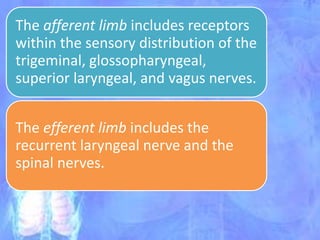
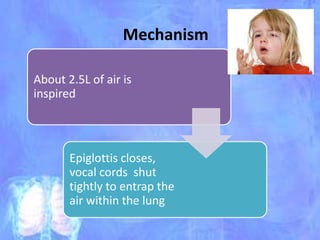
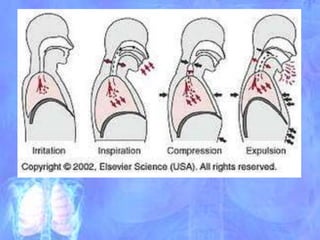
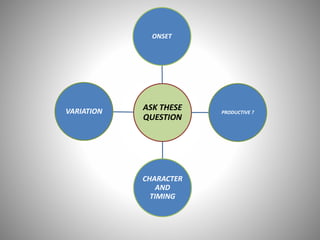
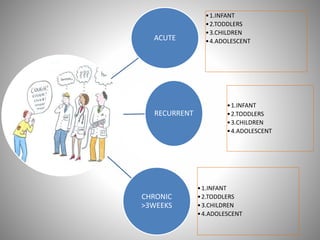
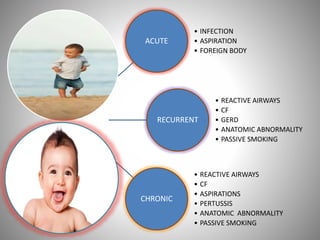
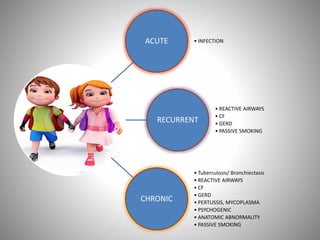
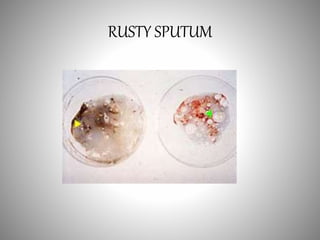
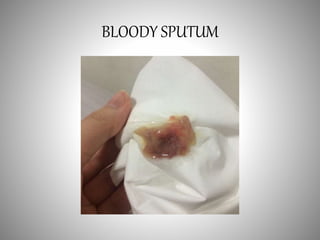
The document discusses the approach to cough and its management. It defines cough and describes the cough reflex mechanism. Cough can be initiated voluntarily or involuntarily and involves both afferent and efferent pathways. Cough receptors are located in various areas including the pharynx, sinuses, stomach and ears. The cause of cough can be extra-pulmonary. A careful history regarding onset, character, production, timing and associated symptoms is important to narrow the diagnosis. Acute, recurrent and chronic cough have different etiologies depending on the patient's age. Proper diagnosis involves considering clinical features, sputum examination and treatment response.