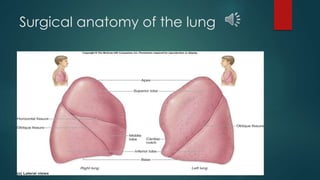
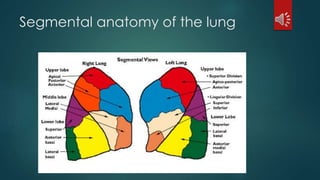
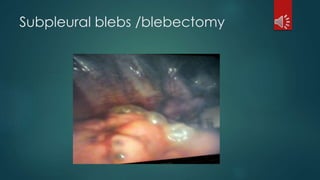
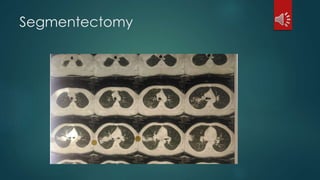
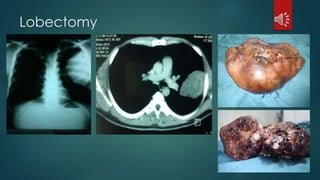
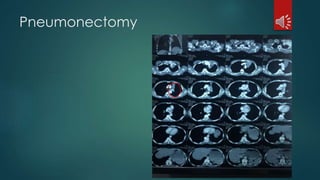
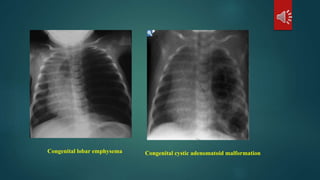
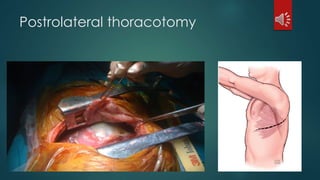
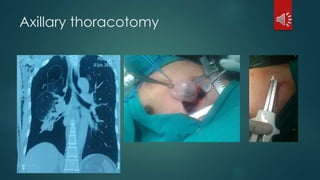
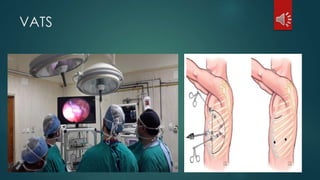
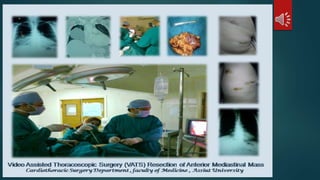
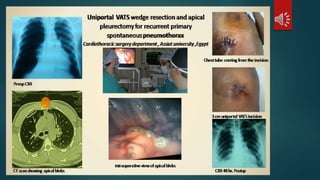
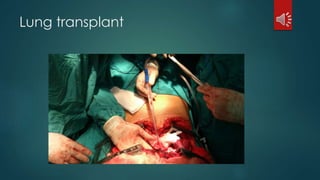
Pulmonary resection involves the surgical removal of part or all of the lung under general anesthesia and includes various techniques such as lobectomy and pneumonectomy. Indications for this procedure range from congenital conditions and trauma to neoplastic diseases, and it may be approached through methods like thoracotomy or video-assisted thoracic surgery. Complications can occur both early and late, including respiratory failure and chronic pain.