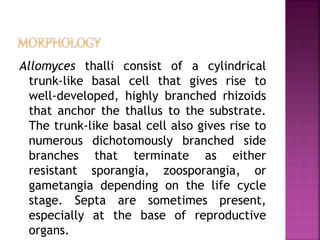
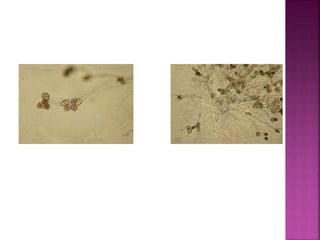
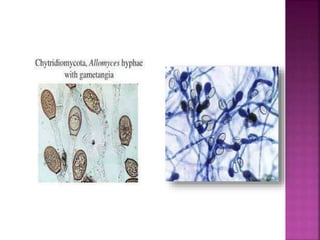
Allomyces is a genus of fungi that reproduces asexually through zoospores with whip-like flagella. Species of Allomyces are commonly found in soils in tropical regions, especially in ponds, rice fields, and slow-moving rivers. The thallus of Allomyces has a trunk-like basal cell that gives rise to branched rhizoids and side branches that terminate in sporangia, zoosporangia, or gametangia depending on the life cycle stage.