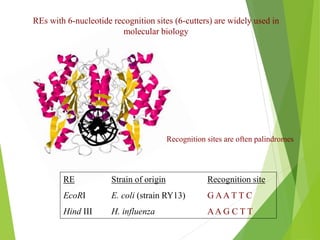
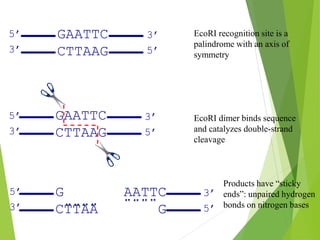
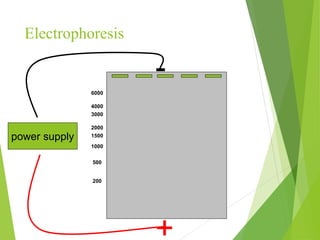
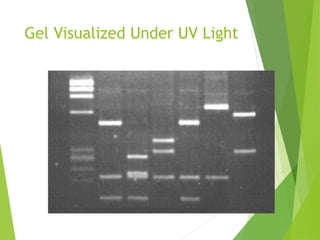
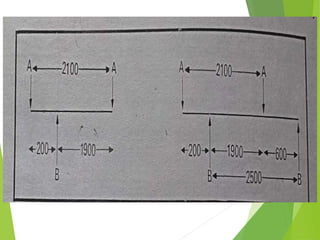
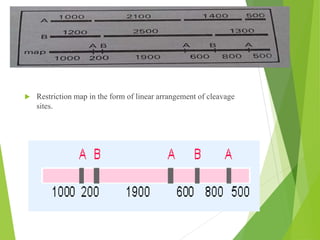
Restriction mapping is a technique that generates a map of DNA molecules by identifying sites for restriction enzymes through data from restriction digests. The process involves the use of restriction endonucleases and gel electrophoresis, which enables visualization of DNA fragments. Historically, the discovery of restriction enzymes has been significant in molecular biology, leading to their application in DNA sequencing and plasmid engineering.