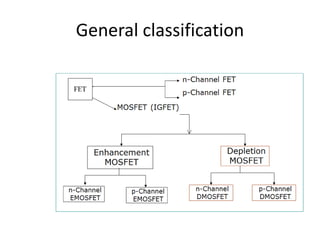
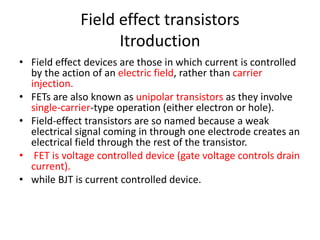
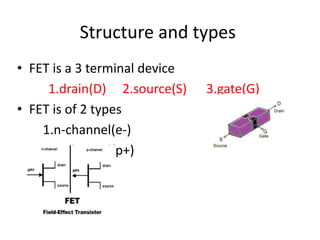
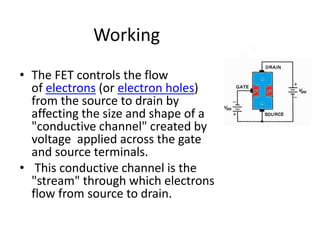
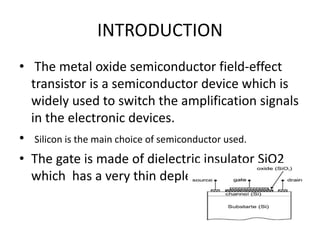
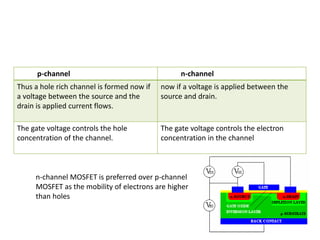
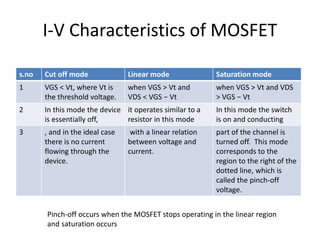
Field Effect Transistors (FETs) are voltage-controlled devices that use an electric field to control current, categorized into n-channel and p-channel types. MOSFETs, a subtype of FETs, operate through variations in channel width, with enhancement and depletion modes. They have applications in integrated circuits and amplifiers due to their high input impedance and small size, despite limitations such as low gain-bandwidth.