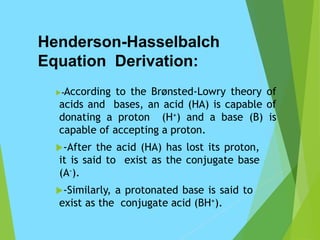
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation describes the relationship between pH and the concentrations of an acid and its conjugate base at equilibrium. Specifically, it shows that pH equals the acid's pKa plus the logarithm of the concentration of the conjugate base divided by the concentration of the acid. This equation is useful for estimating pH in buffer solutions and calculating the isoelectric point of proteins. It is derived from acid/base equilibrium chemistry and the acid dissociation constant Ka.

![The Henderson hasselbalch equation for
acid is :-
pH = pKa + log [ Aˉ ]
[HA]
Here, pKa= -log(Ka)
where Ka is the acid dissociation constant,
that is pKa= -log [H3O+][A-]
[HA]
for the non-specific Brønsted acid-base
reaction:
A-
HA + H20 + H3O+
( Acid ) ( Conjugate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hhequation-210222040454/85/HH-equation-3-320.jpg)
![The Henderson Hasselbalch Equation for
base is :
pOH = pKb + log [ BH+ ]
[B]
where BH+ denotes the conjugate acid of
the corresponding base B.
B + H2O+ BH + OH-
(Base ) (Conjugate acid)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hhequation-210222040454/85/HH-equation-4-320.jpg)


![Acetate is the conjugate base of acetic acid.
Acetic acid and acetate are a conjugate
acid/base pair. We can describe this
relationship with an equilibrium constant:
Ka = [H3O+][A-]
[HA]
Taking the negative log of both sides of the
equation gives
-logKa = -log [H3O+][A-]
[HA]
or, -logKa = -log [H3O+] + (-log [A-] )
[HA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hhequation-210222040454/85/HH-equation-8-320.jpg)
![By definition,
pKa = -logKa and pH = -log[H3O+],
so
pka=pH – log [A-]
[HA]
This equation can then be rearranged to
give the Henderson-Hasselbalch
equation:
pH = pKa + log [A-]
[HA]
= pKa + log [conjugate
base]
[acid]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hhequation-210222040454/85/HH-equation-9-320.jpg)
![Estimating blood
pH
A modified version of the Henderson–
Hasselbalch equation can be used to relate
the pH of blood to constituents of the
bicarbonate buffering system.
pH = pKaH2CO3 + log [HCO3
-]
[H2CO3]
, where:
-pKa H2CO3 is the acid dissociation constant of
carbonic
acid. It is equal to 6.1.
[HCO3
-] is the concentration of bicarbonate in the
blood](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hhequation-210222040454/85/HH-equation-10-320.jpg)
