This document discusses buffers, buffer capacity, and buffer equations. It defines a buffer as an aqueous solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base that resists changes in pH when a small amount of strong acid or base is added. The key points are:
- Buffers work by maintaining an equilibrium between an acid and its conjugate base
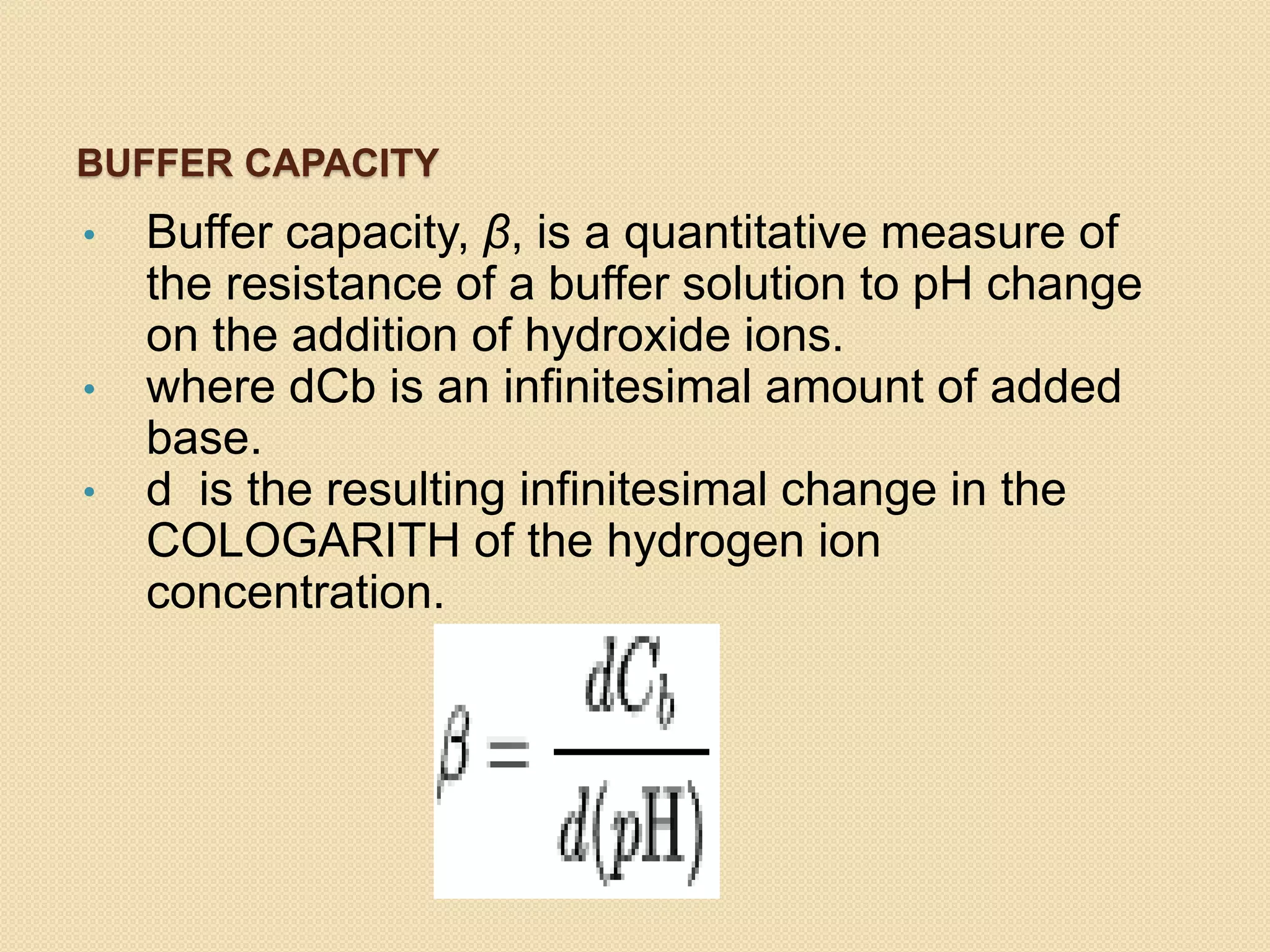
- Buffer capacity is a measure of a buffer's ability to resist pH changes upon addition of acid or base
- The buffer equation relates pH, pKa, and relative concentrations of the acid and conjugate base
- Buffers have important applications in drug formulations, fermentation, blood plasma, and more to maintain stable and optimal pH levels.




![BUFFER EQUATION
• Buffer capacity is the capacity of a buffer solution to
resist change in its pH. The equation is given by, pH =
pKa + log [Salt] / [Acid]
• The pH of any acidic buffer solution is always less than
7 and the pH of any basic buffer solution is always
greater than 7.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofbuffersbuffersequationandbuffercapacity-220219070932/75/Application-of-buffers-buffers-equation-and-buffer-capacity-6-2048.jpg)