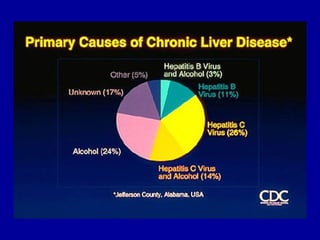
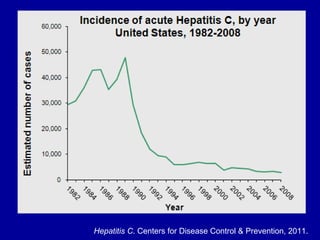
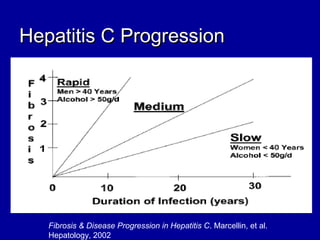
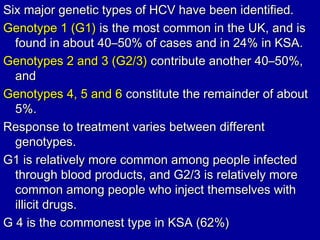
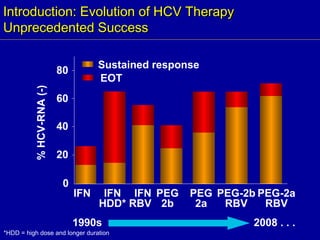
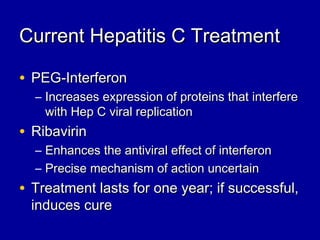
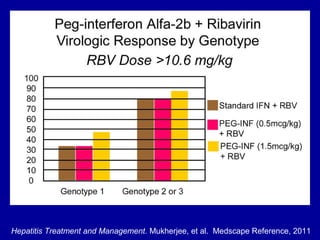
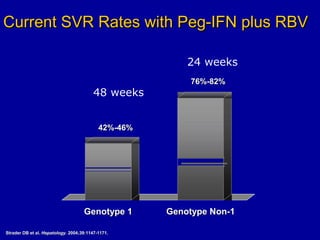
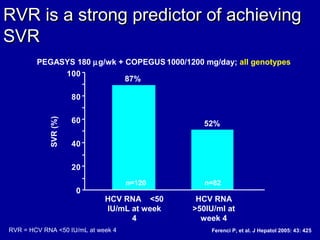
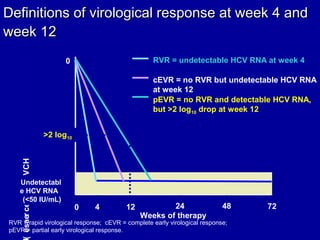
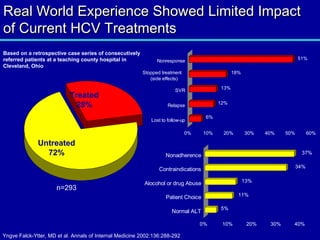
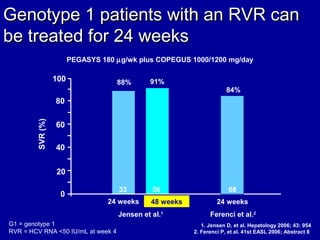
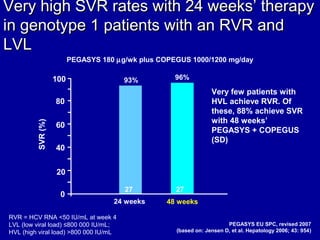
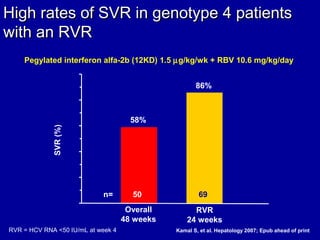
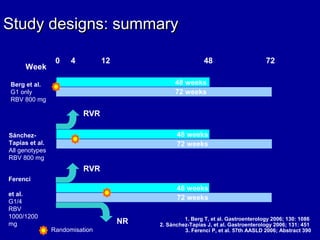
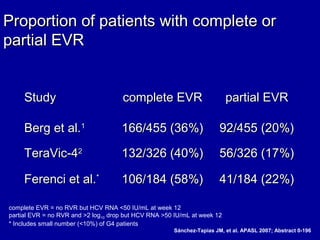
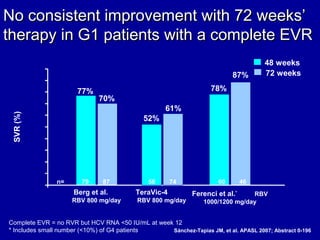
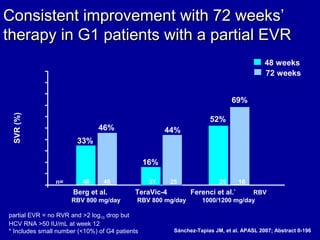
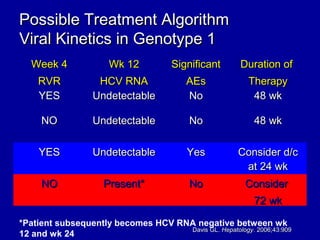
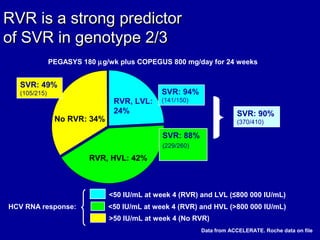
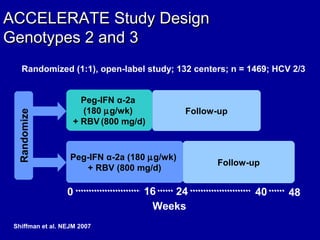
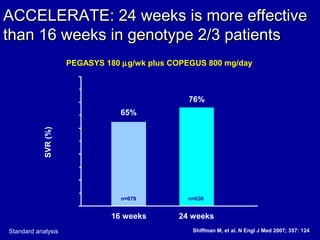
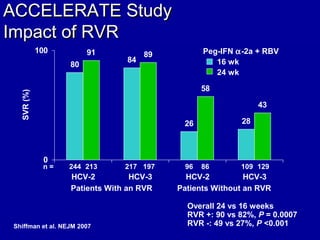
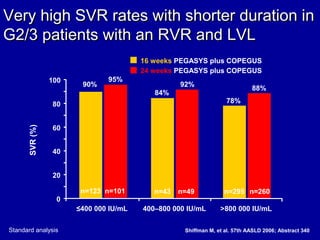
Hepatitis C is a contagious liver disease that can range from mild illness to serious lifelong illness or death. It is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) and is most commonly spread through blood-to-blood contact. While there is no vaccine, current treatment involves pegylated interferon and ribavirin. This therapy cures hepatitis C if it results in a sustained virologic response (SVR), meaning the virus is undetectable 6 months after treatment ends. SVR rates are lower for HCV genotype 1 than other genotypes. Newer treatments are being developed to make therapy easier and more effective. Tailoring treatment based on factors like early viral load response may allow some genotype 1 patients to