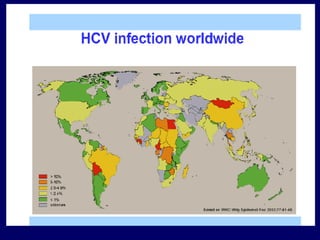
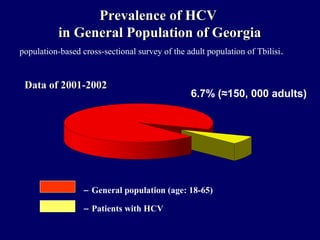
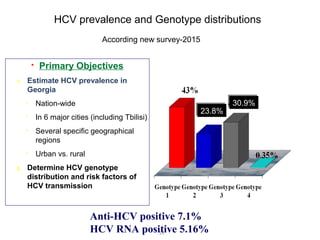
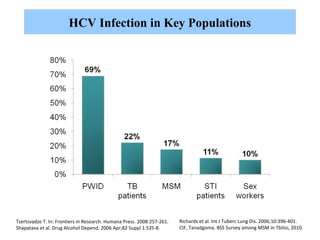
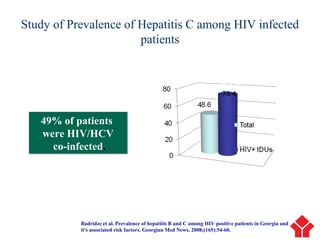
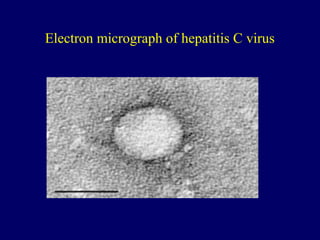
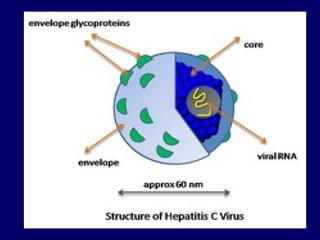
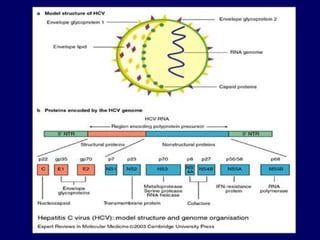
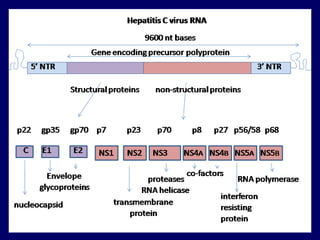
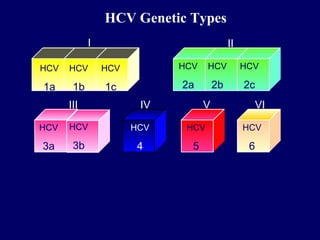
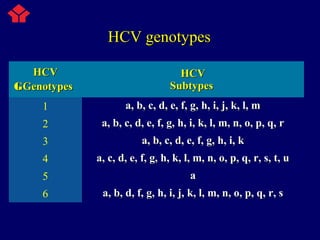
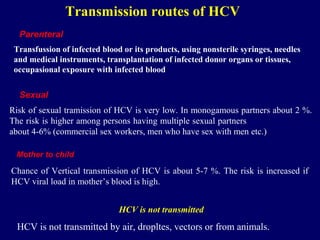
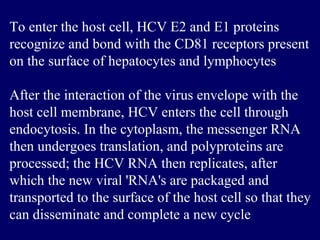
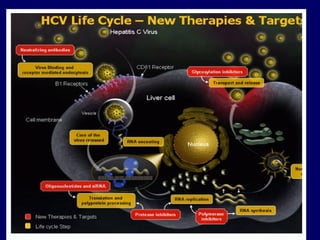
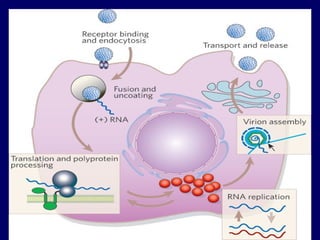
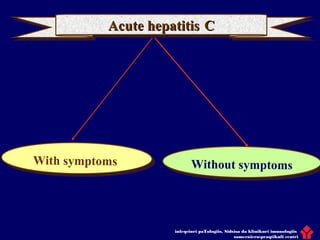
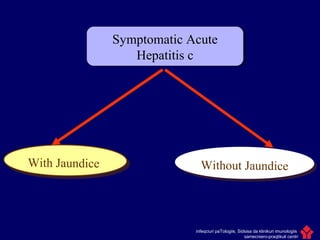
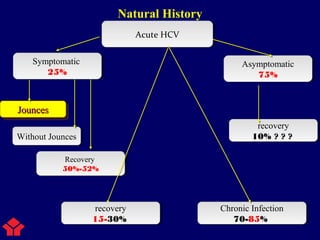
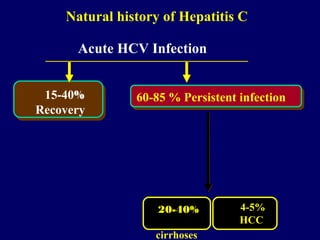
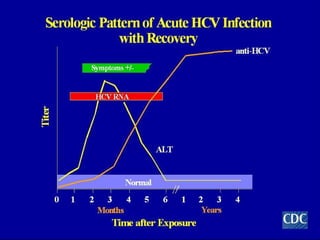
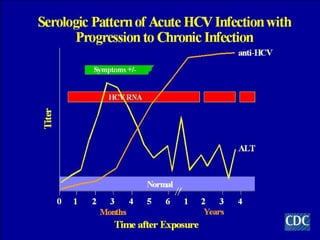
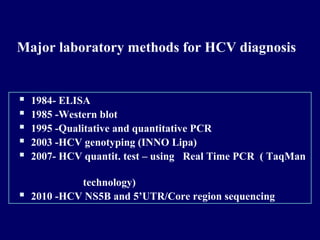
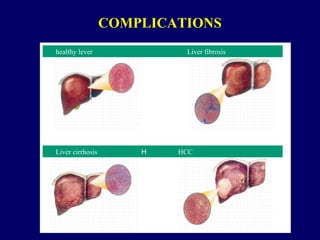
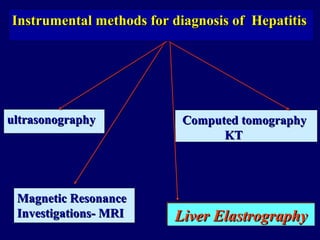
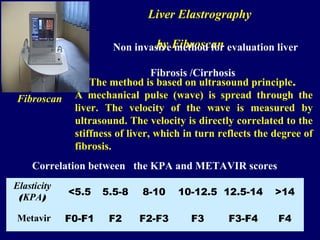
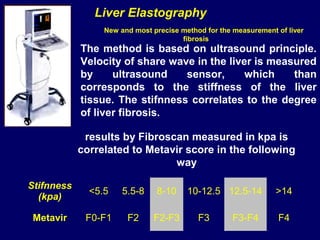
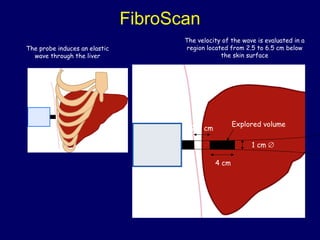
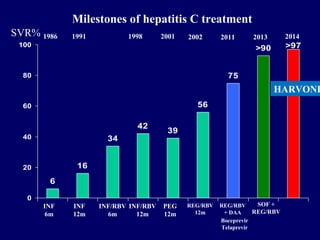
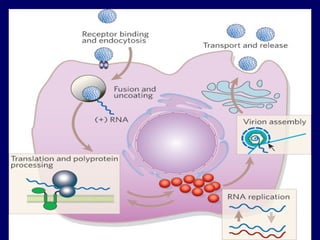
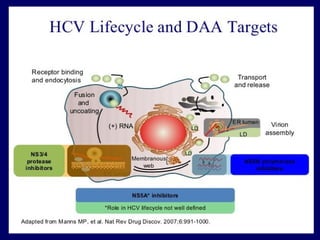
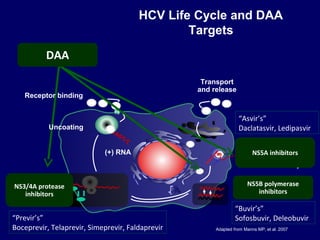
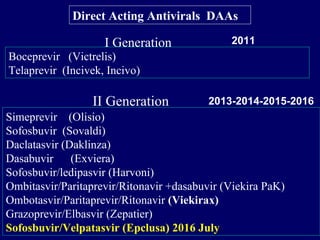
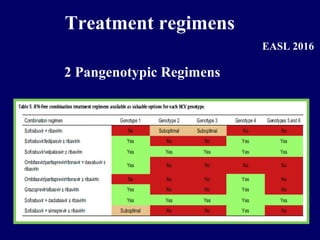
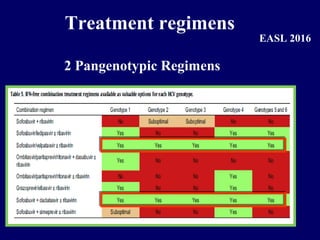
Hepatitis C is a major global public health problem, infecting around 180 million people worldwide. It is a leading cause of liver disease and liver transplants. The hepatitis C virus is a RNA virus that primarily infects liver cells. Around 70-85% of infections become chronic, and 20-40% of chronic infections can lead to severe liver disease like cirrhosis or liver cancer over time. The most common modes of transmission are through blood exposure, though sexual transmission risk is low. There is no vaccine, but effective antiviral treatment exists.