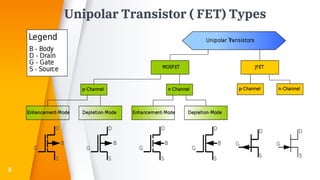
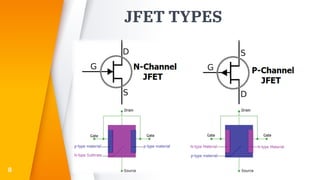
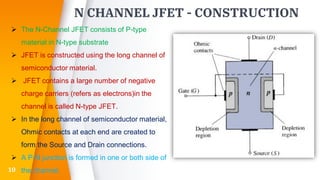
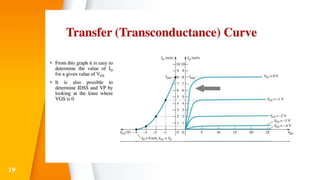
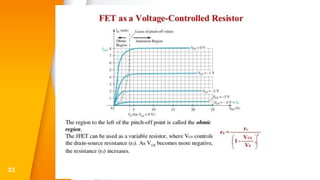
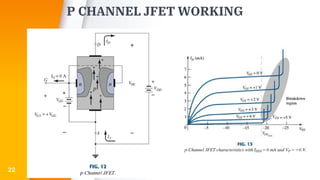
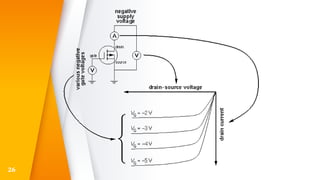
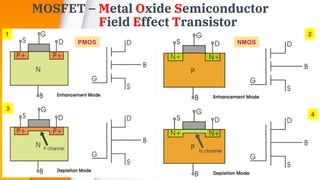
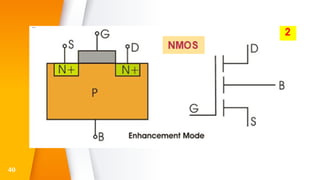
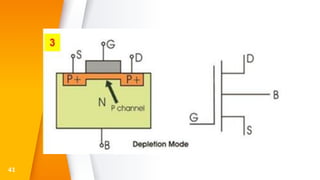
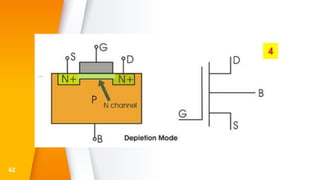
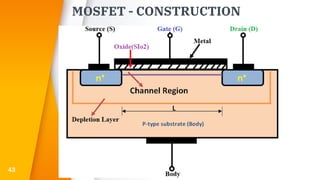
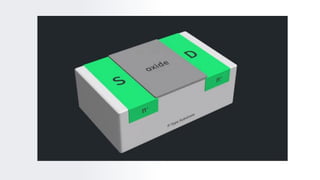
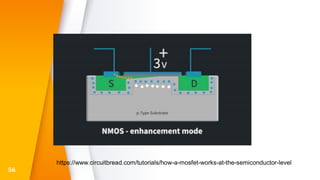
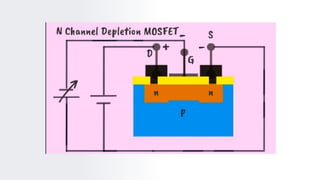
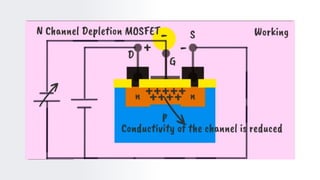
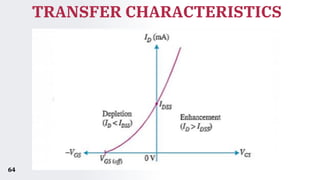
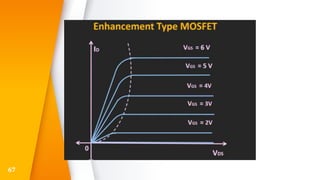
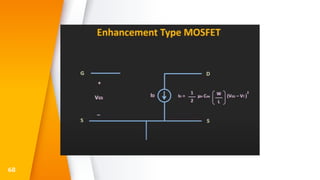
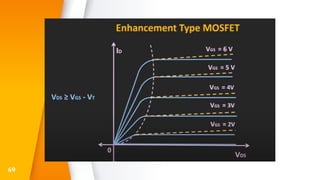
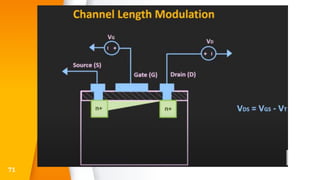
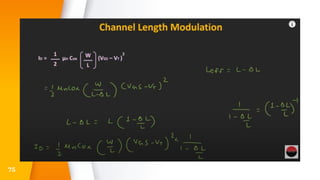
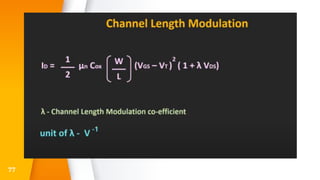
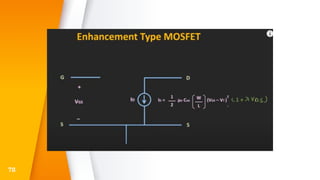
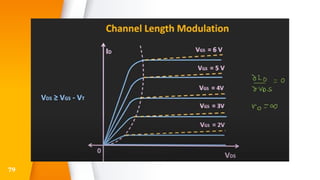
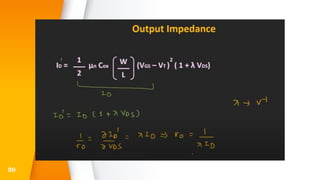
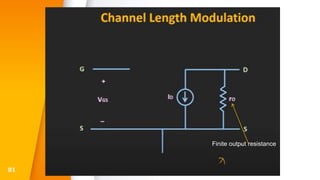
The document provides an overview of field-effect transistors (FETs), focusing on junction field-effect transistors (JFETs) and metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). It discusses their construction, operation, and key differences from bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), highlighting advantages like high input impedance and low noise. Additionally, it covers applications of MOSFETs in modern electronics, including microprocessors and amplifiers.