Embed presentation
Downloaded 35 times


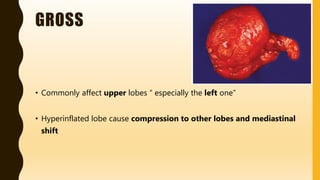
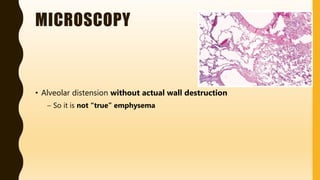





Congenital lobar emphysema is a rare condition where one or more lung lobes are abnormally enlarged due to partial obstruction of the bronchus supplying the lobe. It usually presents within the first 6 months of life with respiratory distress. Grossly, the affected lobe is hyperinflated and can compress other lobes. Microscopically, the alveoli are distended without destruction of walls. It must be differentiated from other congenital lung diseases and pneumothorax.








