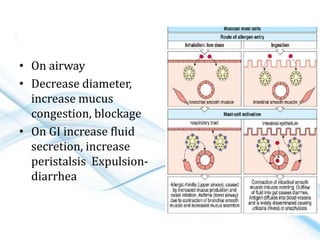
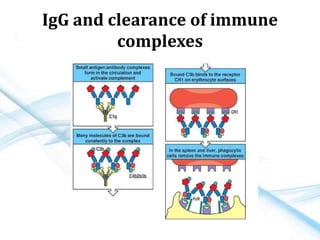
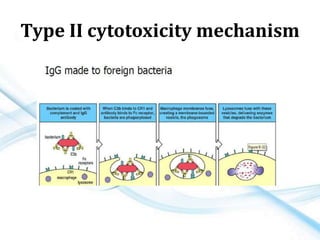
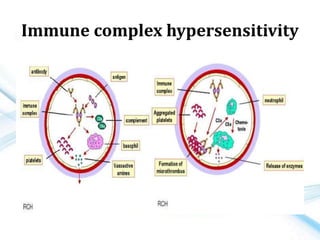
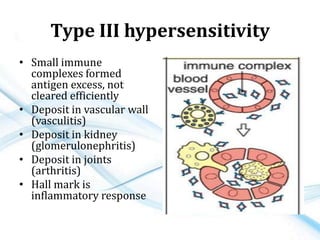
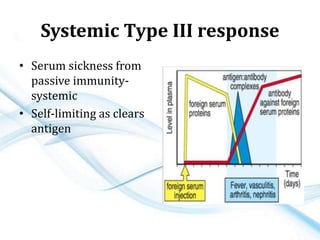
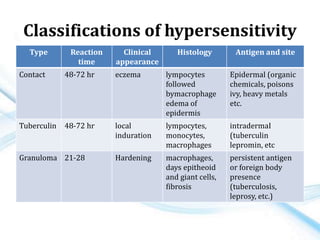
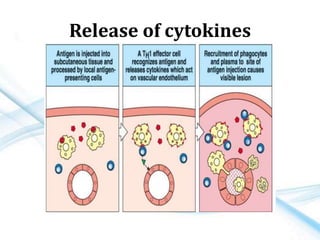
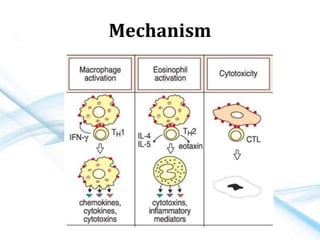
This document discusses allergy and hypersensitivity reactions. It defines allergy as a type I hypersensitivity reaction mediated by IgE antibodies. There are four types of hypersensitivity reactions classified based on the immune mechanisms involved and time taken for the reaction. Type I reactions are immediate and anaphylactic, type II are cytotoxic, type III involve immune complexes, and type IV are cell-mediated or delayed hypersensitivity reactions. The document provides details on the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment of each type of hypersensitivity reaction.