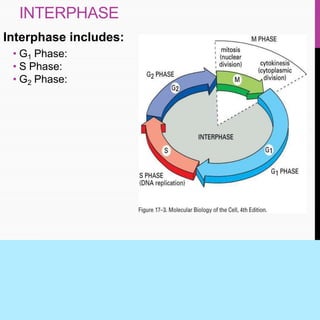
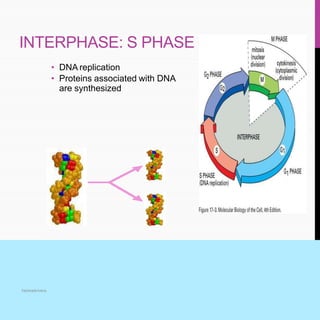
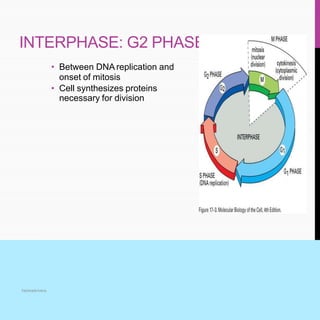
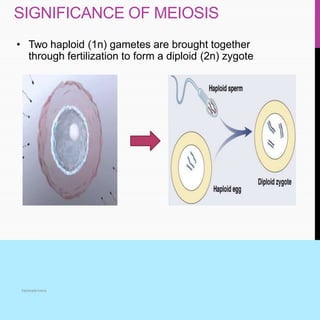
The document summarizes key aspects of the cell cycle, including its main phases (interphase consisting of G1, S, G2 phases and the mitosis phase) and their characteristics. It also discusses meiosis, its two divisions, and its significance in forming gametes. Control of the cell cycle involves positive regulators like cyclins and CDKs that promote the cycle and negative regulators like Rb and p53 tumor suppressor proteins that inhibit the cycle progression under certain conditions. Checkpoints exist at different phases to ensure replication and chromosome separation are completed before progression.