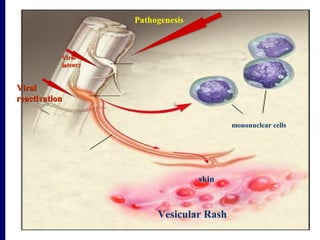
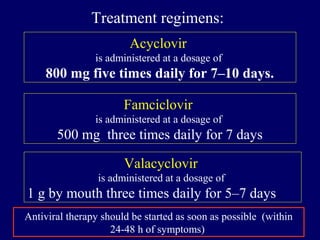
This document discusses human herpesviruses, focusing on varicella zoster virus which causes shingles (herpes zoster) and chickenpox. It describes how varicella zoster virus can reactivate after a latent infection to cause shingles, presenting as a painful skin rash localized to specific dermatomes. Complications of shingles can include postherpetic neuralgia, zoster ophthalmicus affecting the eye, and Ramsay Hunt syndrome impacting the ear and facial nerve. Advanced age is a risk factor for shingles as cellular immunity declines over time.