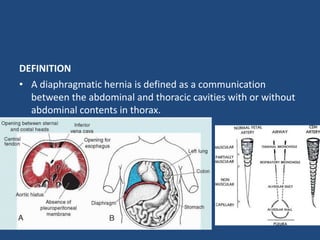
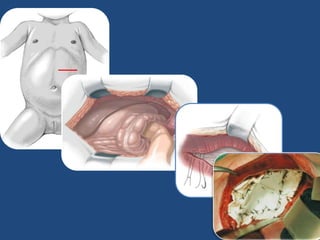
1) A diaphragmatic hernia is a defect in the diaphragm allowing contents from the abdomen to protrude into the chest cavity.
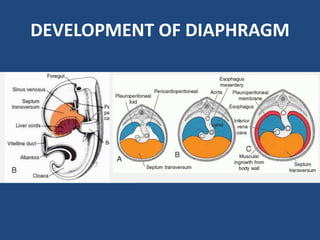
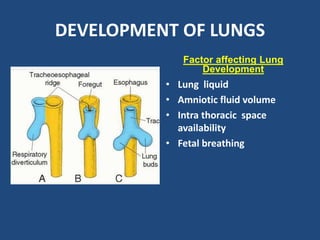
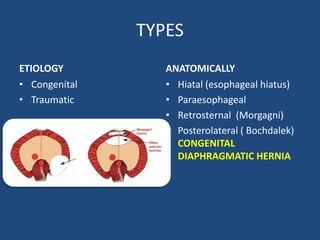
2) Congenital diaphragmatic hernias are the most common type and occur during fetal development when the diaphragm fails to fully form.
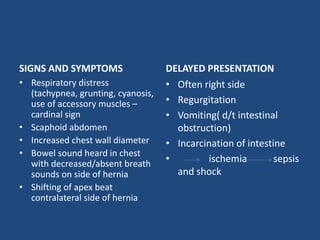
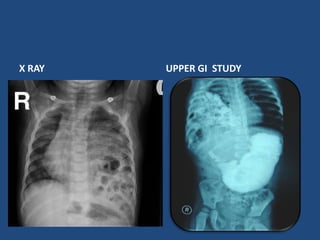
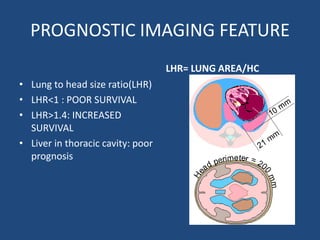
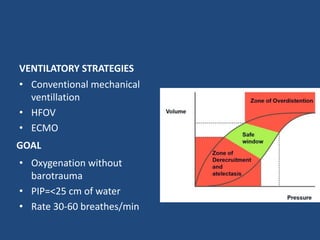
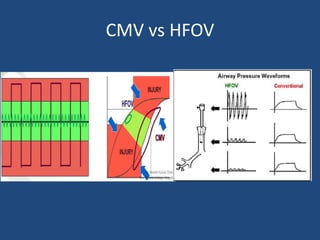
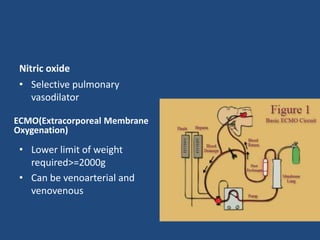
3) Infants present with respiratory distress and treatment involves aggressive respiratory support, surgical repair of the defect, and long term management of complications which can include GERD and intestinal issues.