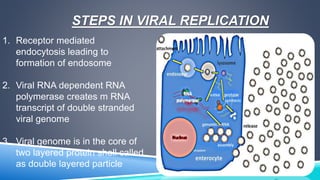
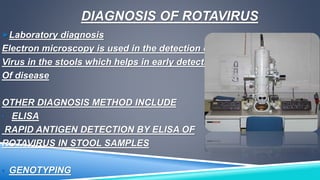
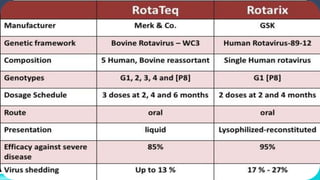
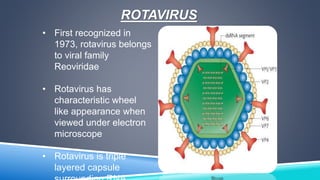
Rotavirus is a major cause of diarrhea in infants and young children worldwide. It spreads easily between people through contaminated food or surfaces. The virus causes infection and inflammation of the intestinal tract, leading to diarrhea and dehydration. Diagnosis involves detecting the virus in stool samples using tests like ELISA or electron microscopy. Treatment focuses on rehydration through oral rehydration therapy. Handwashing and sanitation can help prevent transmission. Two live, oral rotavirus vaccines provide protection against severe diarrhea from the most common strains.


![“TRANSMISSION OF
ROTAVIRUS”
Primary mode of rotavirus transmission is fecal to oral
Highly communicable and transmissible disease
Close person to person contact and environmental
surfaces are common vectors of transmission
Incubation period is 1-3 days
Large quantities of virus are shed in stool from just prior
to onset of symptoms until about 10 days after onset
Amount of virus shed in stool [10-100 billion virion/gram
of stool]infection
Amount of ingested virus required to cause infection as
few as 10 infective virions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rotavirus-141026064221-conversion-gate01/85/Rotavirus-3-320.jpg)
![• The Rotavirus genome consist of 11 double stranded
RNA segments each encoding one viral proteins
• Scientist have describe seven Rotavirus group [A to
G]
• Only groups A, B AND C infect humans
• Group A which has multiple strains cause majority of
childhood infections
• Vaccine candidates are designed to protect against
group A Rotaviruses
• The G type and P type define the serotype
• They are critical to a vaccine development because
they are the vaccine for stimulating a protective
immune response](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rotavirus-141026064221-conversion-gate01/85/Rotavirus-5-320.jpg)
![“ SEROTYPES”
Serotypes are described as variations within species of
bacteria or viruses or among immune cells of different
individuals
G1P[8] is the most common serotype worldwide and
accounts for over two thirds of rotavirus infections
worldwide
Infections with G1,G2,G3,G4 AND G9 together
comprise almost 95% of rotavirus serotype observed
Because the two gene segments that encode these
protein can segregate independently, A typing system
which consist of both G and P type is used i.e.
G1P[8],G2P[4],G3P[8],G4P[8],G9P[8] and G9P[6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rotavirus-141026064221-conversion-gate01/85/Rotavirus-6-320.jpg)