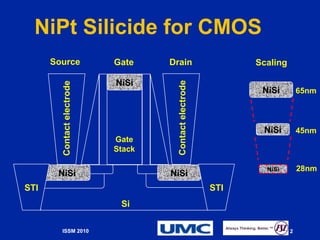
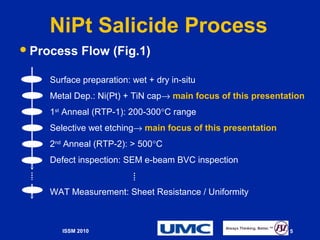
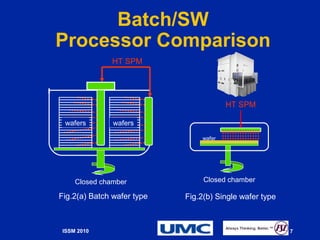
The document presents the optimization of the nickel silicide (NIPT) process for 28nm CMOS manufacturing, focusing on improving film thickness, platinum (Pt) additive levels, and wet selective etch processing. It highlights significant performance improvements, including a 15-fold enhancement in cycle time and NISI encroachment reduction. Additionally, it emphasizes the successful outcomes in sheet resistance and uniformity due to the co-optimization of these factors.