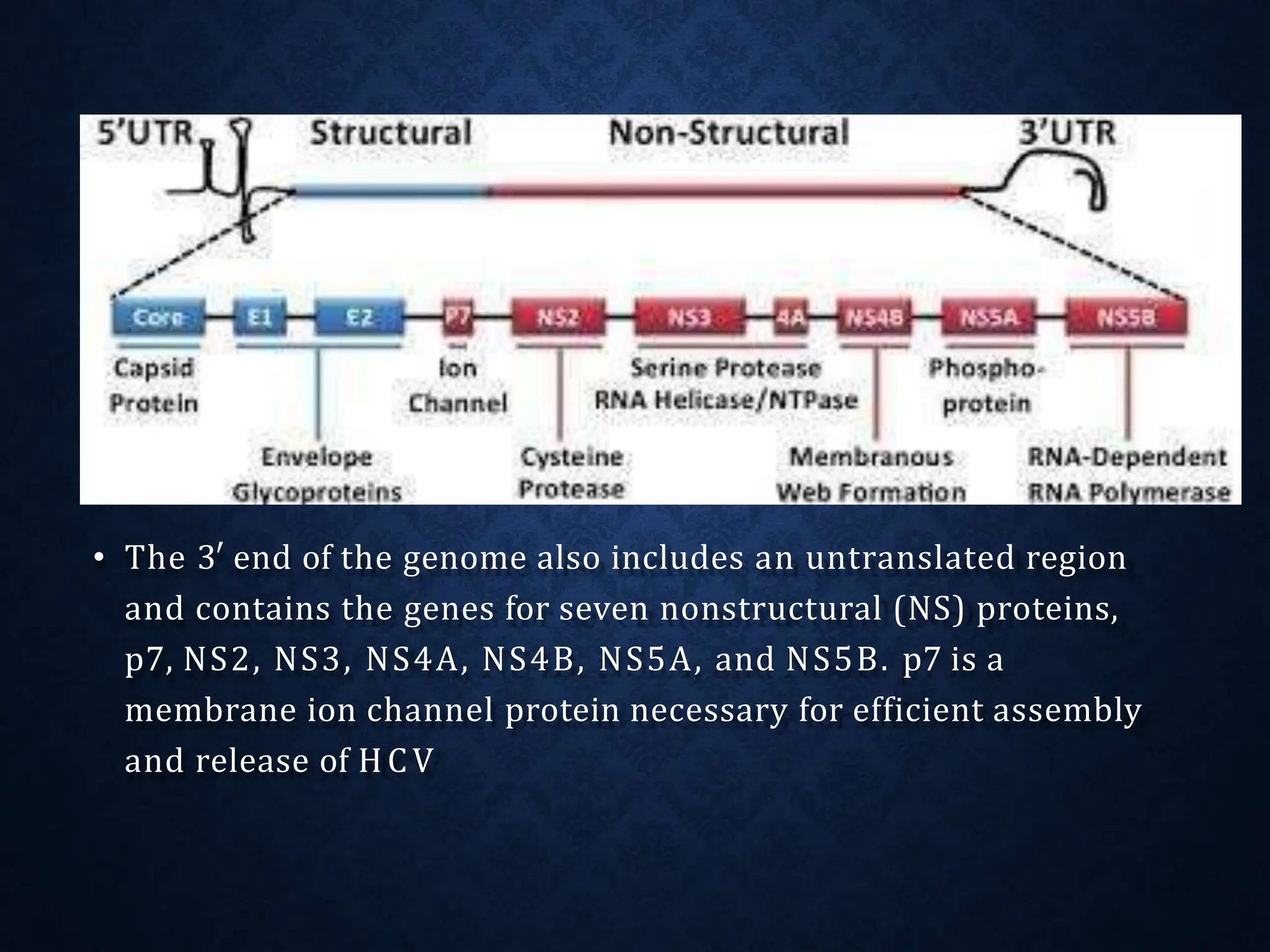
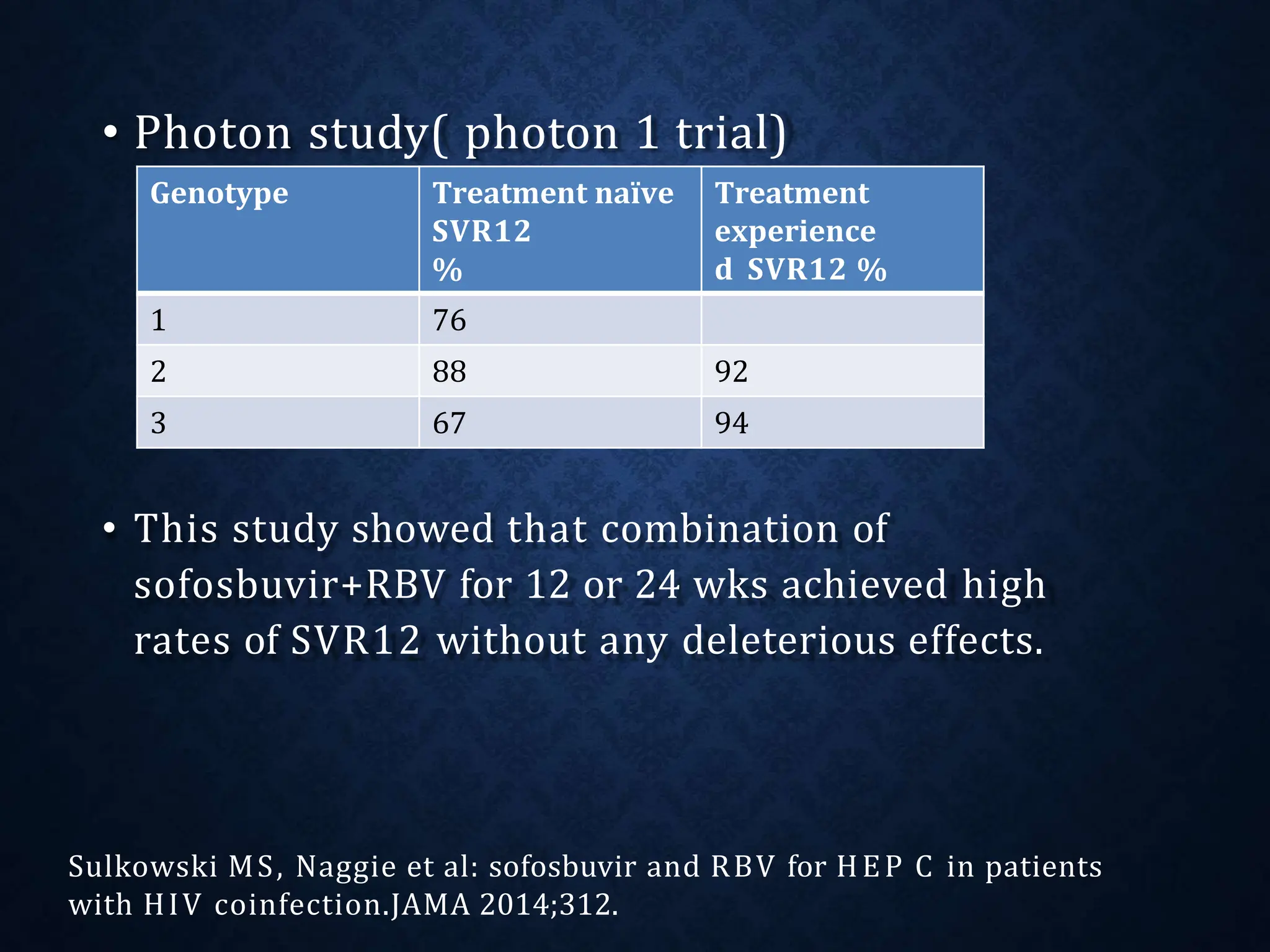
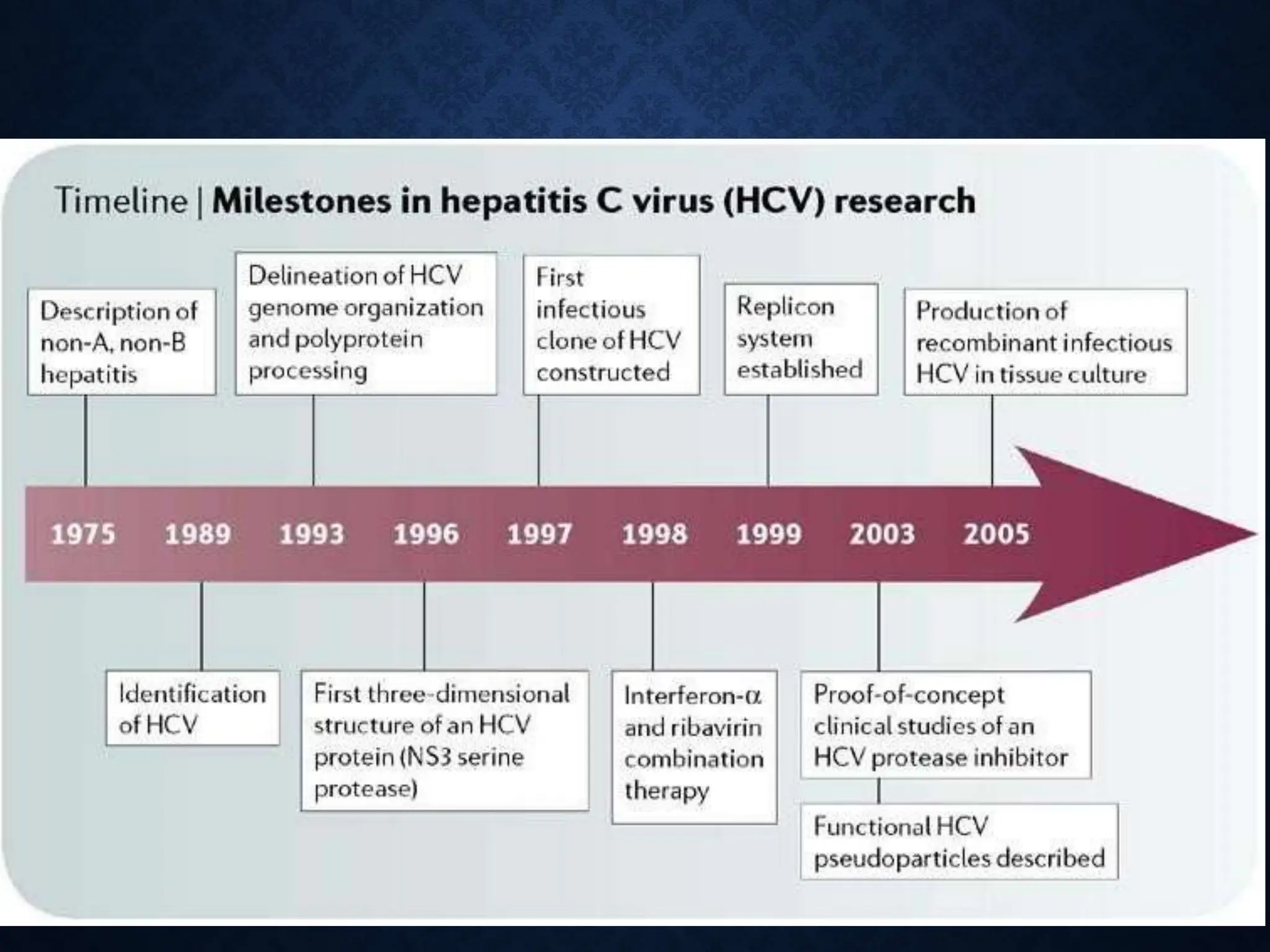
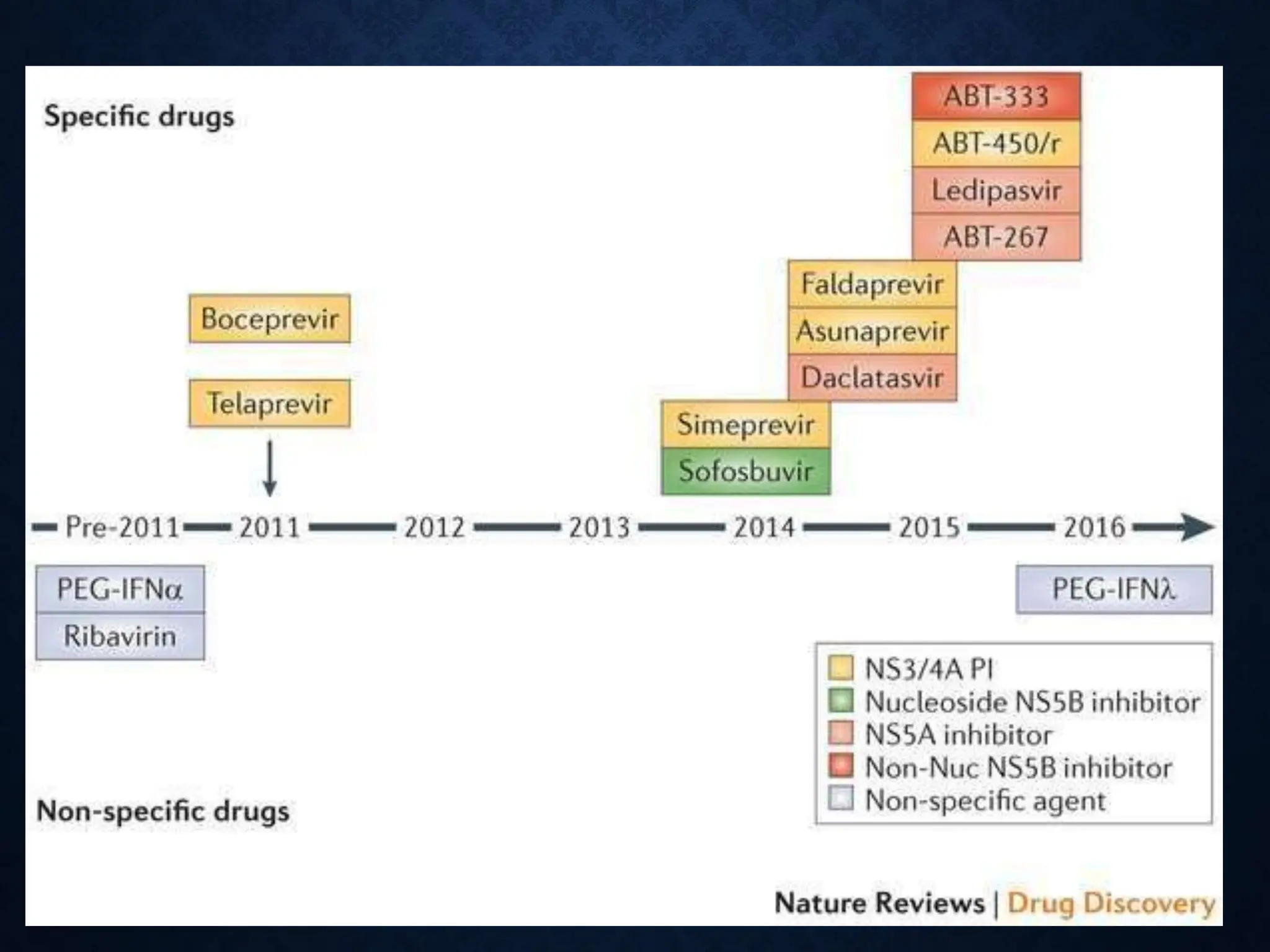
The document discusses hepatitis C virus (HCV), including its structure, genome, genotypes, epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Some key points:
- HCV is a single-stranded RNA virus of the Flaviviridae family with a genome encoding both structural and nonstructural proteins.
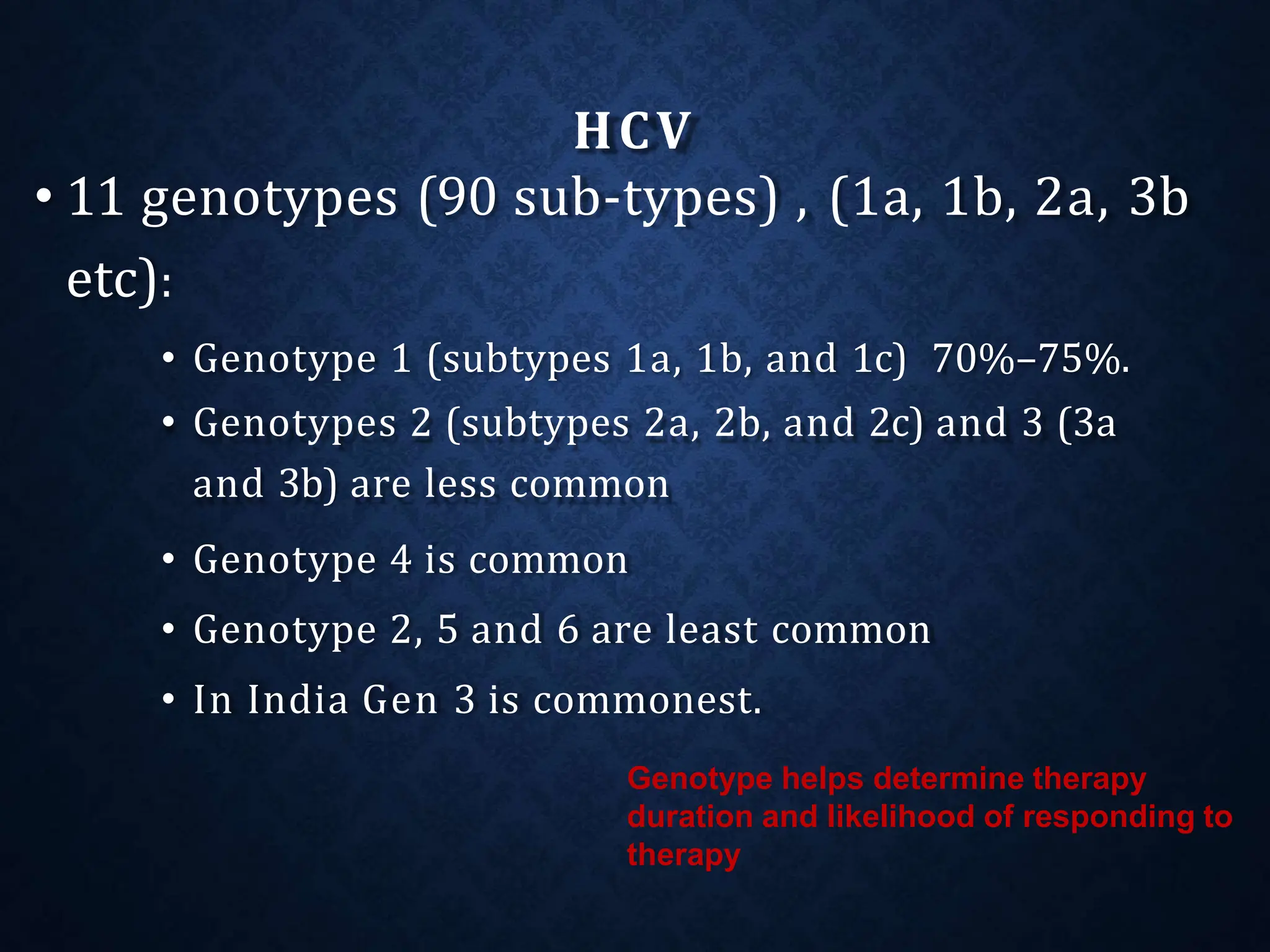
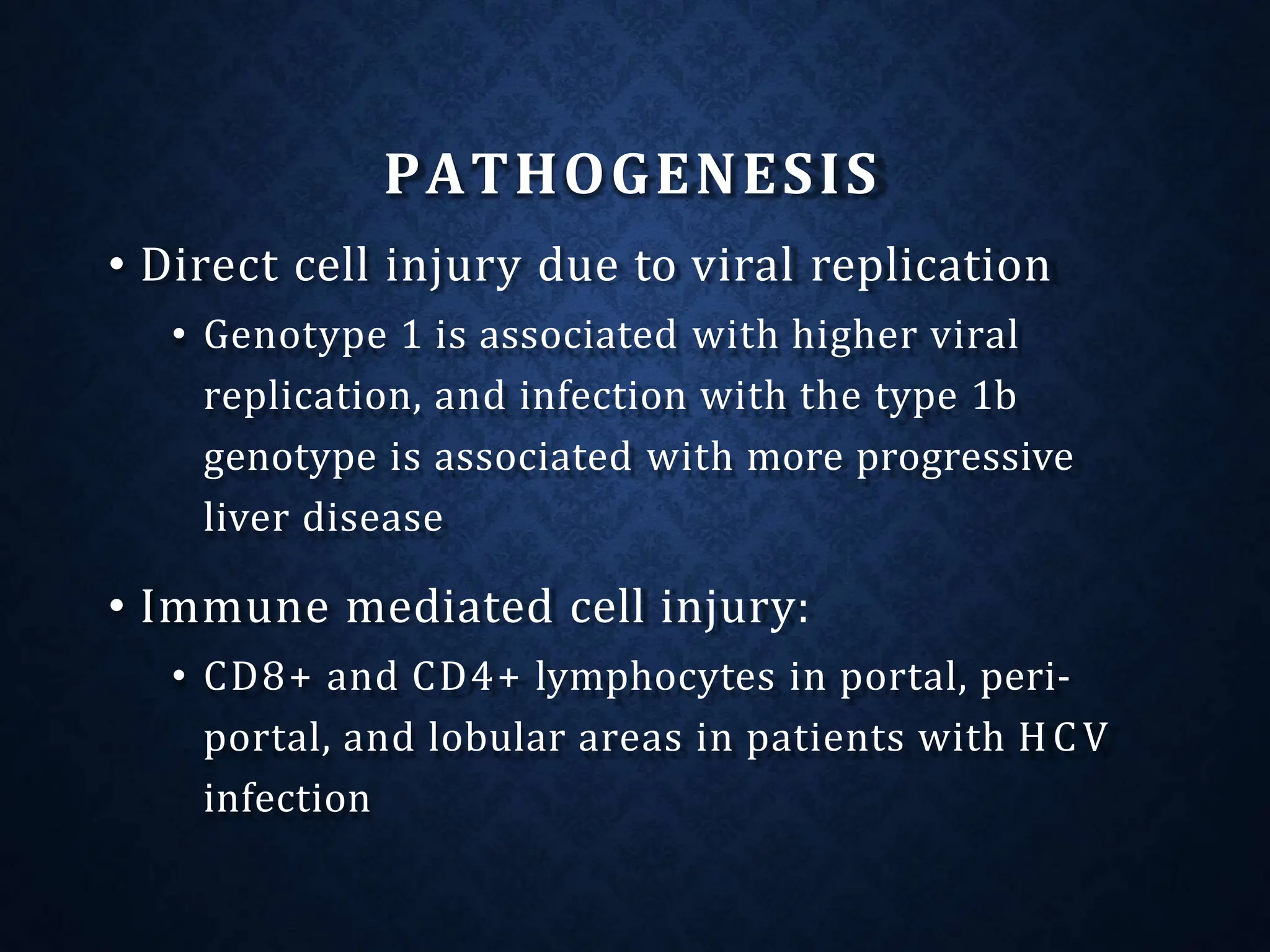
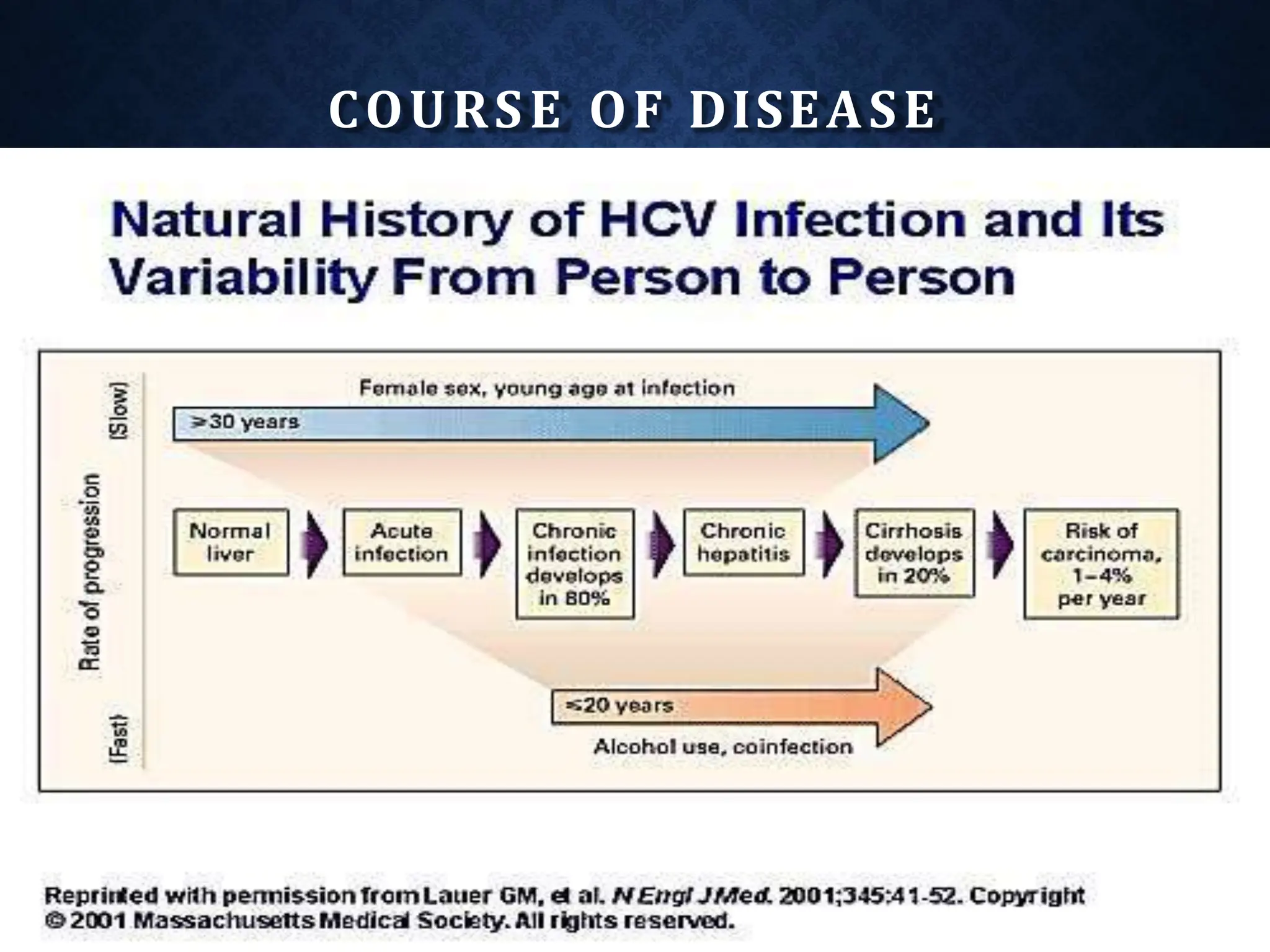
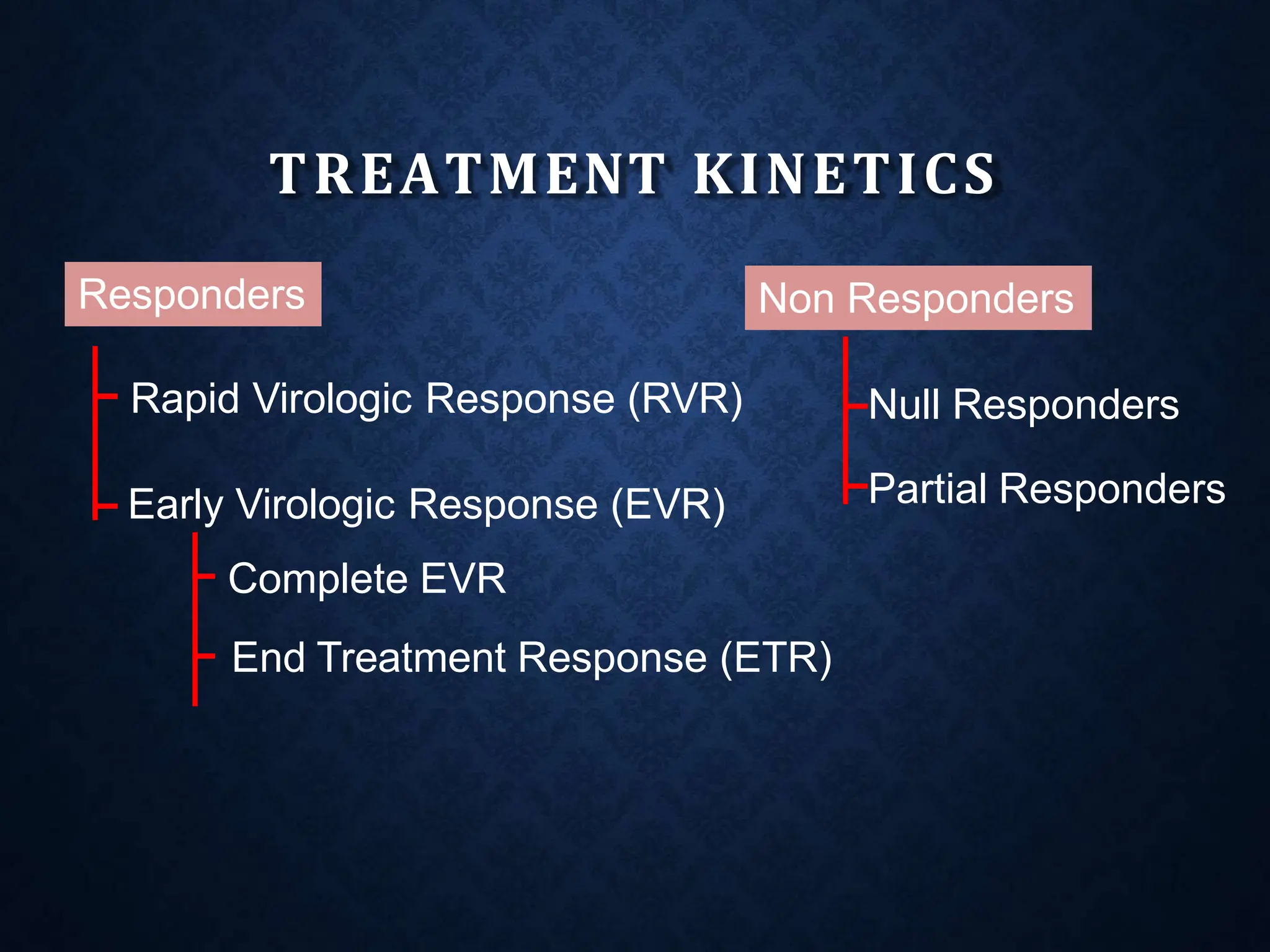
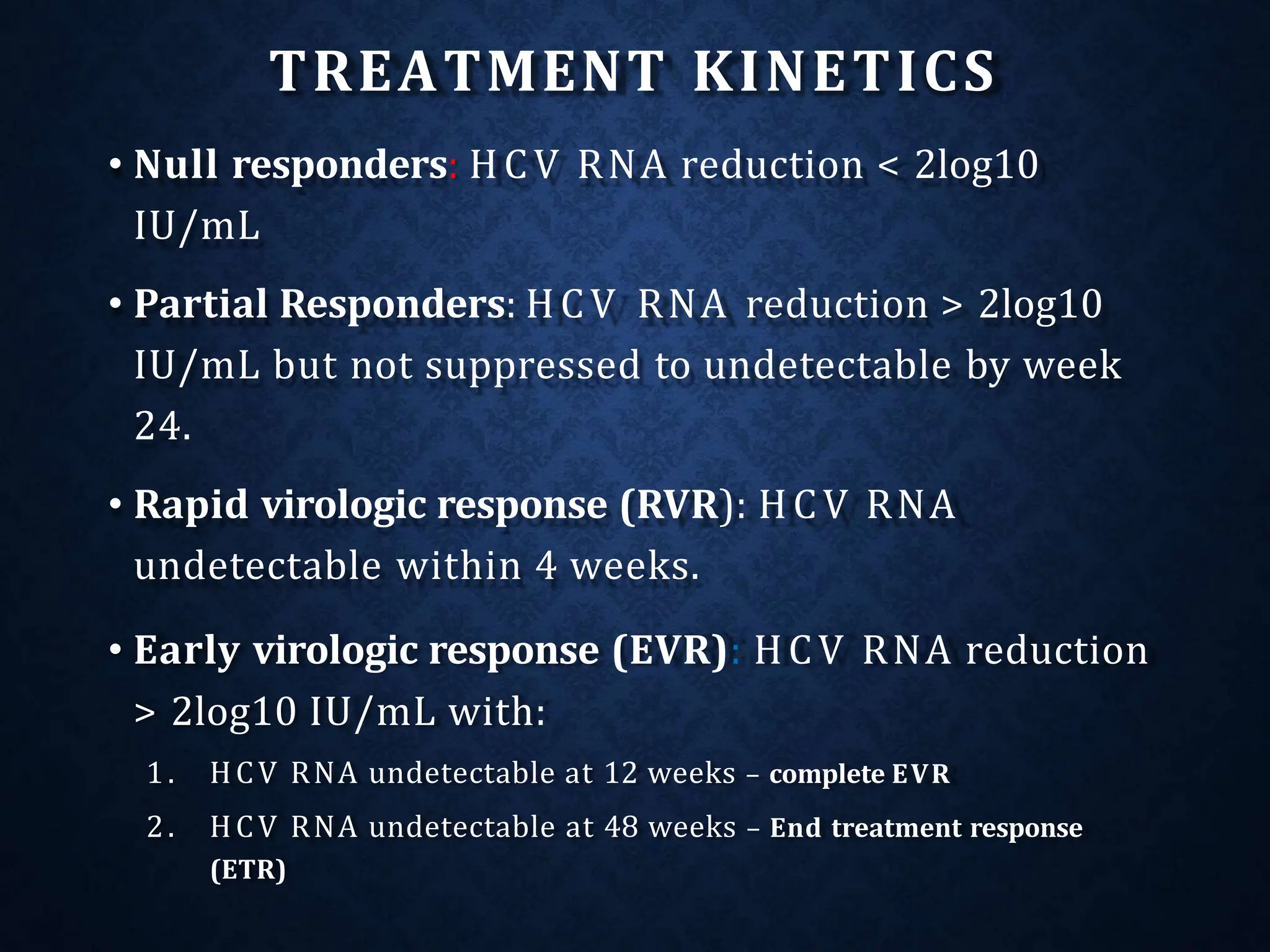
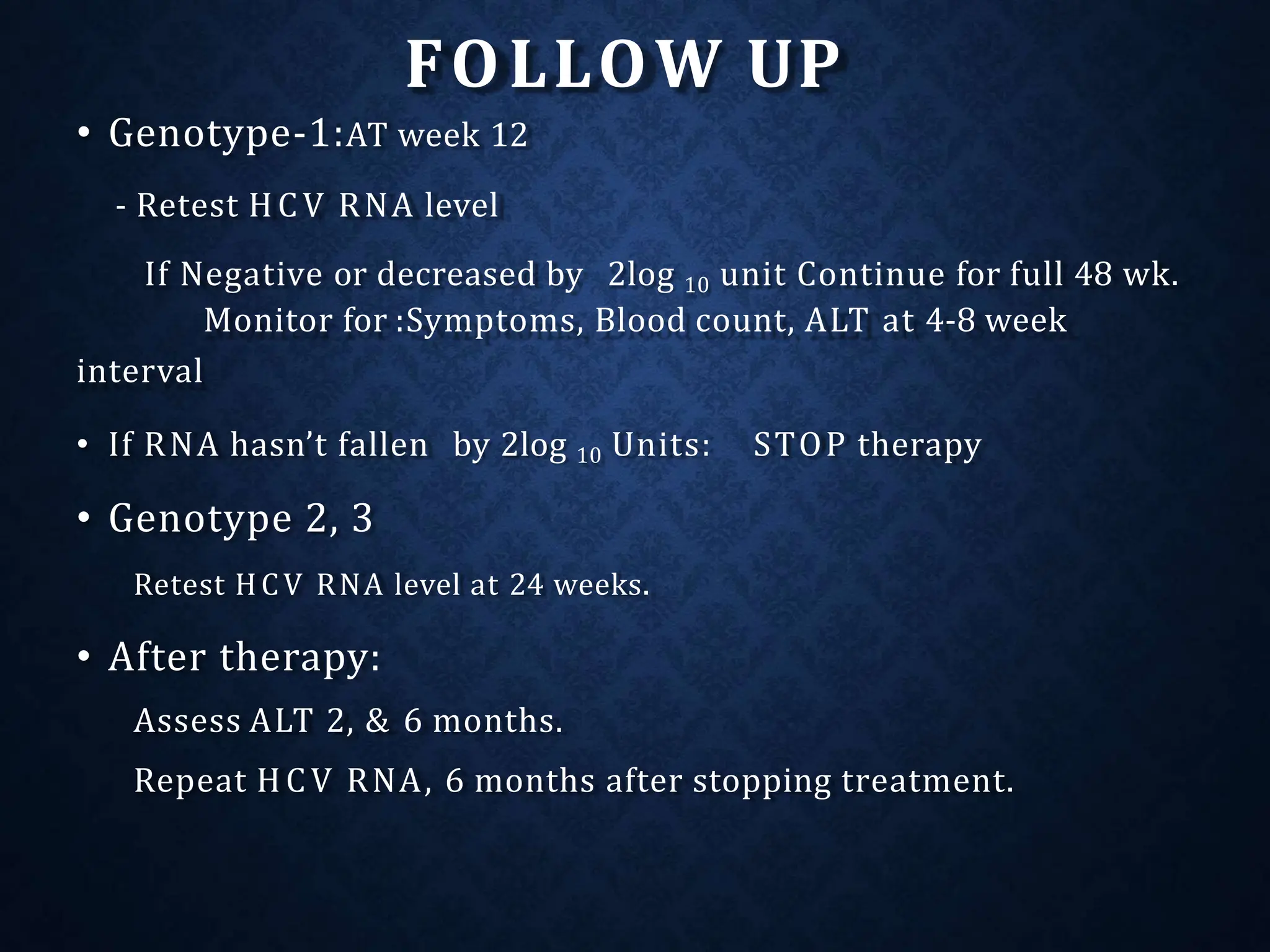
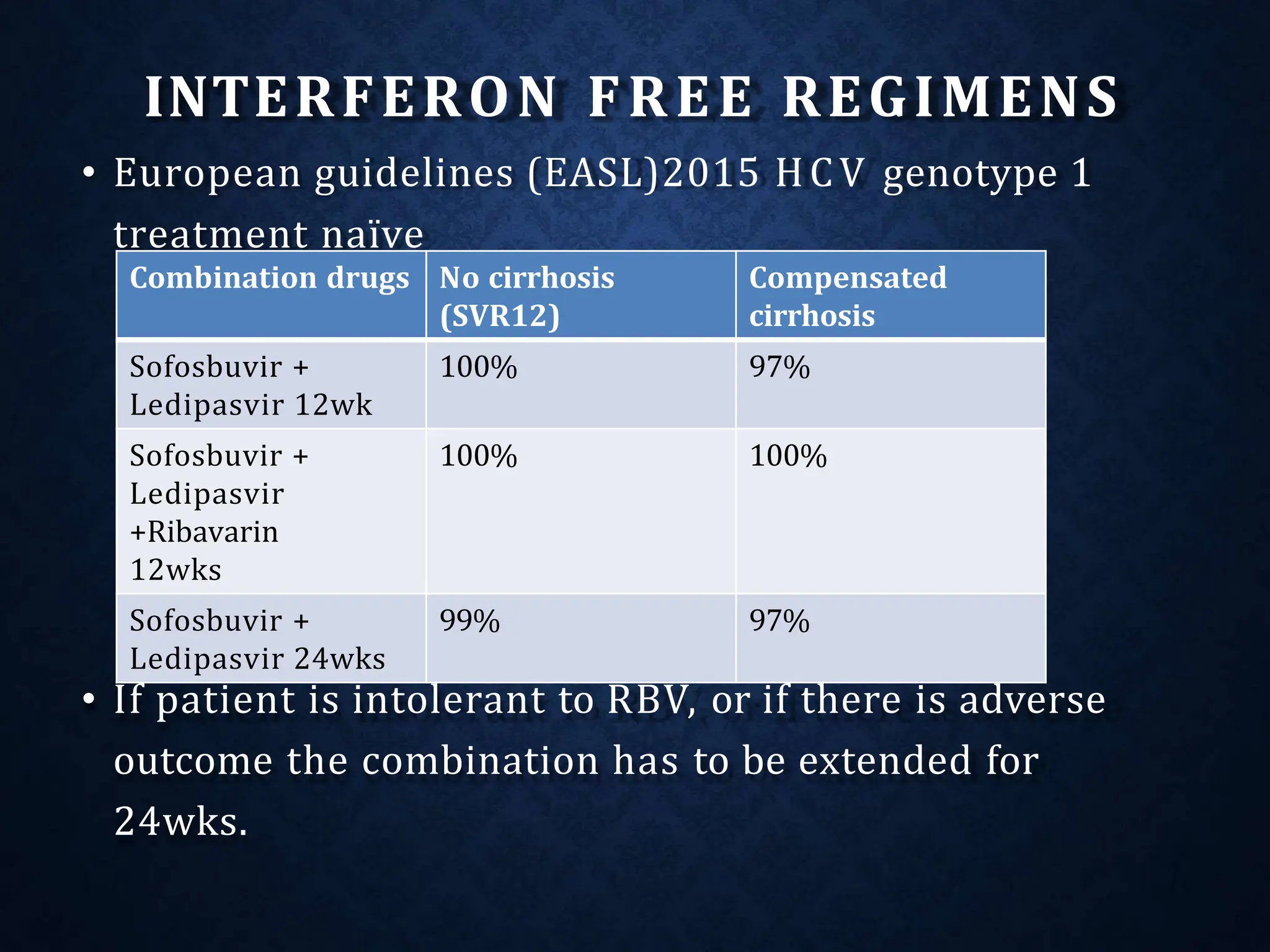
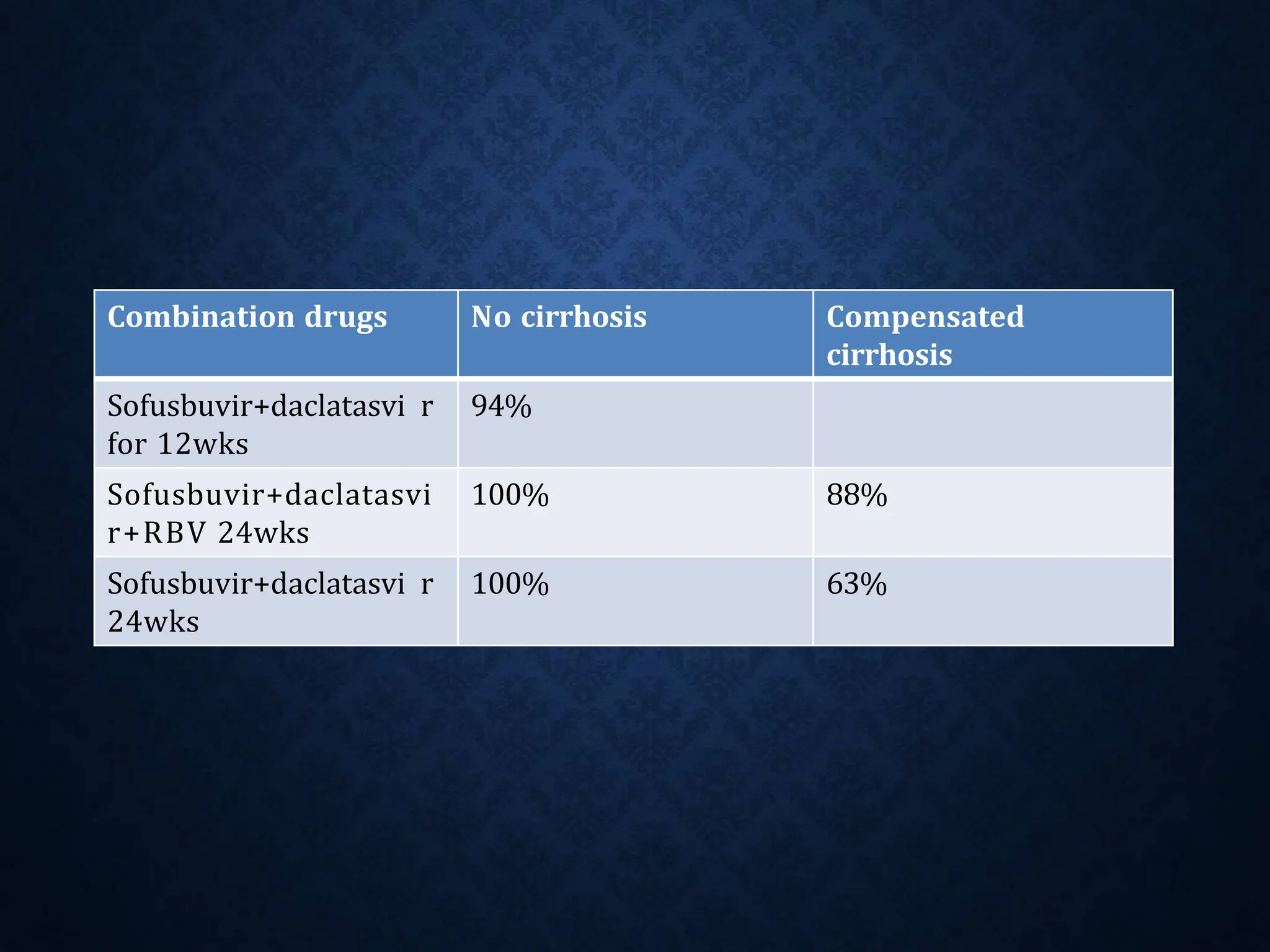
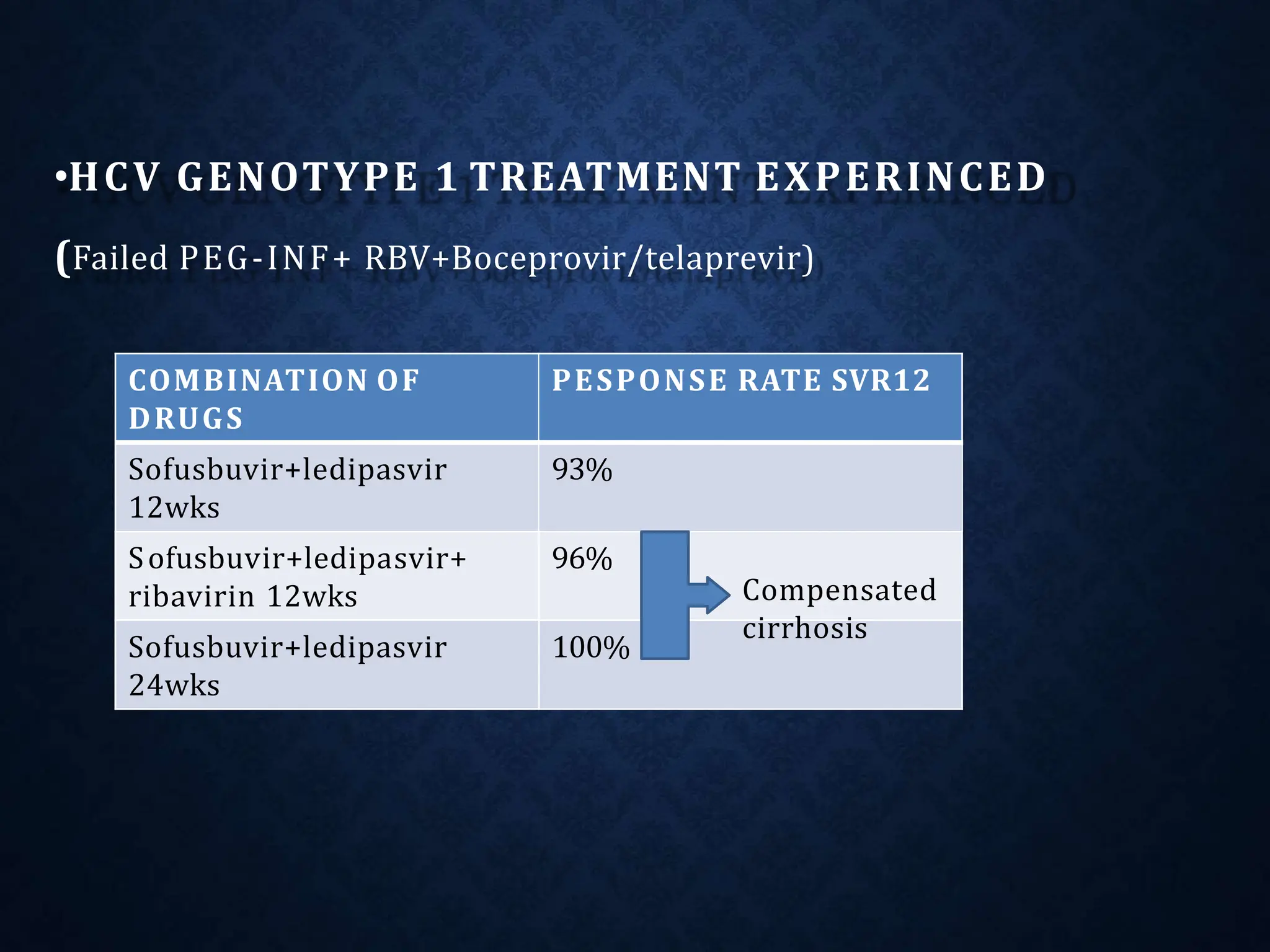
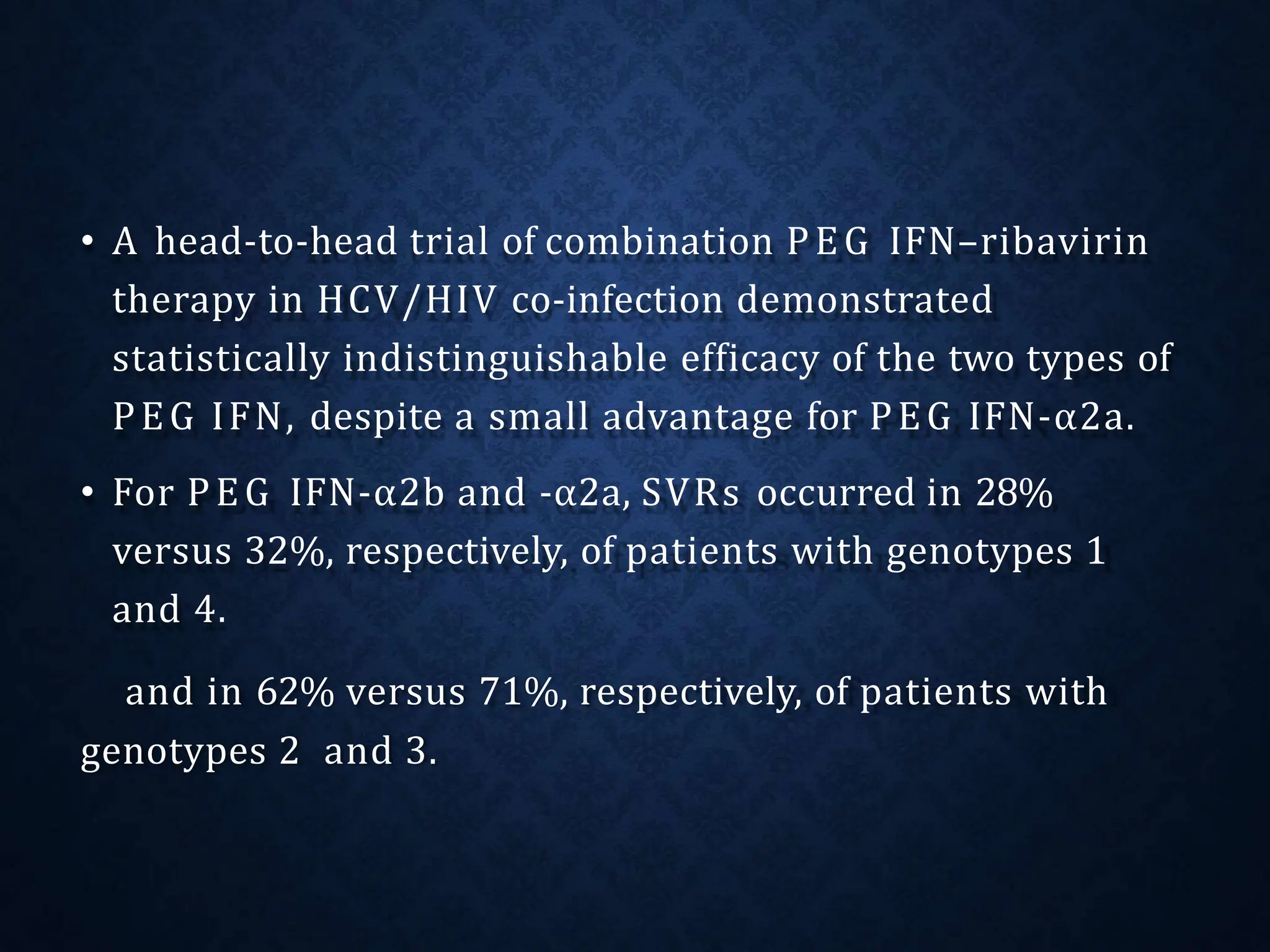
- It exists as different genotypes globally, with genotypes 1, 2, 3 being most common. Genotype helps determine treatment duration and response.
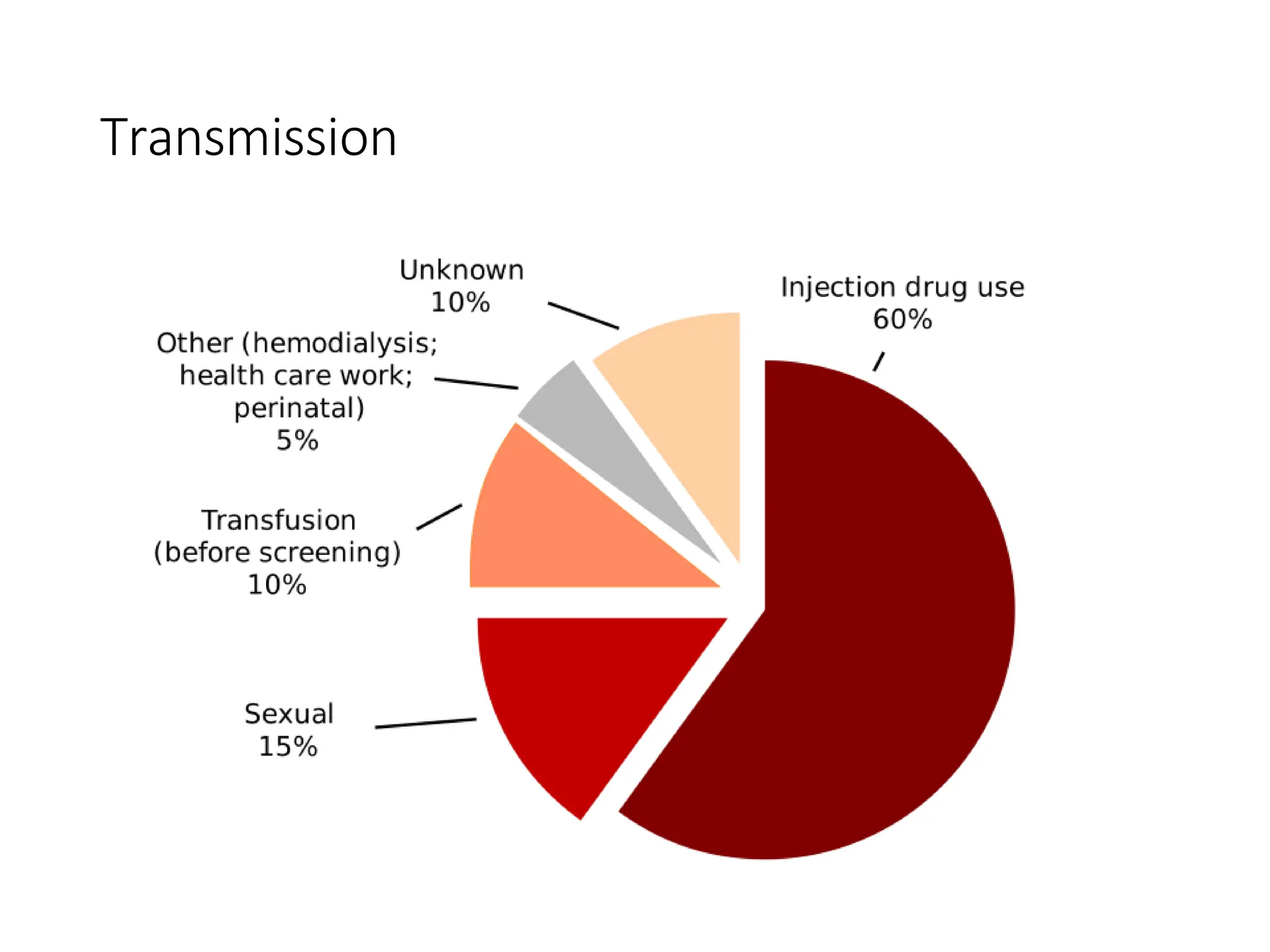
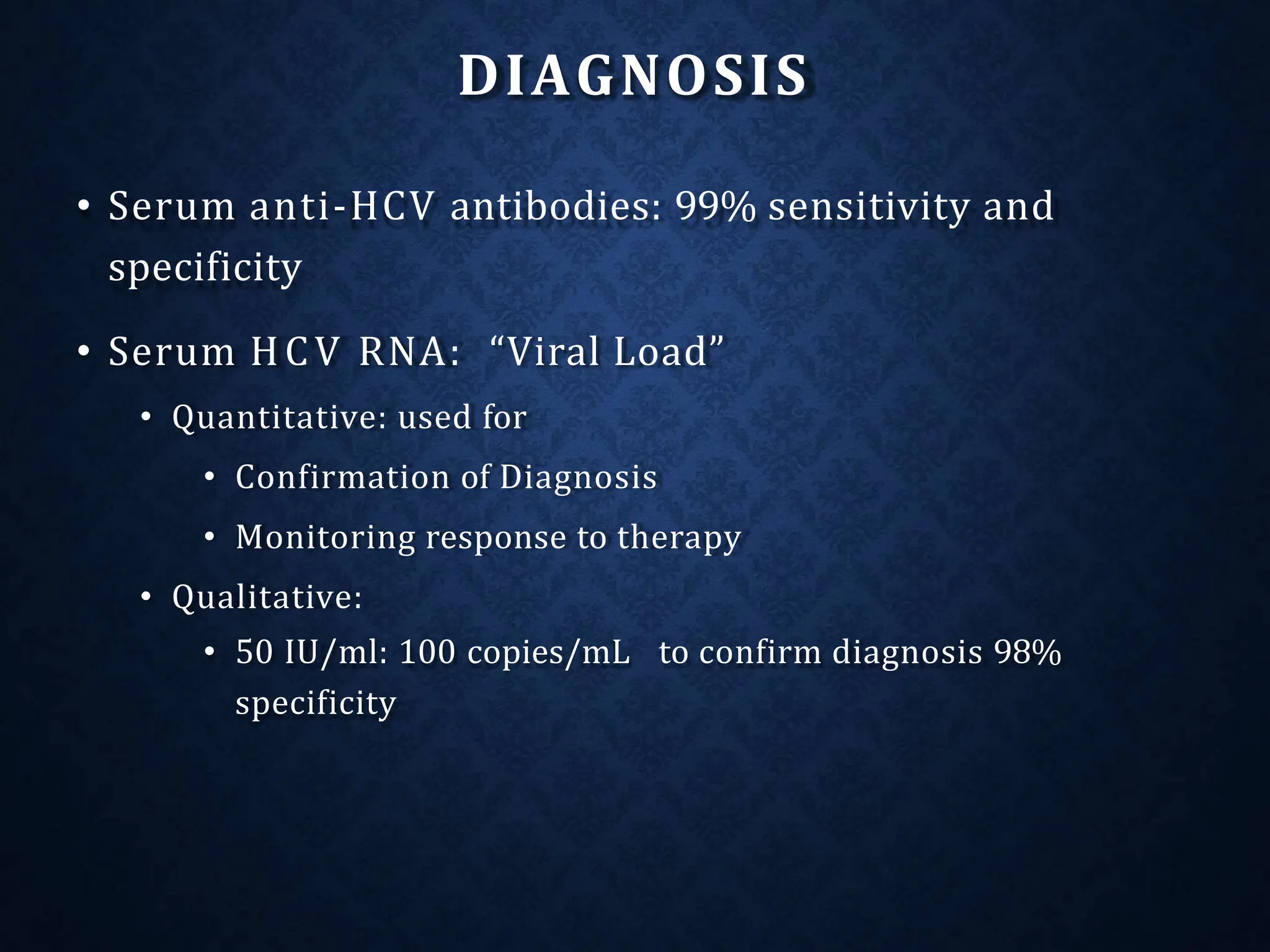
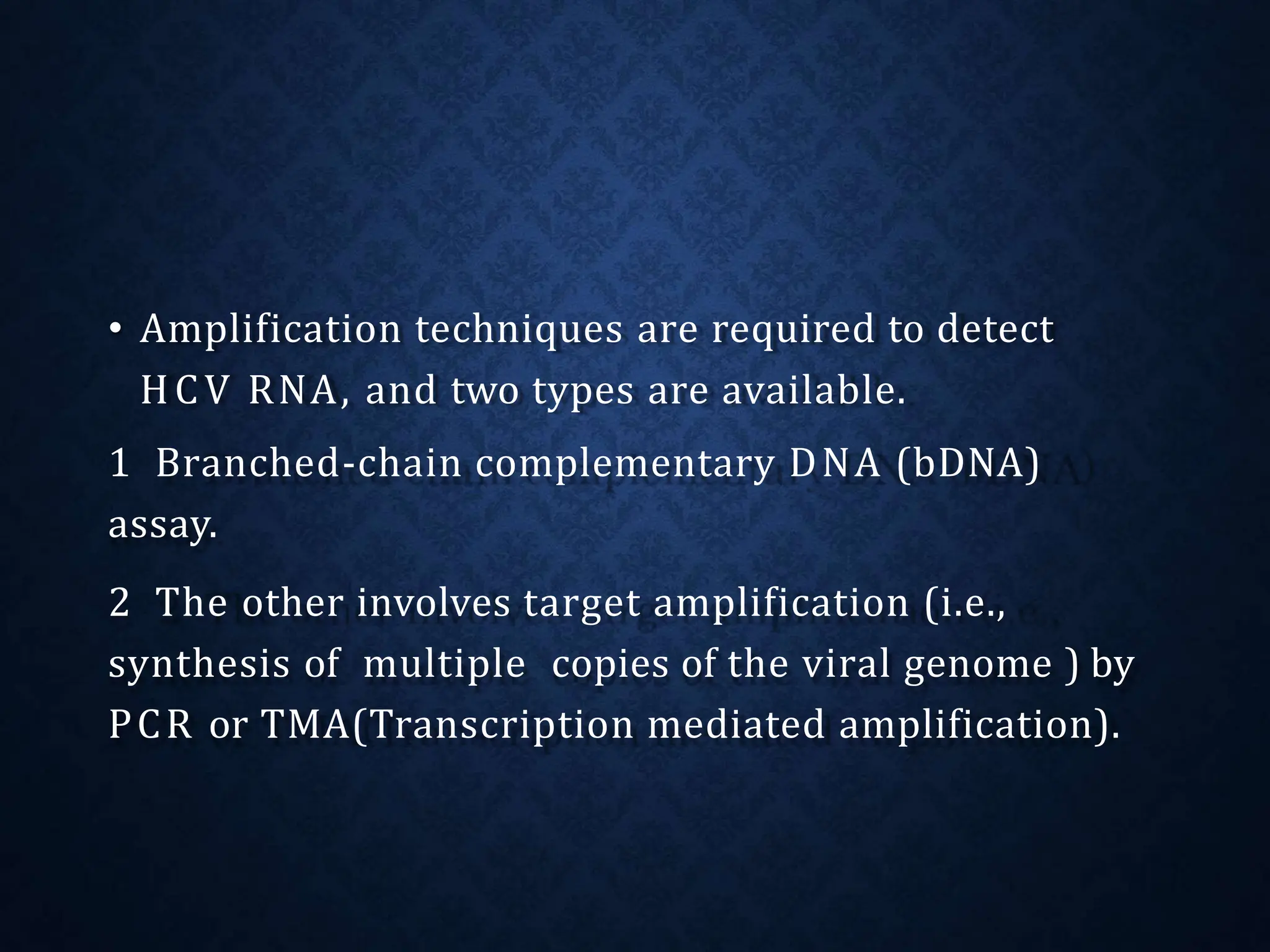
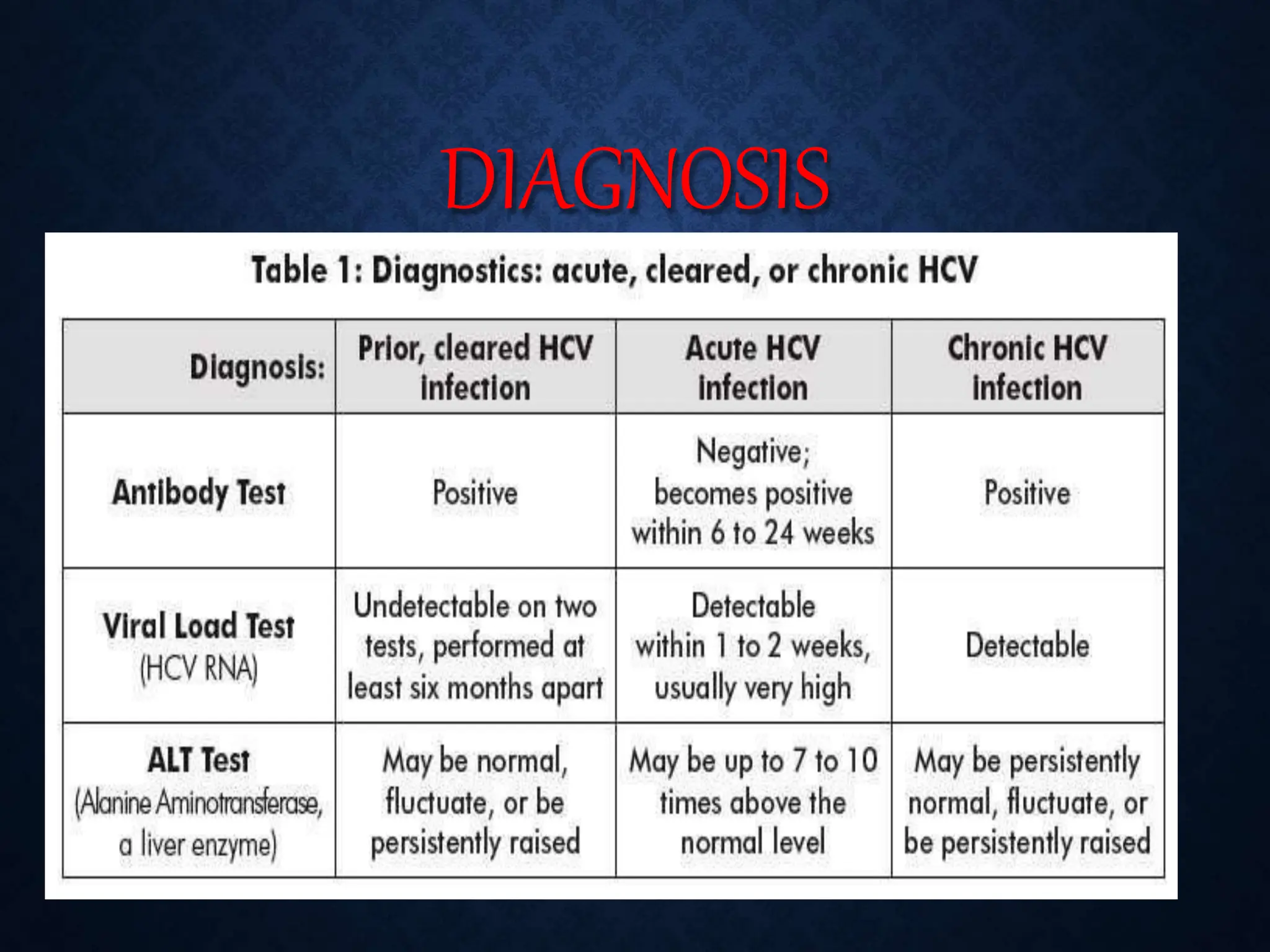
- HCV is a major cause of liver disease worldwide and is transmitted through blood exposure. Diagnosis involves HCV antibody and RNA testing.
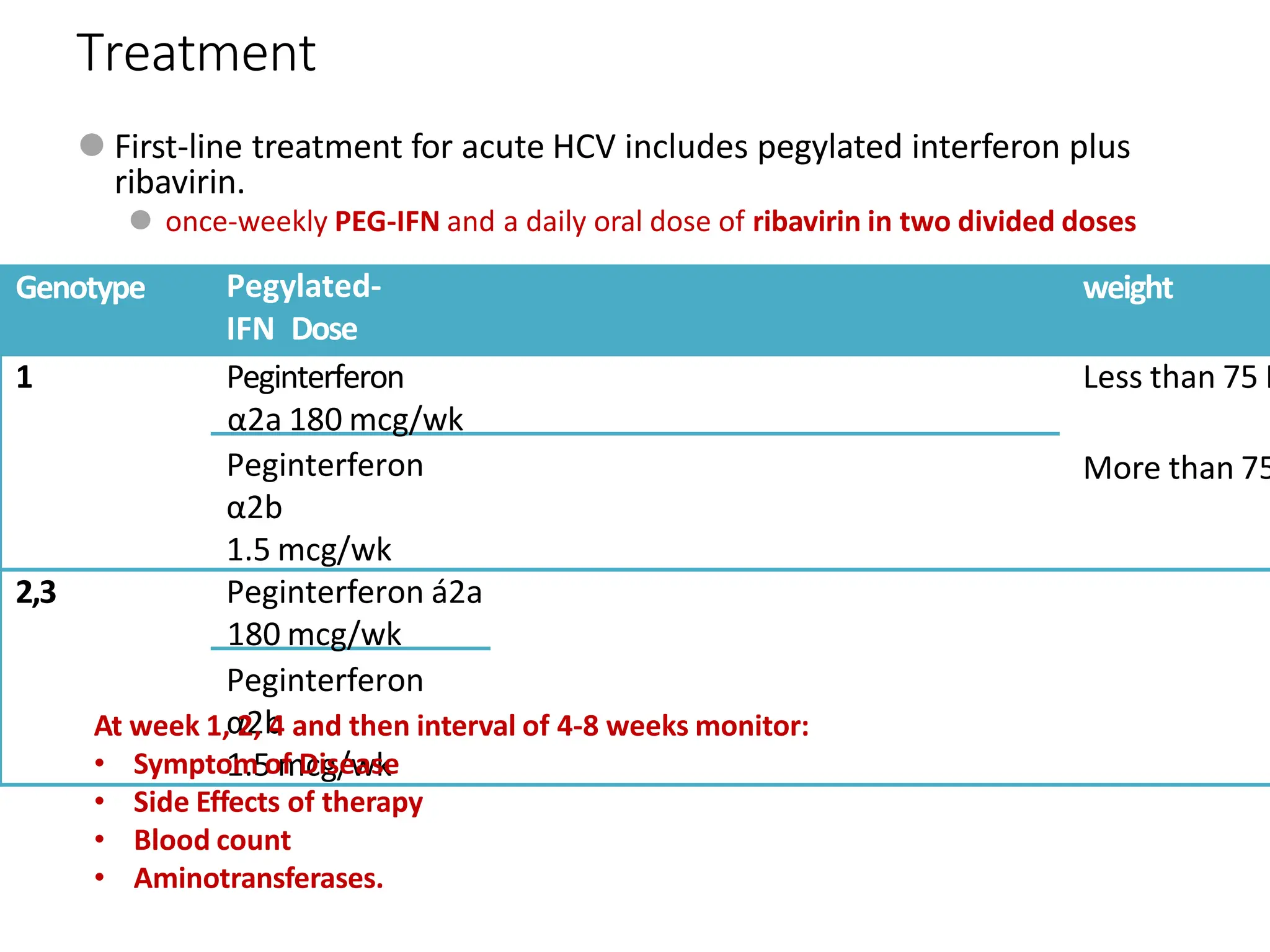
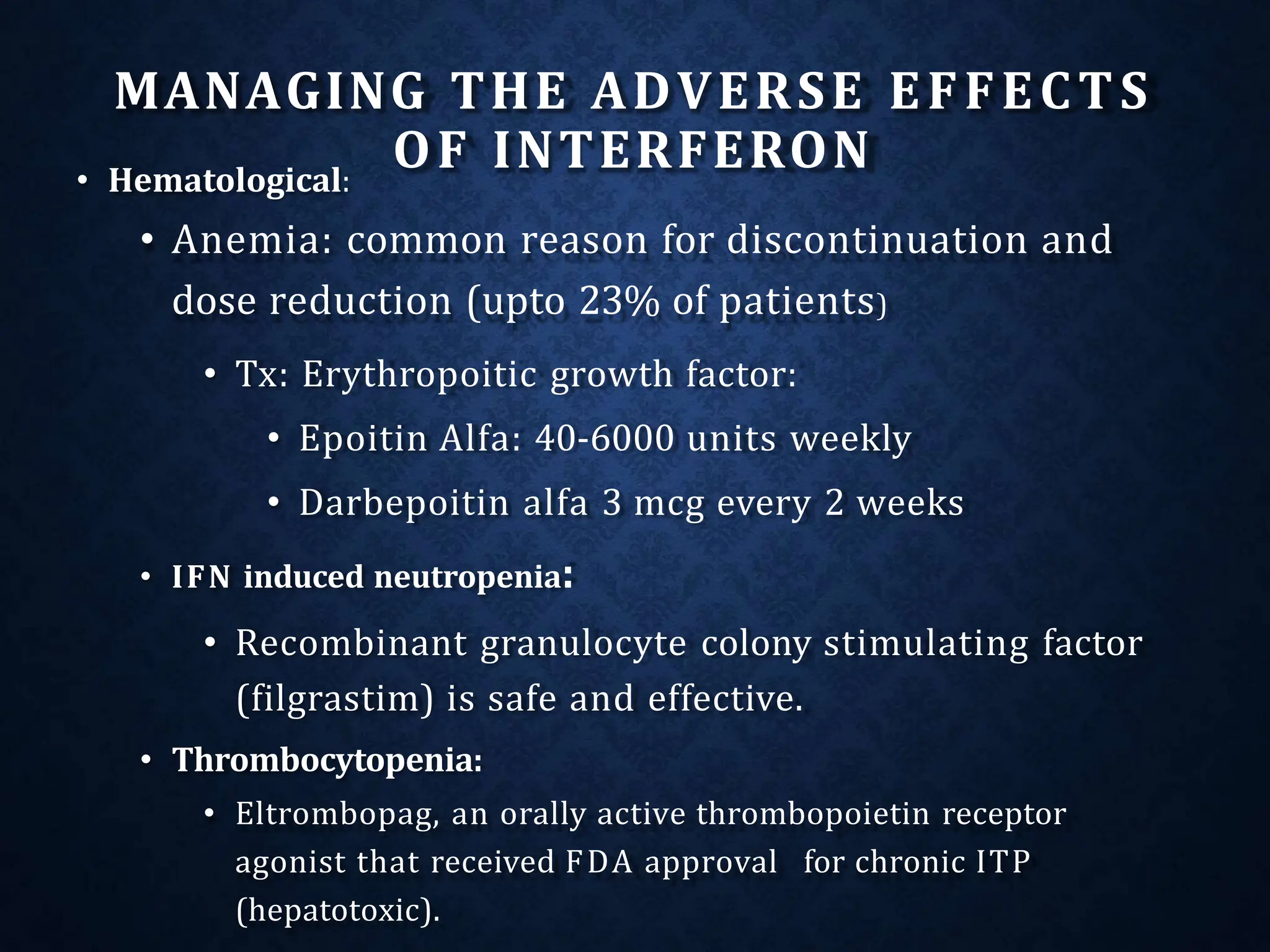
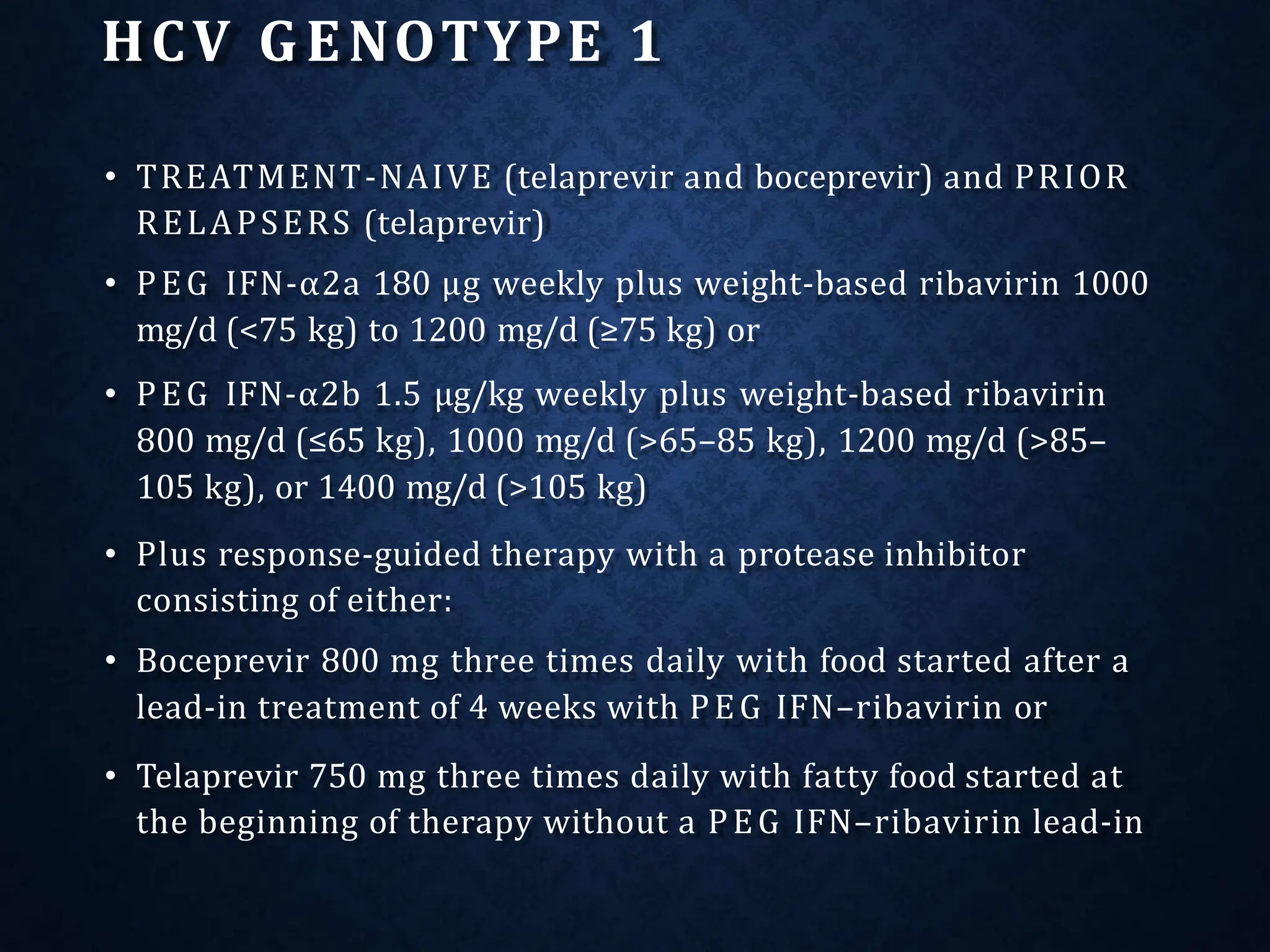
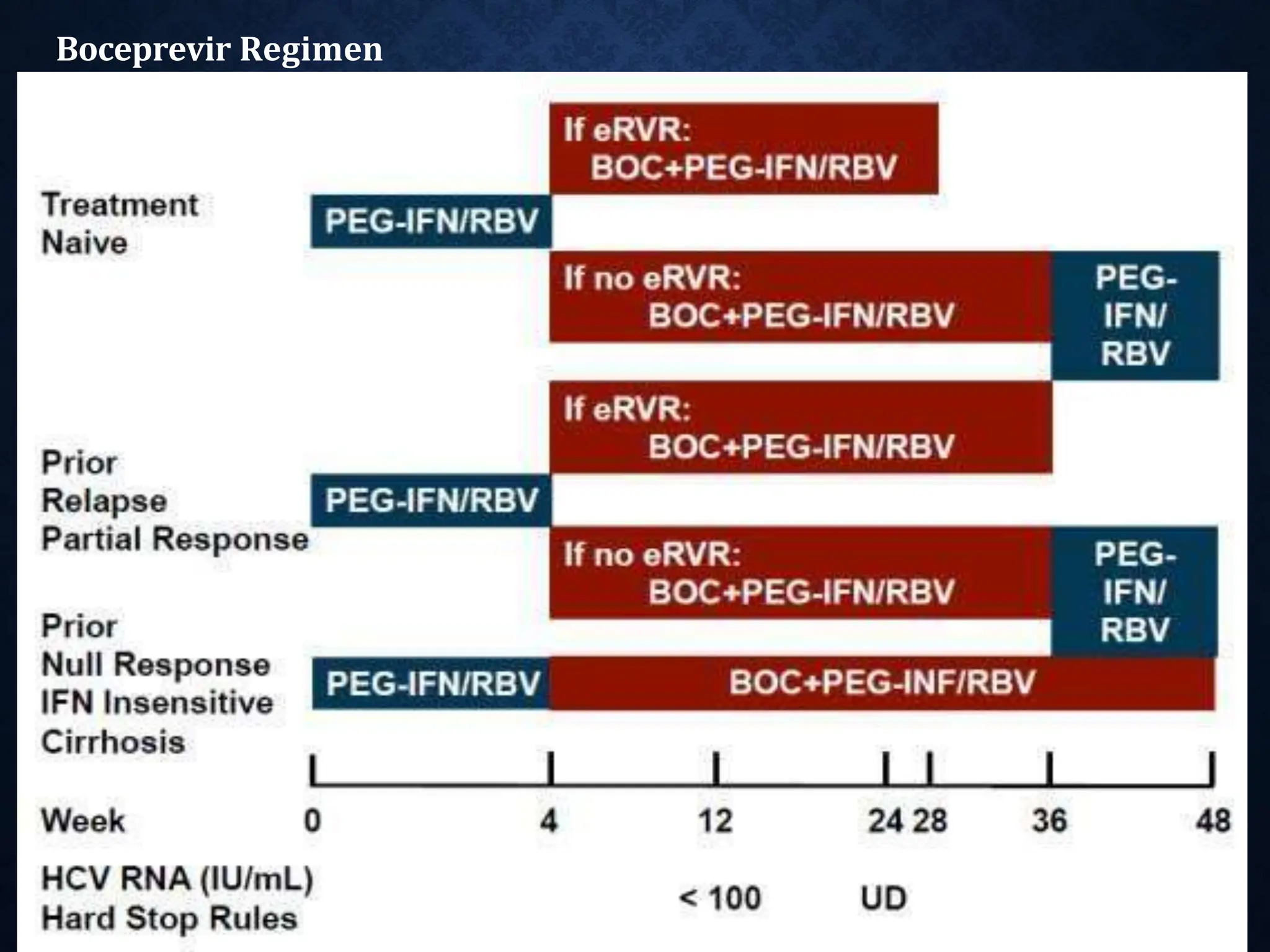
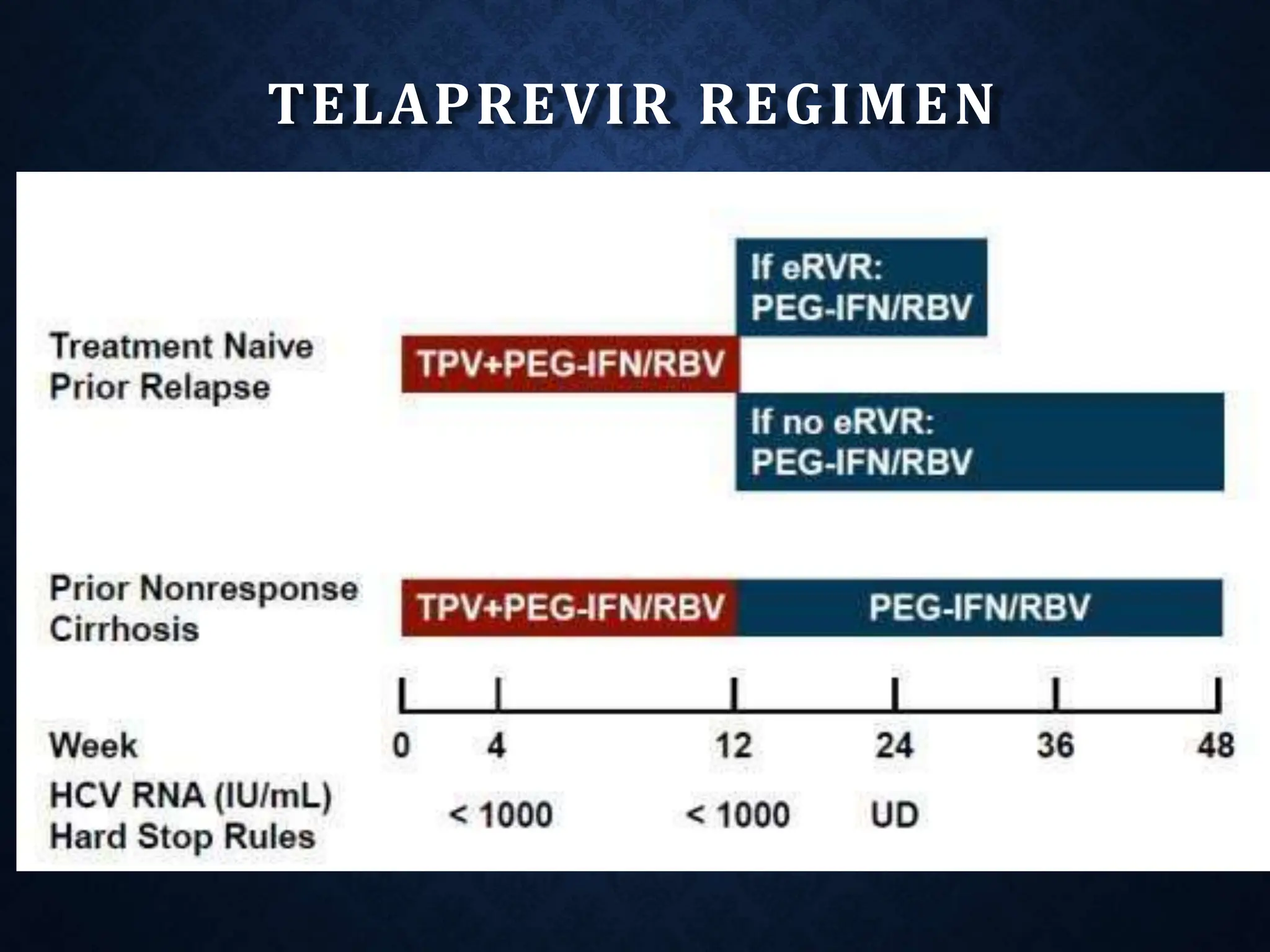
- Treatment aims to eradicate the virus and involves use of pegylated interferon and ribavirin