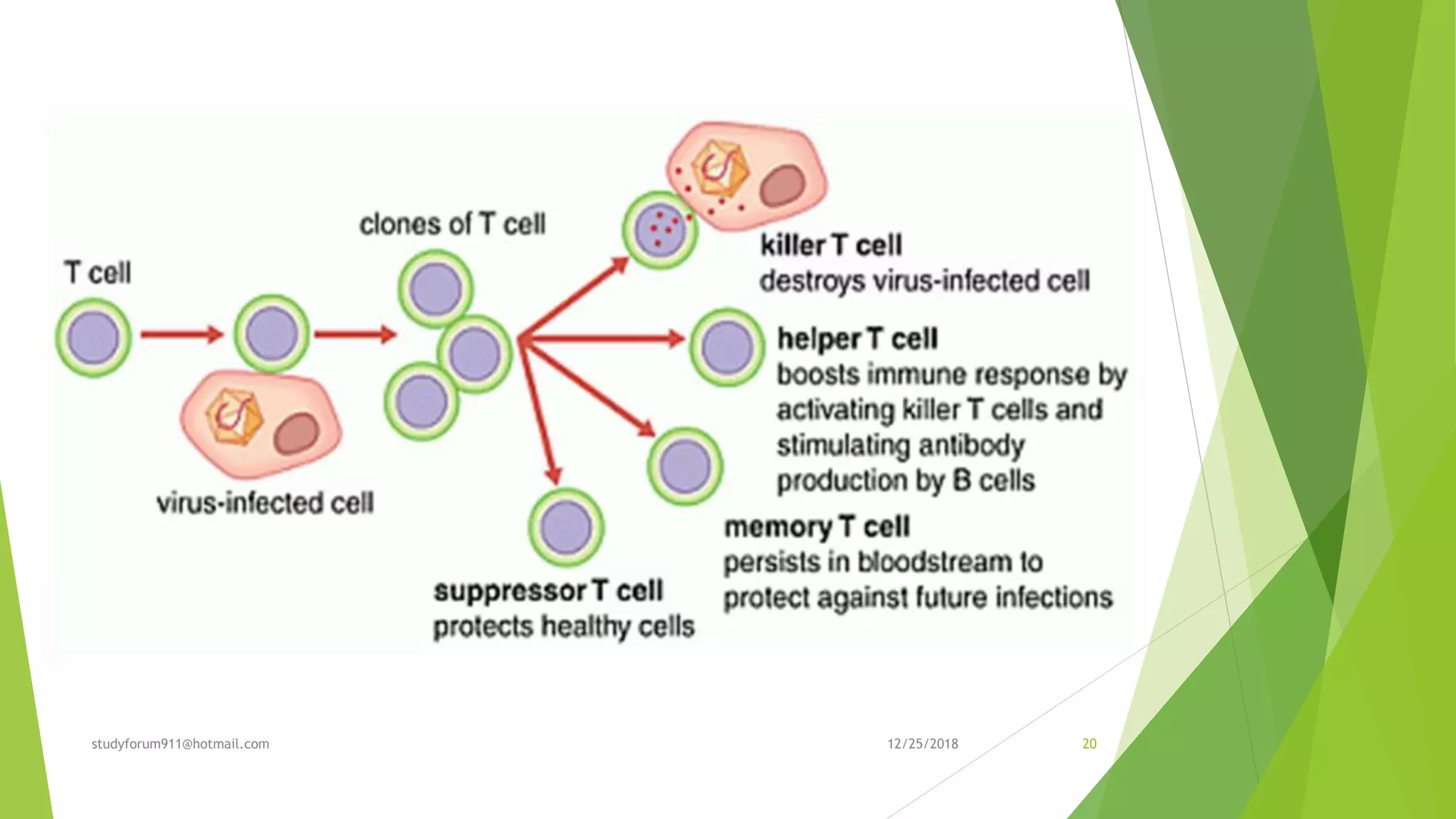
Cell-mediated immunity involves T lymphocytes, macrophages, and natural killer cells. It provides defense against viruses, fungi, and some bacteria through these cells, without involving antibodies. When antigens from invading microbes are presented on antigen-presenting cells like macrophages and dendritic cells, helper T cells are activated and stimulate cytotoxic T cells and B cells. Cytotoxic T cells then directly attack and destroy infected cells. Memory T cells also enhance future immune responses. Overall, cell-mediated immunity protects against intracellular pathogens through cellular immune responses.