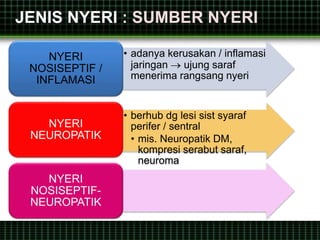
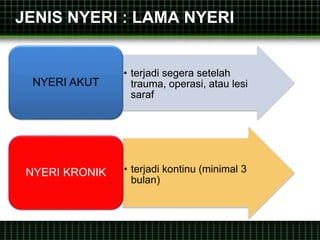
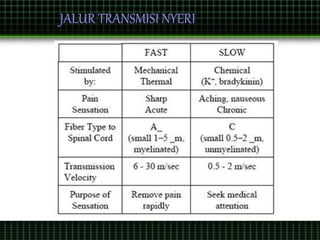
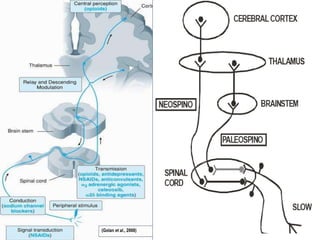
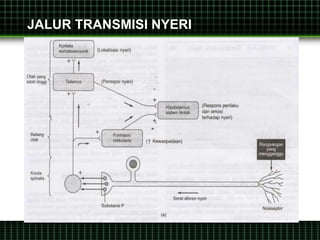
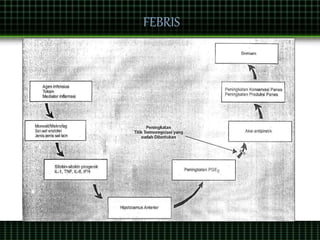
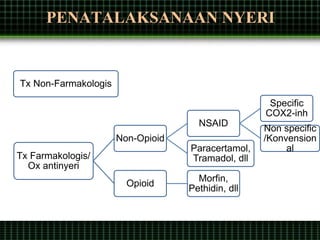
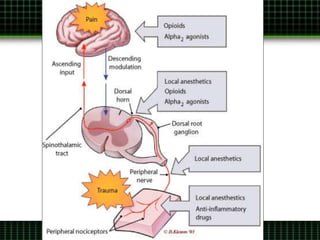
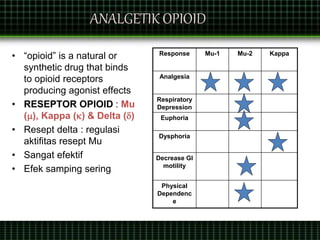
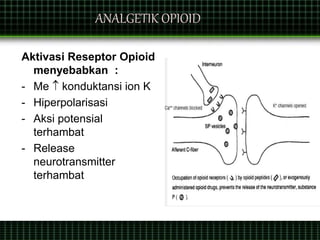
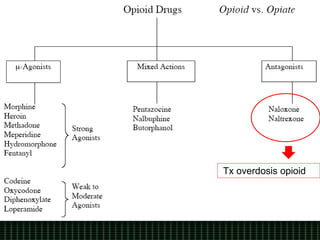
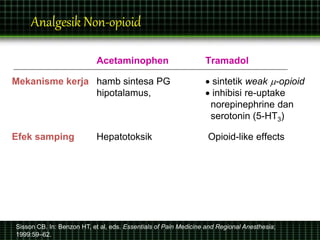
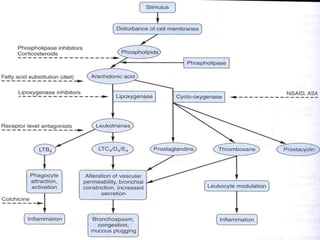
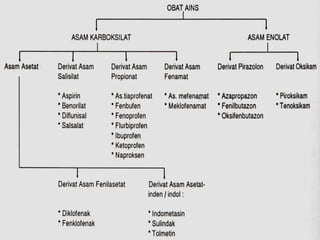
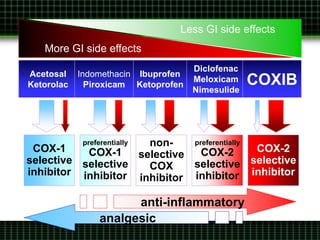
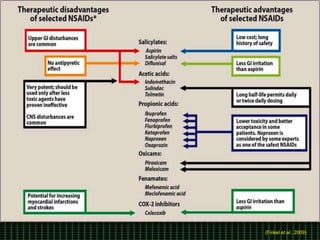
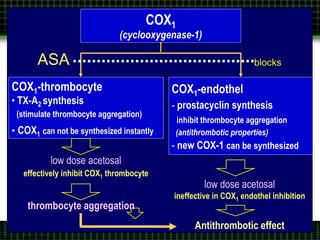
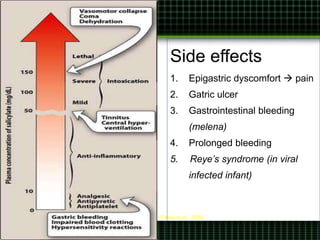
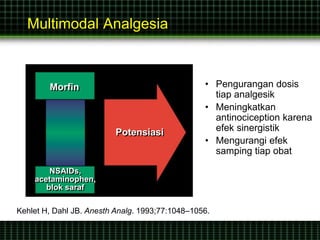
This document discusses pain management through pharmacological therapies. It defines pain and describes the physiological mechanisms of pain. It discusses the types and causes of pain such as nociceptive, neuropathic, acute, and chronic pain. The pathways of pain transmission and modulation are explained. Various classes of pain medications are described including non-opioid analgesics like NSAIDs, opioids, and adjuvant analgesics. The mechanisms of action, effects, and side effects of different analgesic drugs are provided. Multimodal analgesia combining different classes of analgesics to improve pain relief and reduce side effects is also mentioned.