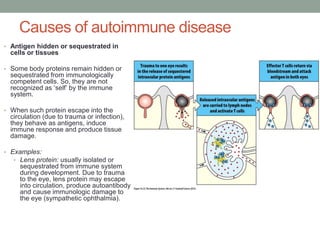
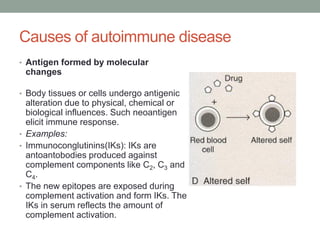
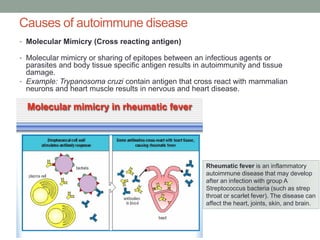
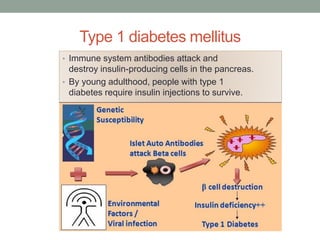
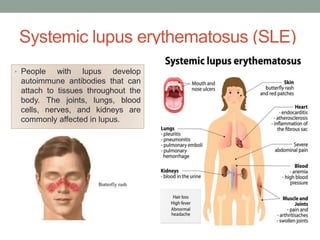
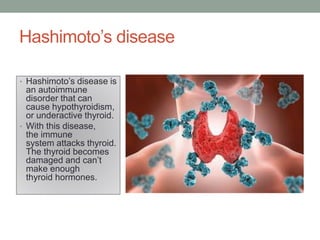
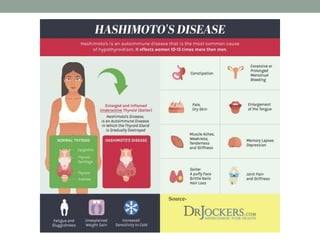
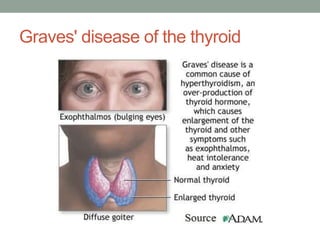
Autoimmunity is a condition where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells, leading to various autoimmune diseases classified as organ-specific or systemic. Common examples include type 1 diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, and Hashimoto's thyroiditis, each with distinct effects on the body. Factors contributing to autoimmunity include hidden antigens, molecular changes in tissues, and molecular mimicry from infectious agents.