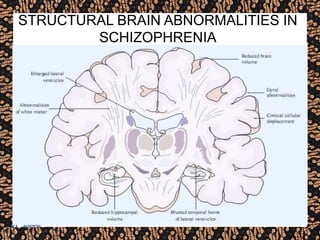
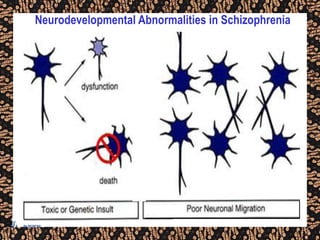
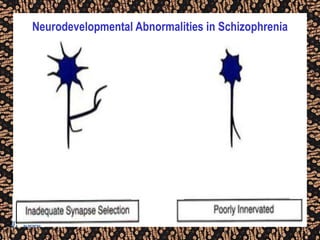
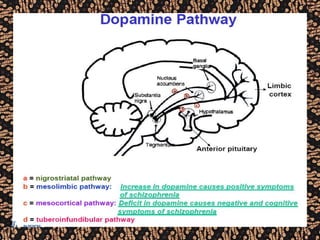
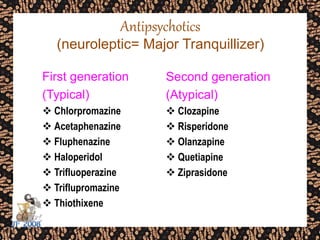
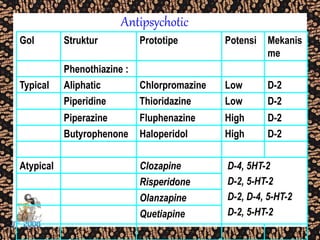
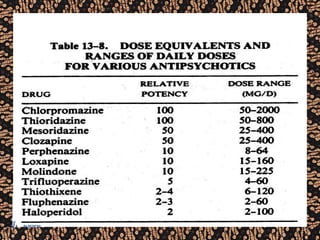
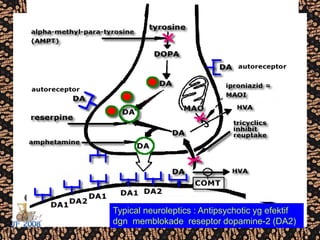
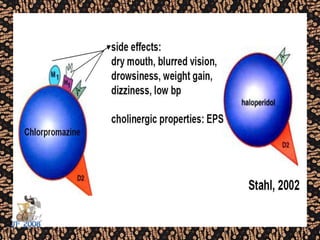
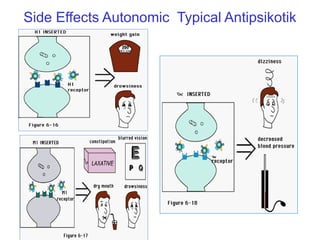
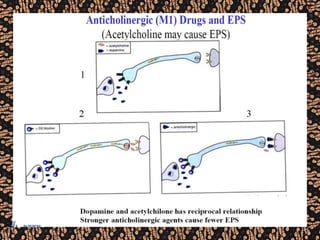
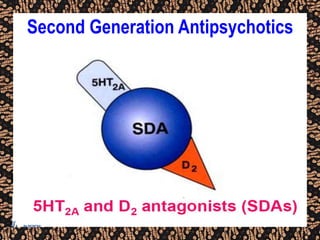
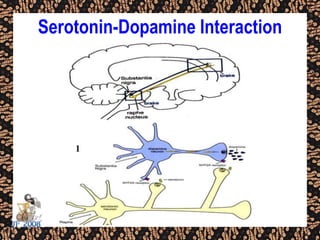
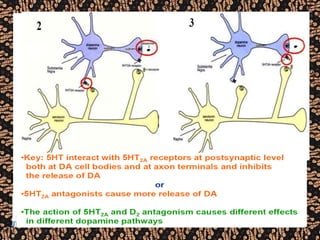
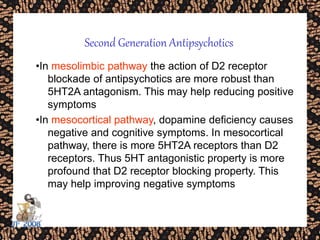
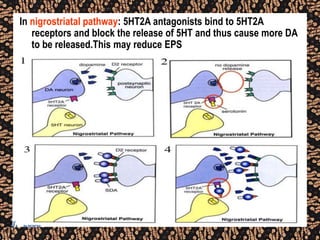
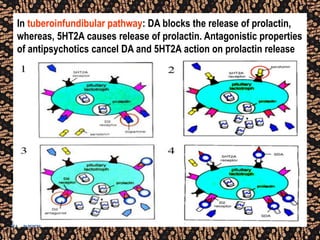
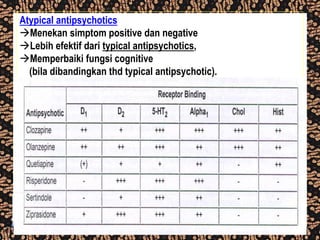
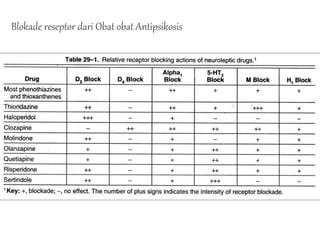
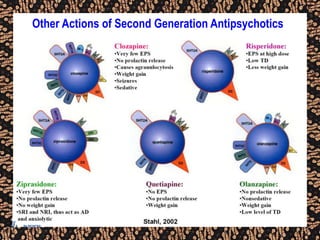
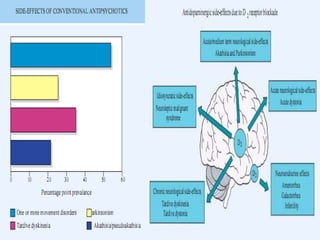
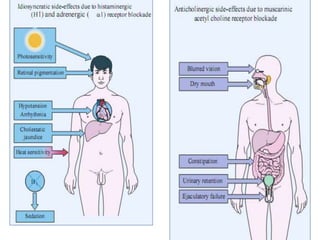
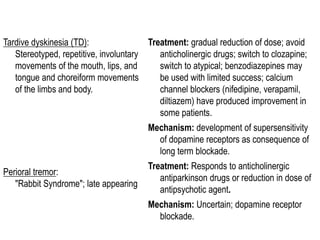
The document discusses schizophrenia and antipsychotic drugs. It defines schizophrenia and lists its structural brain abnormalities and dopamine hypothesis. It describes first and second generation antipsychotics, including their mechanisms of action, side effects, and issues with long term use such as tardive dyskinesia and neuroleptic malignant syndrome.