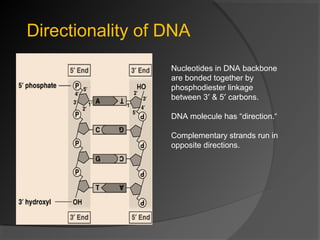
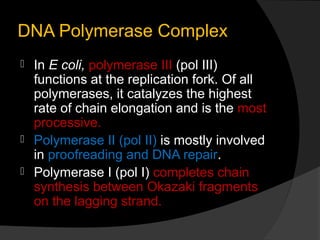
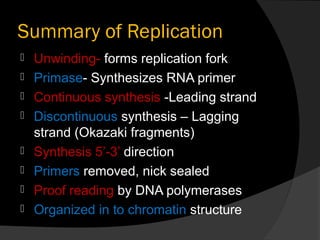
DNA replication is the process whereby a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA before cell division. It ensures faithful inheritance of genetic material during cell division. DNA replication is semi-conservative and bidirectional, occurring simultaneously on both strands of the DNA double helix to produce two identical copies. It involves unwinding of the DNA double helix by helicase, synthesis of new strands by DNA polymerases along leading and lagging strands using existing strands as templates, and ligation of fragments by DNA ligase. DNA replication is tightly regulated during the S phase of the cell cycle and is essential for accurate transmission of genetic information from parent to daughter cells.