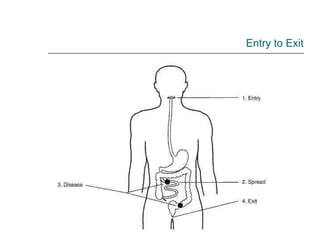
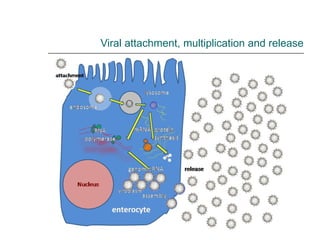
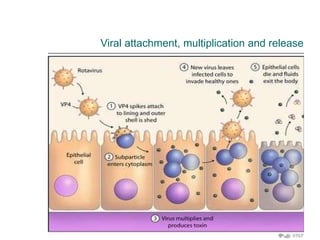
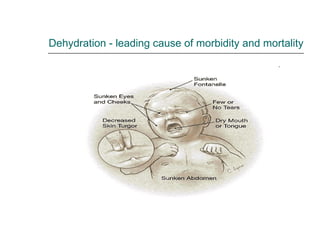
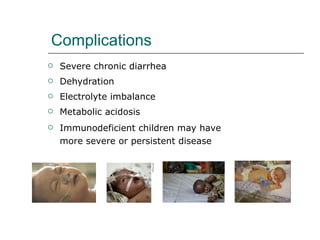
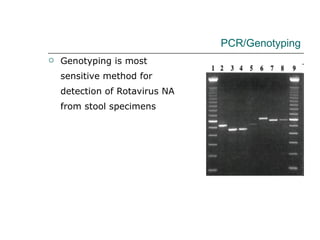
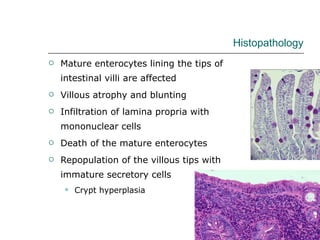
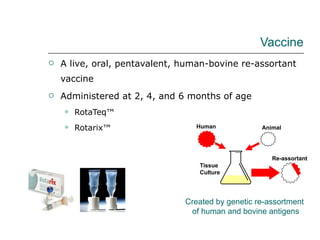
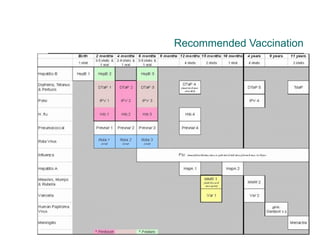
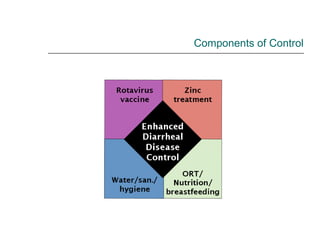
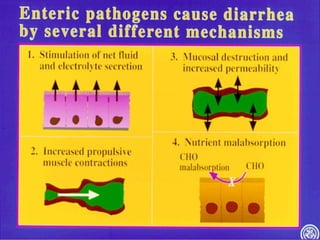
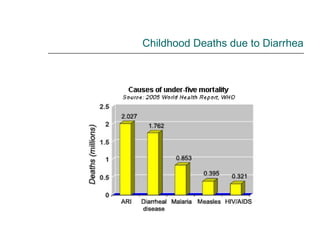
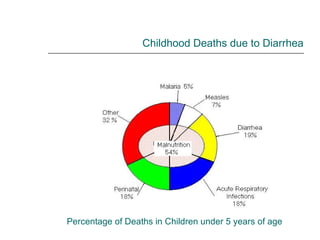
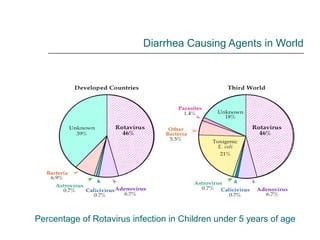
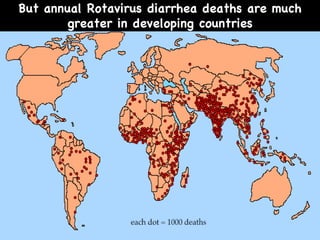
Rotavirus is a common cause of diarrhea in infants and children worldwide. It is spread through fecal-oral transmission and causes gastroenteritis. Nearly all children have been infected by rotavirus by age 5. The virus attaches to and damages cells lining the intestines, causing watery diarrhea that can lead to dehydration. Replacing lost fluids and electrolytes is the primary treatment for rotavirus diarrhea. Vaccines are available to help prevent rotavirus infection in children.

![Rotavirus - Structural features Reovirus (RNA) 60-80nm in size Double stranded (ds) RNA Non-enveloped virus A rotavirus has a characteristic wheel-like appearance when viewed by electron microscopy The name rotavirus is derived from Latin, meaning "wheel" Group A is important human pathogen [7 Groups (A to G)] 5 predominant strains (G1-G4, G9), account for 90% of isolates Strain G1 accounts for 73% of infections](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rotavirus-100504140456-phpapp01/85/Rotavirus-8-320.jpg)