This document discusses biological buffers and acid-base balance in the human body. It covers:
1) Definitions of acids, bases, and pH. Buffers resist changes in pH when acids or bases are added.
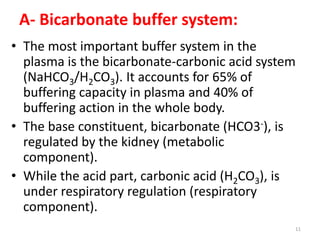
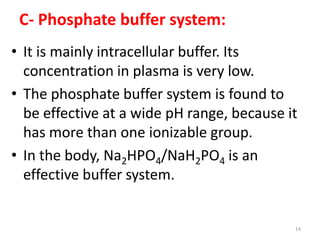
2) The major buffer systems in the body are bicarbonate-carbonate and phosphate. Bicarbonate buffering is the most important for maintaining pH between 7.38-7.42.
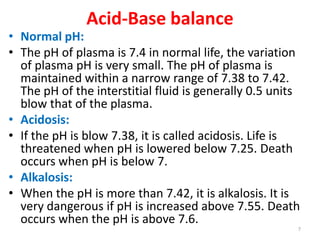
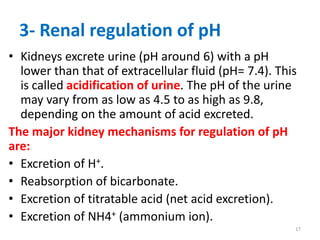
3) The body regulates pH through buffers, respiration, and renal excretion of acids and bases. Respiration controls carbonic acid levels while the kidneys regulate bicarbonate.


![• Acidity of a solution and pH:
• The acidity of a solution is measured by
noting the hydrogen ion concentration in the
solution.
• pH = log 1/[H+]
• Thus, the pH value is inversely proportional
to the acidity. Lower the pH, higher the
acidity or hydrogen ion concentration while
higher the pH, the acidity is lower. The pH 7
indicates the neutral pH.
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec9-level4-debiologicalbuffer-130202064553-phpapp01/85/Lec-9-level-4-de-biological-buffer-3-320.jpg)