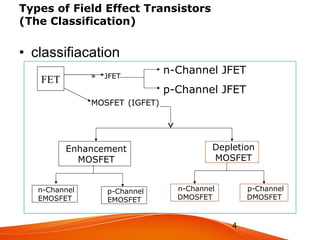
There are several types of field effect transistors (FETs) that are classified based on their construction and operation:
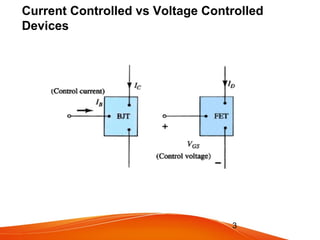
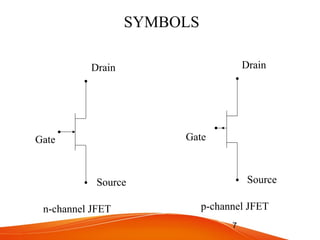
- JFETs operate using only one type of charge carrier and have either an n-channel or p-channel. The gate voltage controls the drain current.
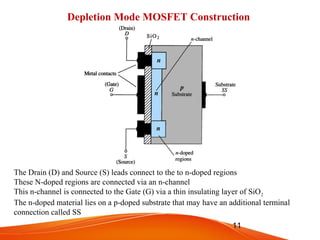
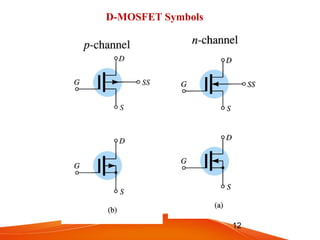
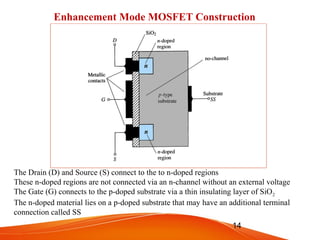
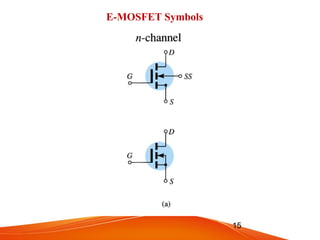
- MOSFETs also come in n-channel or p-channel varieties and include depletion mode and enhancement mode types. Depletion mode MOSFETs operate in depletion mode like JFETs when the gate-source voltage is less than or equal to 0 and in enhancement mode when it is greater than 0. Enhancement mode MOSFETs only allow drain current when the gate-source voltage exceeds the threshold voltage.
-