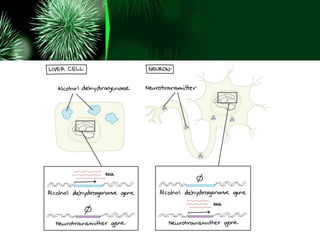
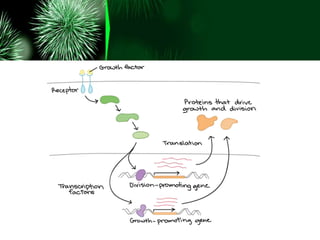
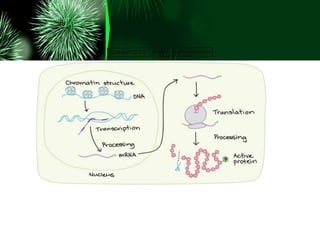
Gene expression in eukaryotes is regulated at multiple stages including transcription, RNA processing, translation, and protein modification. Regulation allows different genes to be expressed in different cell types through the actions of transcription factors and other proteins that control if and how genes are expressed. Differences in gene regulation between species help explain variations in form and function even when genomes are highly similar at the DNA level.